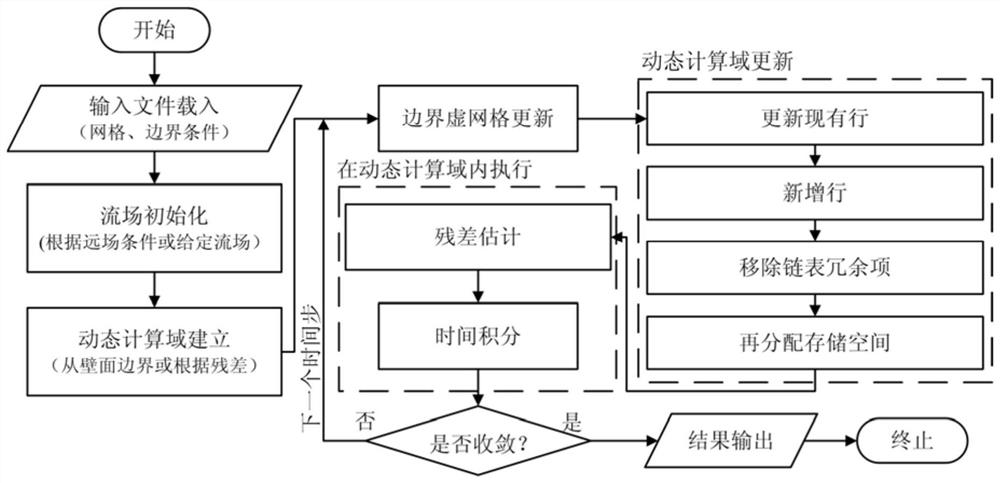
Disturbed Region Update Method for Steady Compressible Flow
A region update and dynamic technology, applied in the field of computational fluid dynamics, can solve problems such as numerical errors and flow parameters without actual beneficial contributions, and achieve the effect of reducing the total number of iteration steps, reducing the amount of solutions, and reducing storage requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
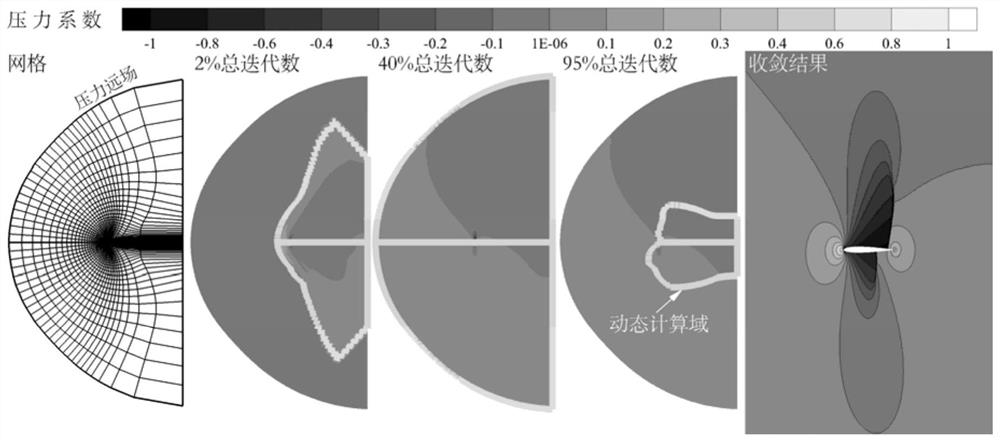
[0133] Example 1: The NACA 0012 airfoil is simulated under the conditions of incoming flow Mach number 0.85 and angle of attack 1°, and the flow field is initialized with far-field boundary conditions. The grid adopts C-type topology; in order to avoid the influence of the limited outer boundary on the results, the given computational domain is about 20 times the chord length. figure 2 The sparse mesh, dynamic computational domain changes, and final simulation results are illustrated. figure 2 In the convergence results shown, the shock waves on the upper and lower surfaces of the airfoil can be clearly captured. The relative error between the airfoil surface lift and drag coefficient obtained by the disturbance area updating method proposed by the invention and the result of the traditional global updating equation is less than 1 / 10,000.
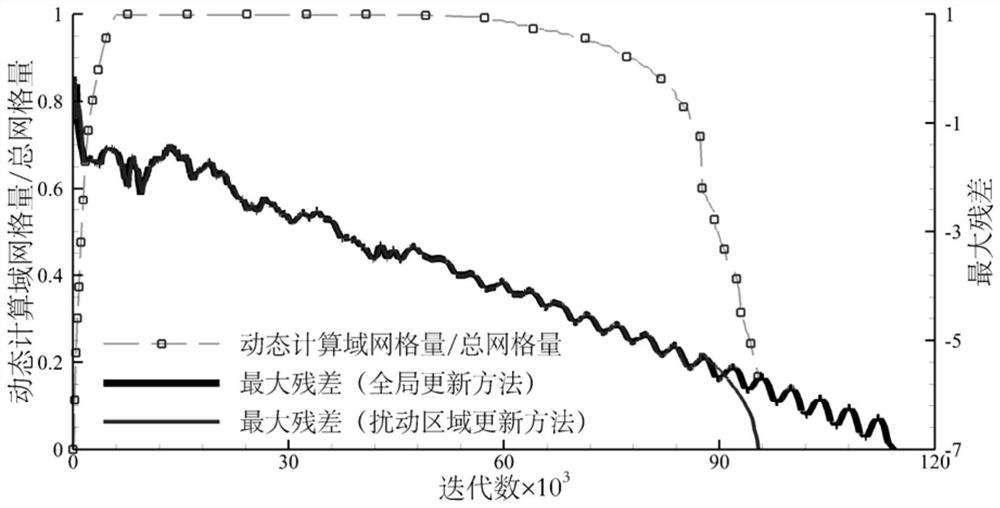
[0134] image 3 The variation of the grid cell size of the dynamic computational domain with iterations is given. The dynamic calcula...
Embodiment 2
[0136] Example 2: Simulate the flow around a cylinder with an incoming flow Mach number of 2.5, and the flow field is initialized with far-field boundary conditions. Figure 4 The dynamic computational domain change of sparse grid, explicit / implicit time format, and the numerical simulation comparison of the explicit / implicit time format perturbed region update method with the shock wave assembly method and the implicit global update method are presented. Figure 4 The comparison of the sub-figures on the right shows that the shock wave position and flow field characteristics of the flow field obtained by the disturbance area update method proposed by the present invention and other methods can be well matched; and whether it is explicit time advance or implicit time advance, The perturbed region update method can obtain numerical results with the same precision as the global update.
[0137] Figure 5 The variation of the grid cell size of the dynamic computational domain wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com