Optical waveguide
An optical waveguide and optical absorption technology, applied in the field of optical waveguides, can solve the problems of deterioration of S/N ratio, unstable optical communication, etc., and achieve the effect of improving the suppression of crosstalk
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
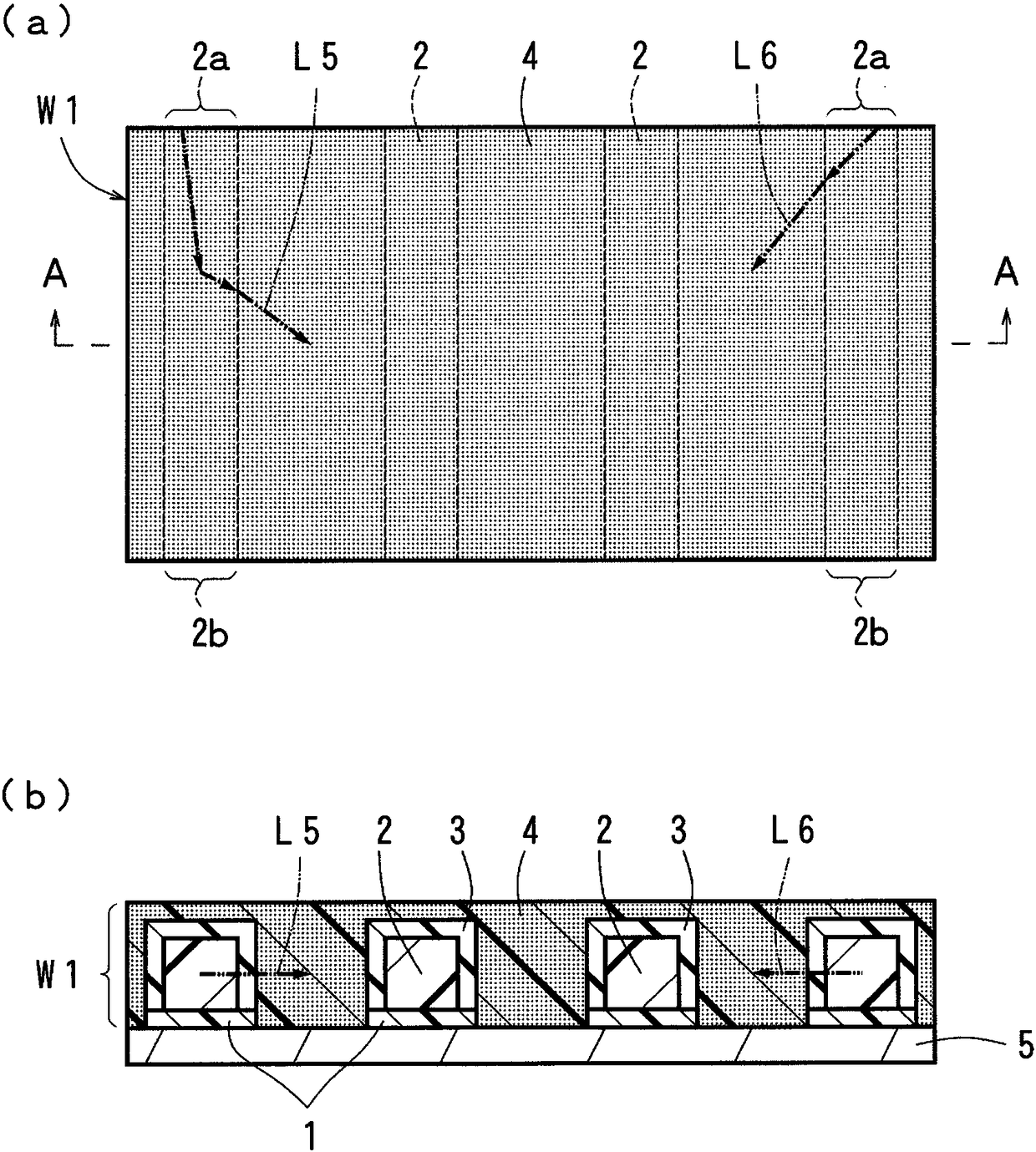
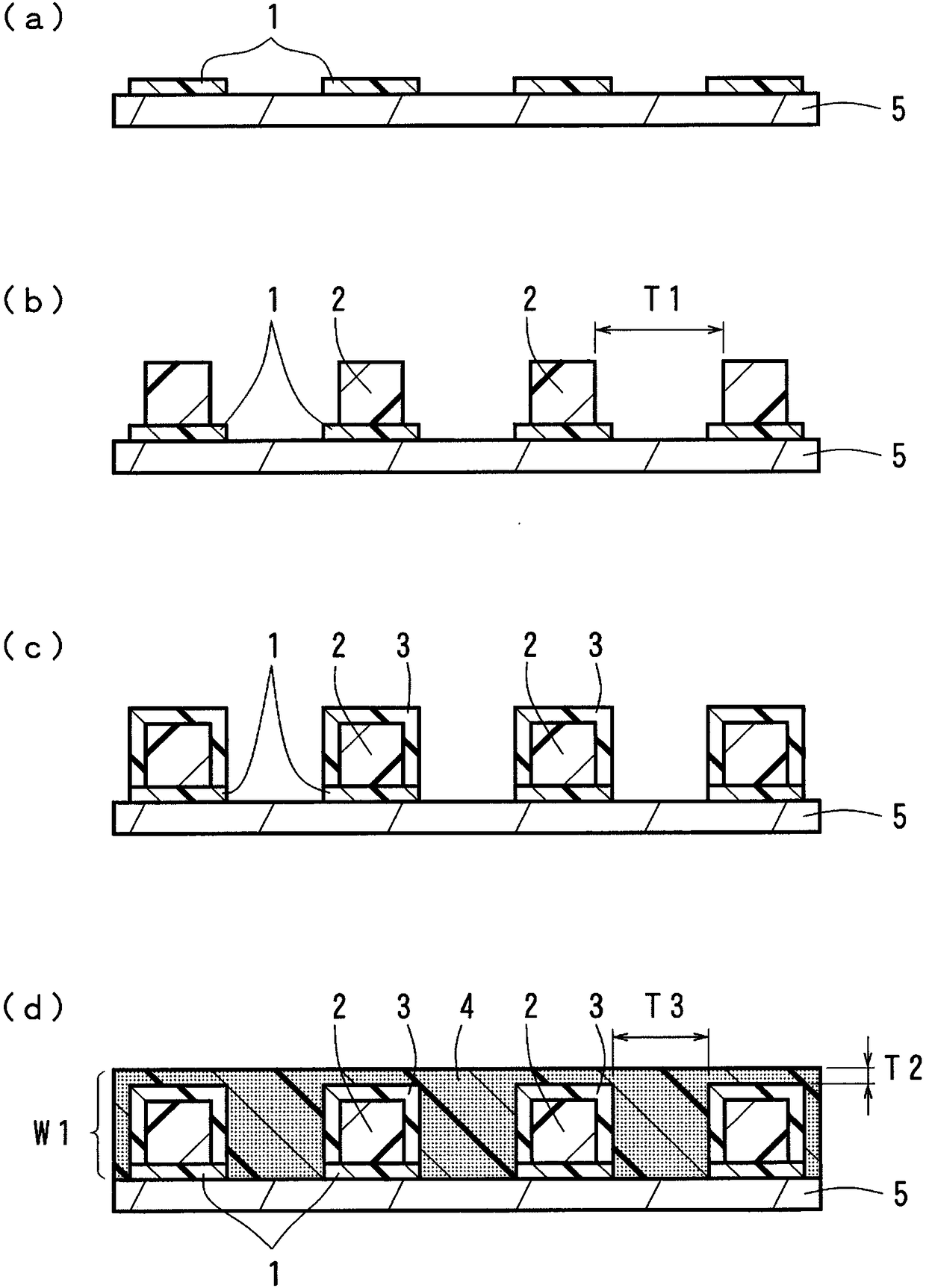
[0101] Using the above-mentioned forming materials, the surface of the resin substrate was fabricated such as figure 1 of (a), figure 1 The optical waveguide (50 mm in length) of the first embodiment shown in (b). Regarding the size of the under cladding layer, its thickness was set to 40 μm, its width was set to 100 μm, and the width of the gap between adjacent under cladding layers was set to 150 μm. Regarding the size of the core, the thickness was set to 40 μm, the width was set to 40 μm, and the formation pitch was set to 250 μm. The thickness of the overcladding layer was 30 μm for the portion covering the side surface of the core, and 30 μm for the portion covering the top surface of the core. Regarding the size of the light absorbing portion, the width of the portion sandwiched between the adjacent upper cladding layers was set to 150 μm, and the thickness from the top surface of the upper cladding layer was set to 15 μm.
Embodiment 2
[0103] Fabricated on the surface of a resin substrate using the above forming materials image 3 The optical waveguide (50 mm in length) of the second embodiment shown. The thickness of the layer of the light absorbing portion provided between the under cladding layer and the substrate was set to 20 μm. The dimensions of other parts were the same as those of the first embodiment described above.
Embodiment 3
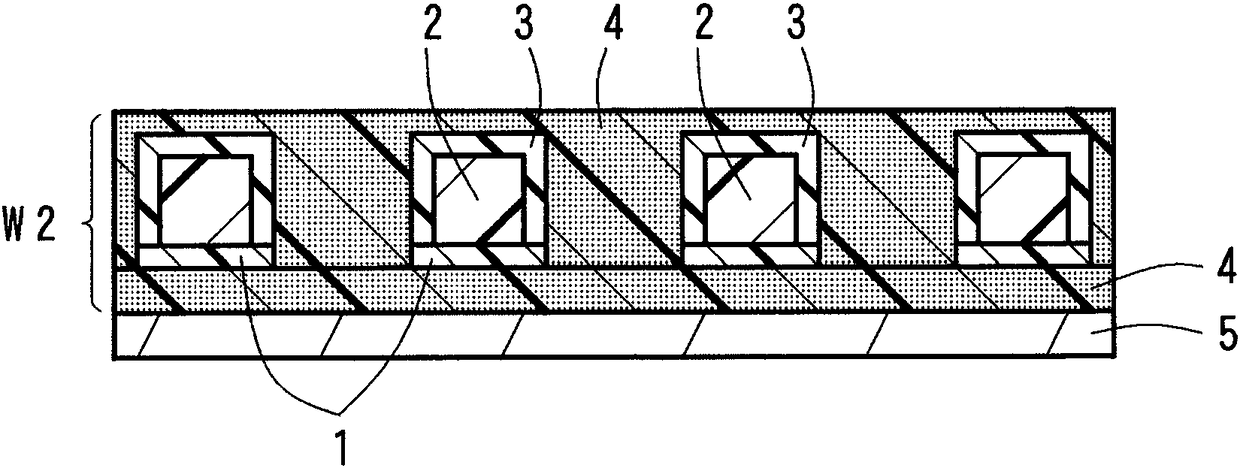
[0105] Fabricated on the surface of a resin substrate using the above forming materials Figure 5 The optical waveguide (50 mm in length) of the fourth embodiment is shown. Dimensions of structures such as a core were set to be the same as those in Example 1 above.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com