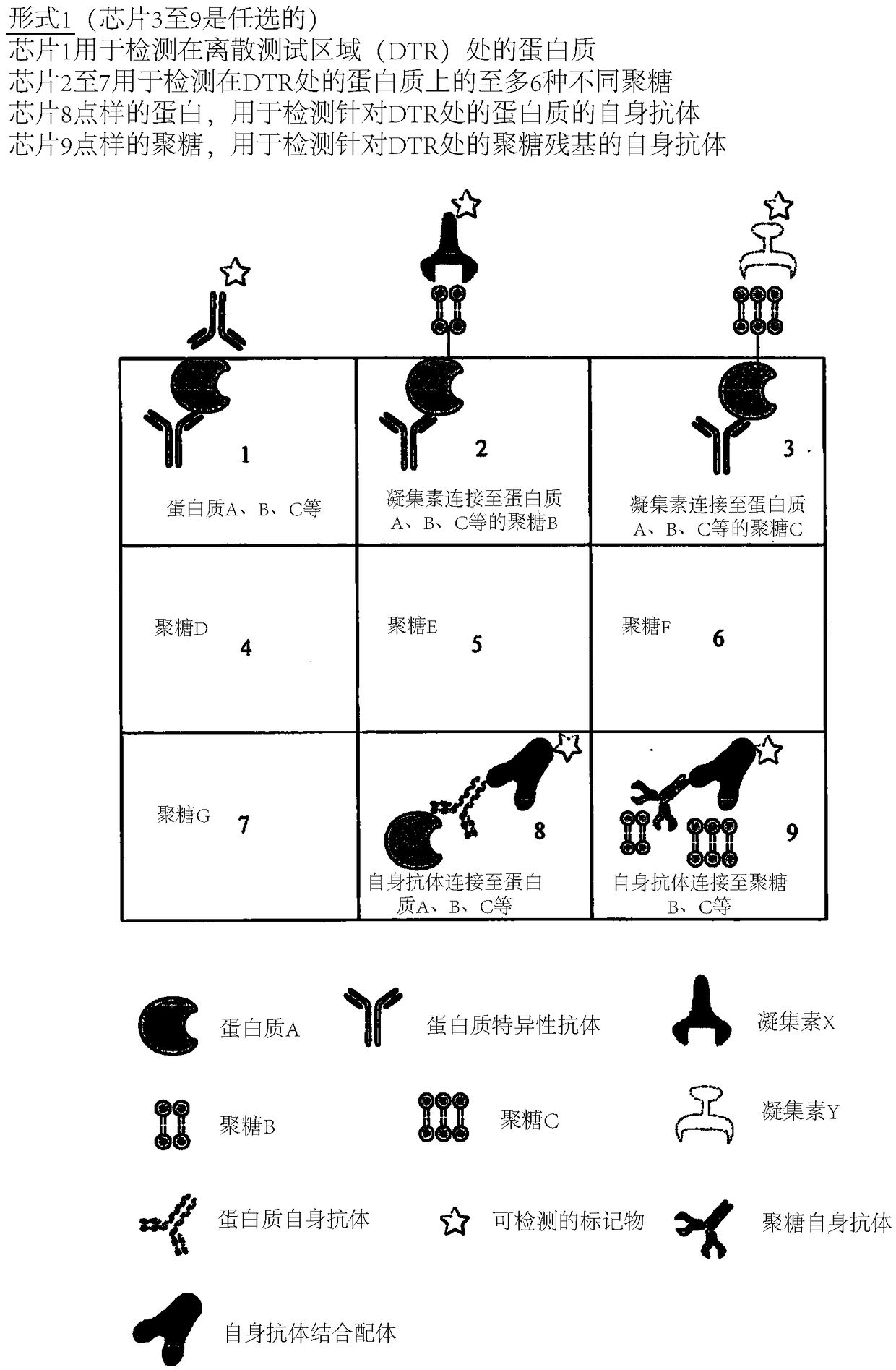
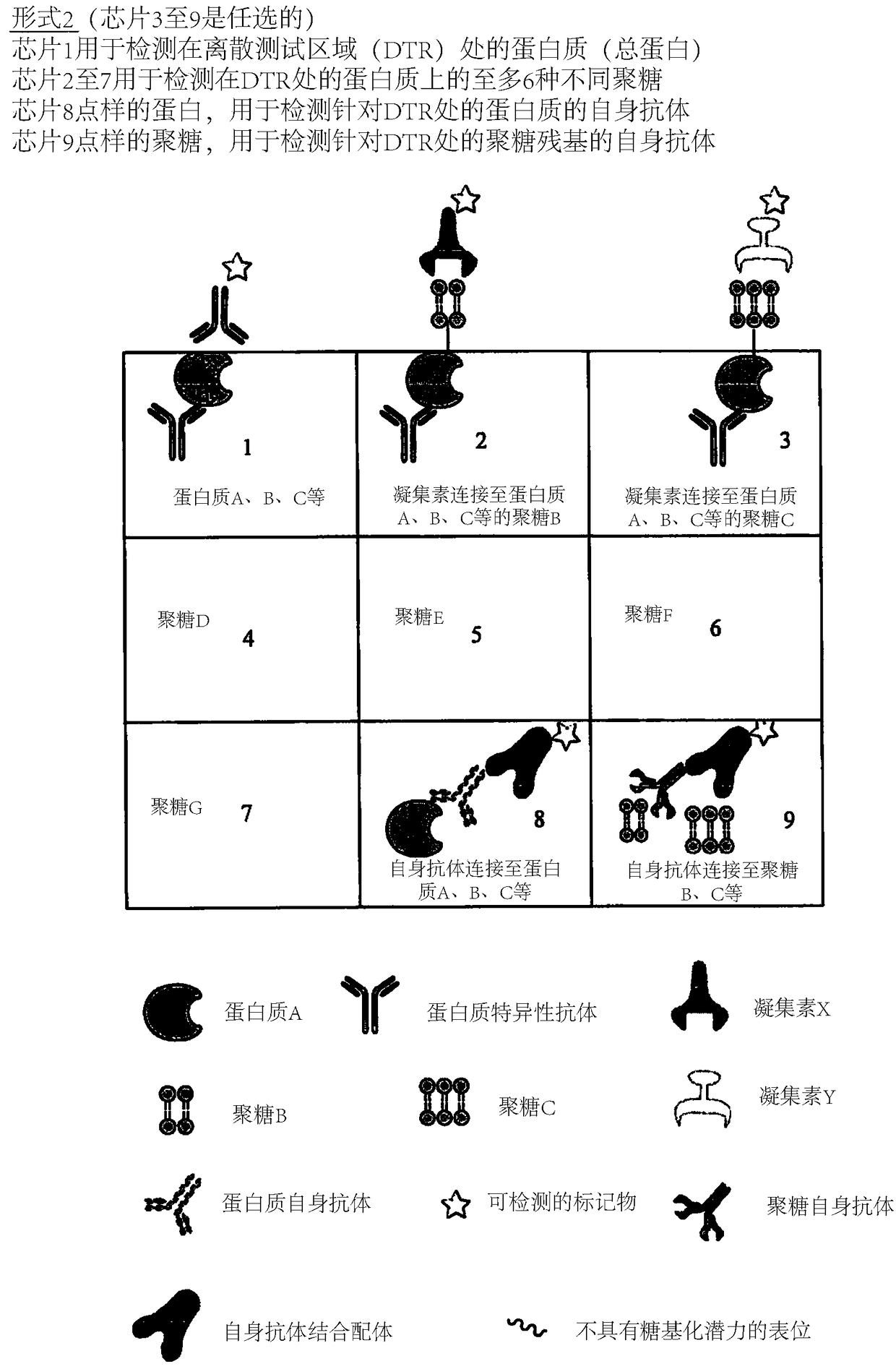
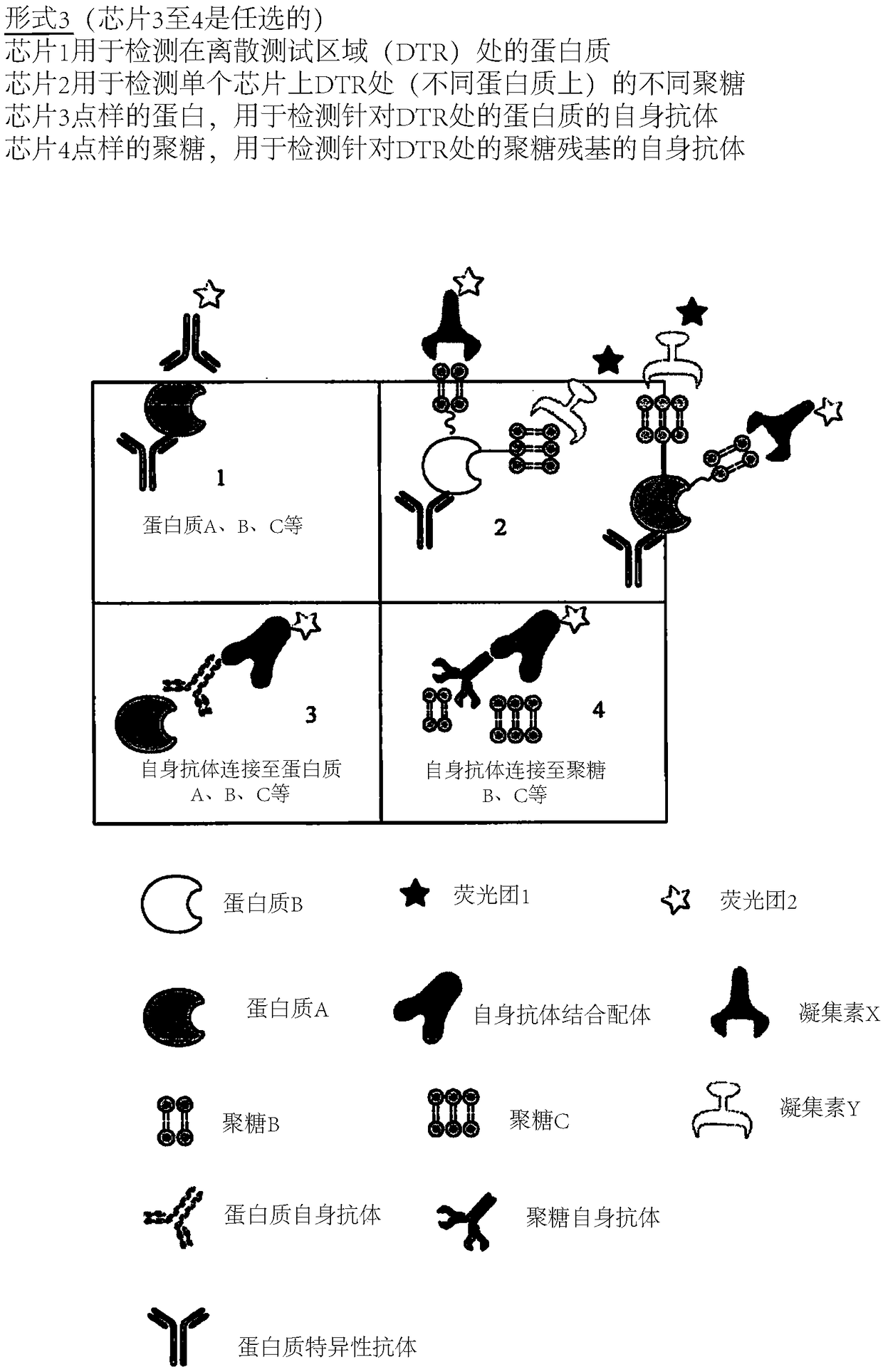
Determination of glycosylation signature
A glycan, substrate technology, applied in the field of glycosylation signature determination, which can solve the problem of underestimating protein levels and false results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0087] Enhanced biomarker detection using lectin / antibody epitopes masked by glycosylation
[0088] Fetuin A detection using lectins and antibodies
[0089] Fetuin A is an acute-phase anti-inflammatory glycoprotein secreted by the liver into the circulation and has been identified as a mediator of growth signaling in breast cancer cells. There are six reported glycosylation sites on fetuin A with four O-linked n-acetylgalactosamine sites for the C-terminus of the protein. The potential of these glycosylation modifications to mask the detection of fetuin A captured in sera from normal or breast cancer patients was assessed. Figure 10 showed that in patients with breast cancer, the n-acetylgalactosamine-containing fetuin A protein was detectable and indeed elevated relative to normal controls using the VVA lectin. However, using a specific detection antibody (called Ab1, Figure 10 B) Instead of detecting similar levels of protein across sample sets, alternative assays (Ab...
Embodiment 2
[0091] Rationale for additional benefit from multiplex analysis of glycoprotein markers
[0092] Detection of pancreatic cancer by a single circulating disease biomarker has been shown to be insufficient due to poor identification of patients with early-stage disease. Thus, the concept has emerged that multifaceted pathology can be reflected in the simultaneous detection of multiple disease markers. Figure 11 A proof of principle for improved diagnostic capability in pancreatic cancer (pancreatic cancer serum samples vs. ROC AUC values for CA19-9, CEA or A1AG.
Embodiment 3
[0094] Examples of Additional Clinical Benefits of Glycosylation
[0095] Improved detection of pancreatic cancer biomarkers in patient serum samples using glycosylation
[0096] A comparison was made between classical immunoturbidimetric total protein and biochip-based detection of glycosylated alpha-1 acid glycoprotein (A1AG). Subsequent analyzes were used to determine the diagnostic ability of each assay platform to identify pancreatic cancer in the developing patient sample cohort. The total protein detection method returned a ROC AUC value of 0.648, which did not reach statistical significance (p: 0.2155, Figure 12 A). In addition, there was no statistically significant difference in total protein overall between pancreatic cancer and normal controls (p: 0.1614, Figure 12 B). However, using the AAL-mediated fucosylated A1AG assay, a significant improvement in ROC output (0.919) was observed, which reached statistical significance (p Figure 12 C). RLU output repre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com