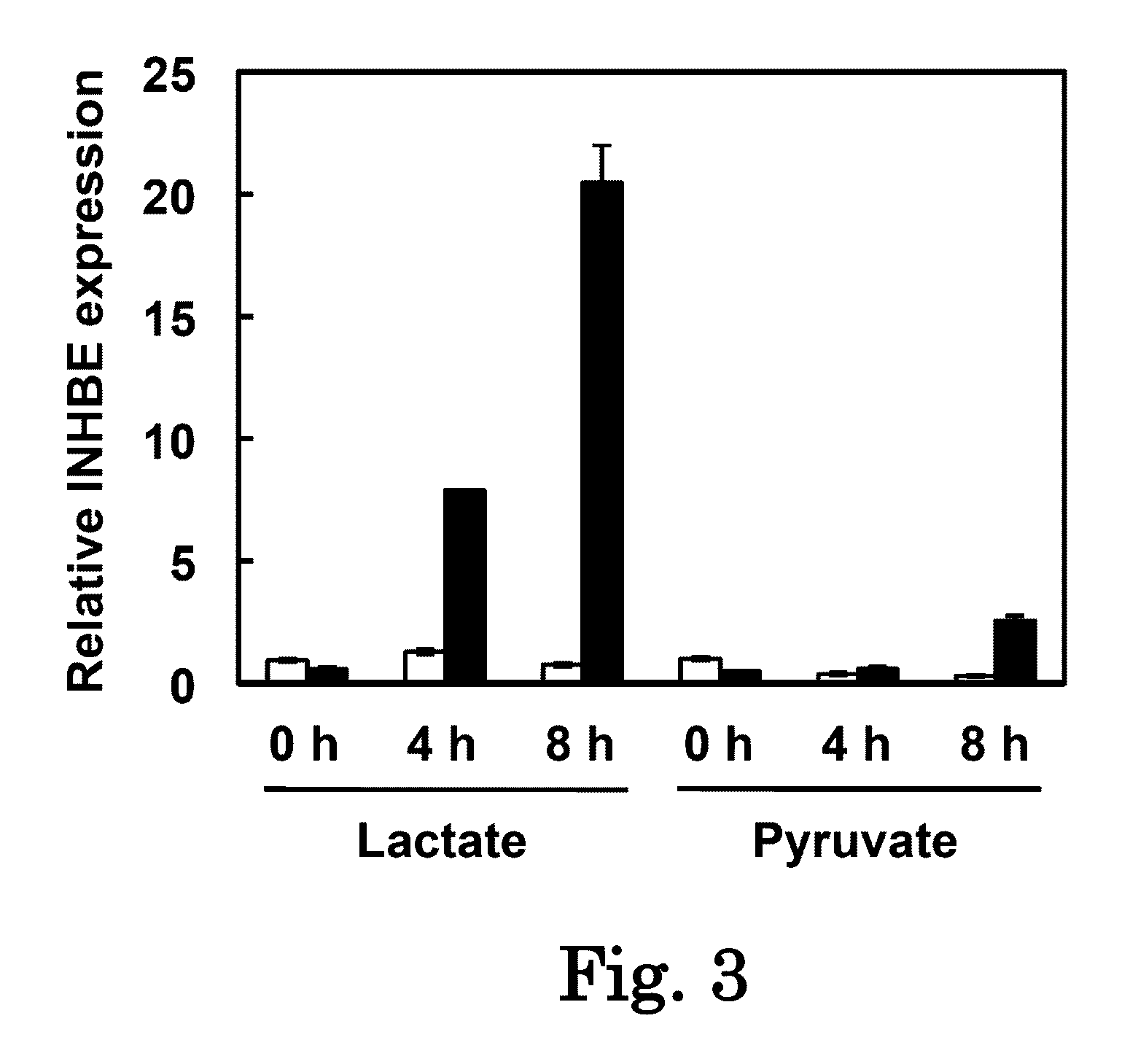
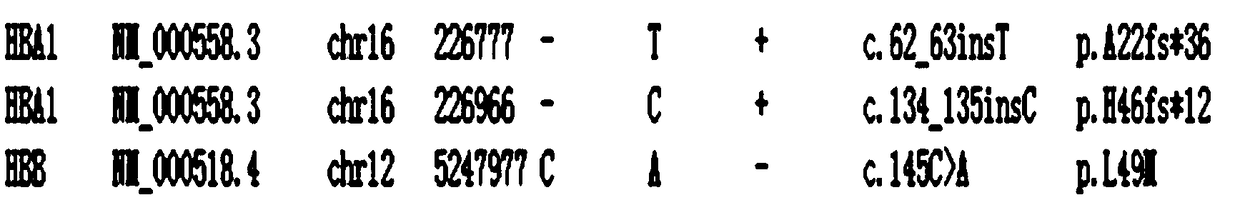Patents
Literature
39 results about "Protein S level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for reducing complexity of a sample using small epitope antibodies
InactiveUS20050131219A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsEpitopeProteomics
The present invention relates generally to methods for reducing the complexity of a sample. More specifically, the present invention relates to proteomics, the measurement of the protein levels in biological samples, and analysis of proteins in a sample using antibodies that recognize small epitopes.
Owner:TETHYS BIOSCI
Universal construction method for protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound
InactiveCN103265635AReduce the numberImprove discovery efficiencyHybrid peptidesSpecial data processing applicationsChemical synthesisUniversal construction
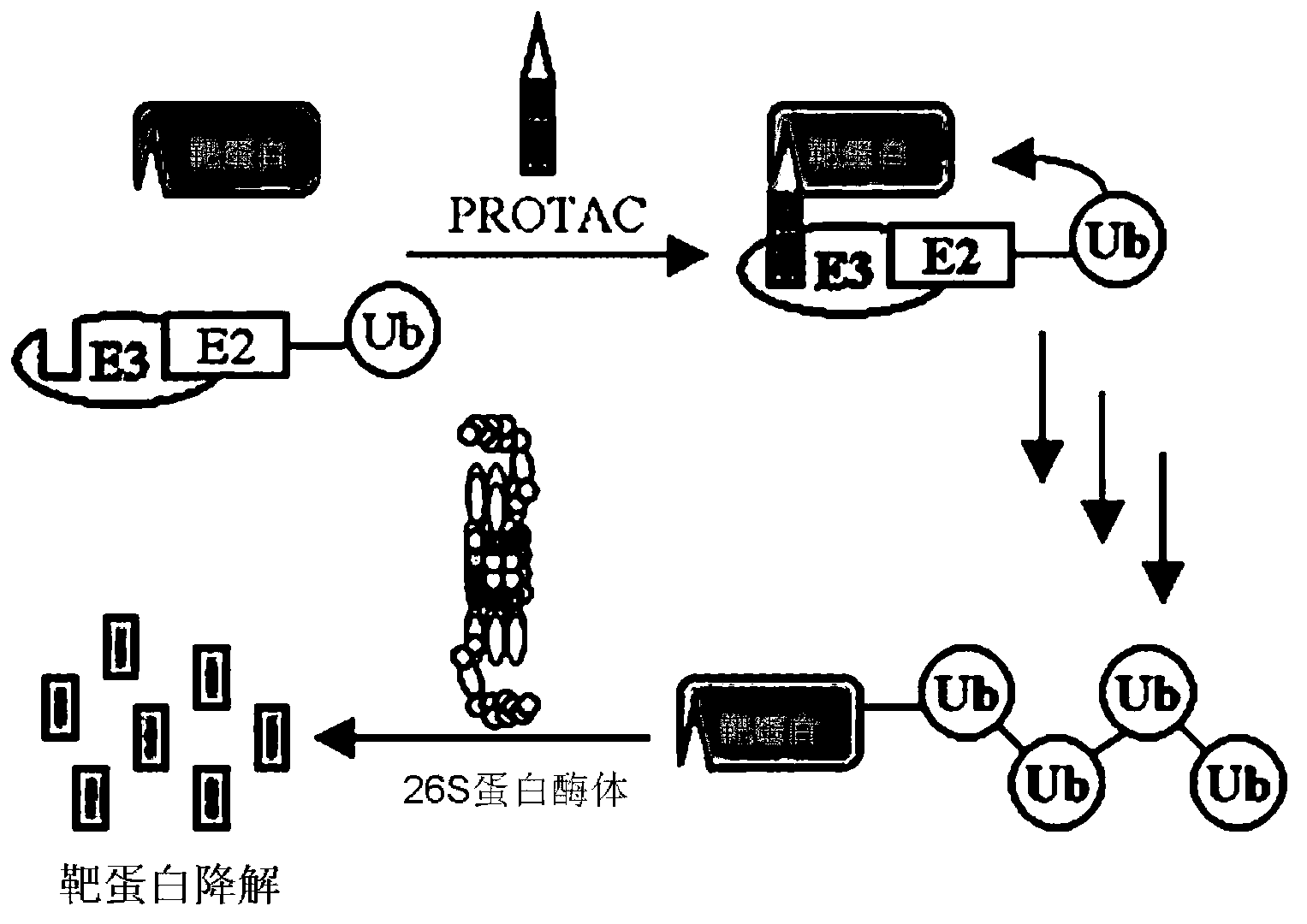
The invention discloses a universal construction method for a protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound. The objective of the invention is to provide a method for adjusting the level of proteins by degrading the proteins through targeted ubiquitination. The construction method mainly comprises the following steps: 1) locating and analyzing a three-dimensional structure of a target protein and predicting active sites; 2) selecting a compound database; 3) virtually screening ligand compounds having high degrees of adaption to the target protein by using a computer; 4) acquiring the screened ligand compounds and screening an optimal ligand compound of the target protein through detection of interaction between micromolecules and the proteins; 5) constructing a protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound composed of the optimal ligand compound of the target protein, ubiquitin ligase E3 identification ligand and Linker connecting the optimal ligand compound of the target protein to the ubiquitin ligase E3 identification ligand by using a combination manner simulated by the computer; and 6) chemically synthesizing the protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound. With the method provided by the invention, the protein-targeting chimeric molecule compound can be rapidly and highly efficiently prepared, and specific degradation of intracellular target proteins is realized.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
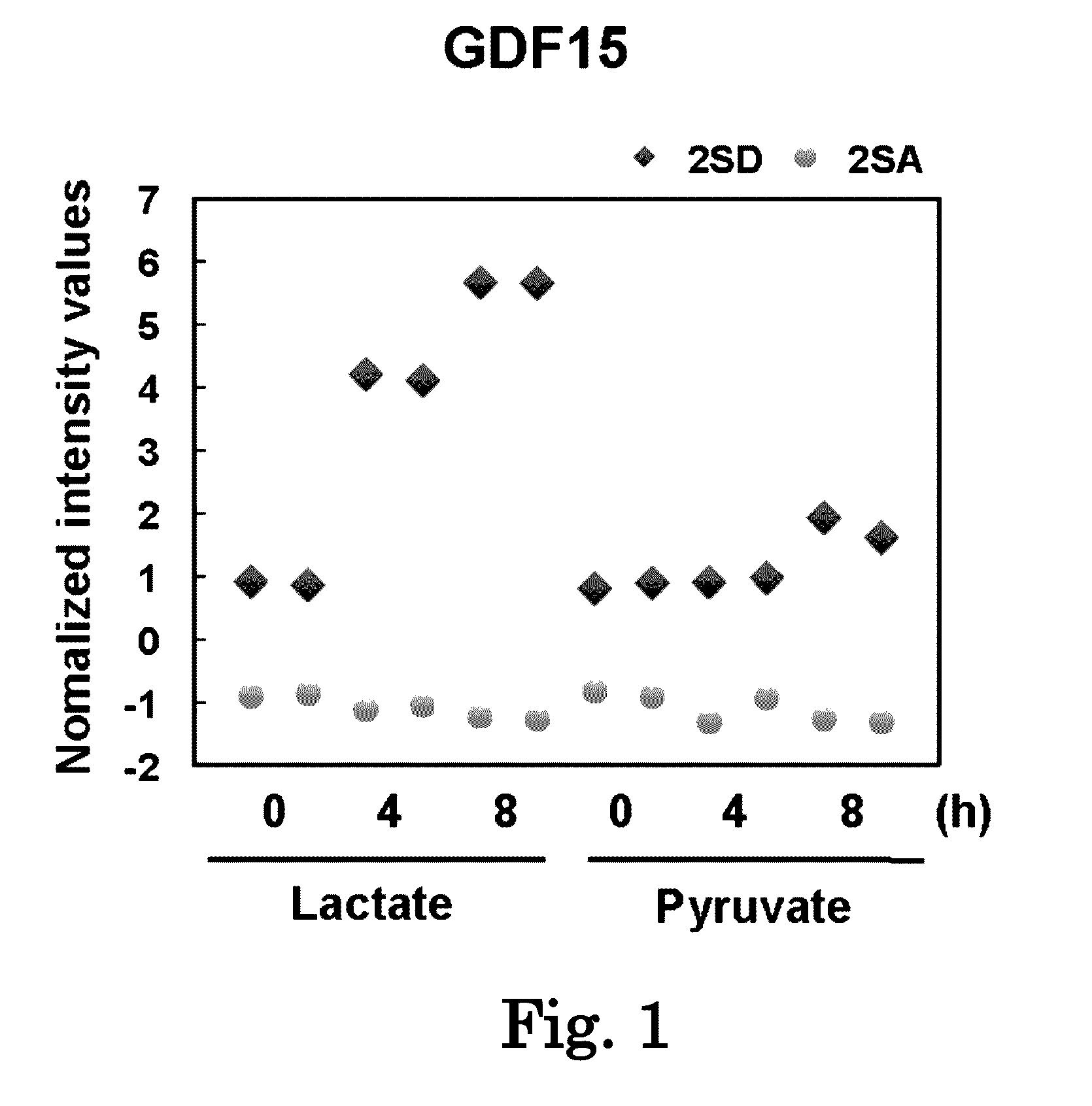
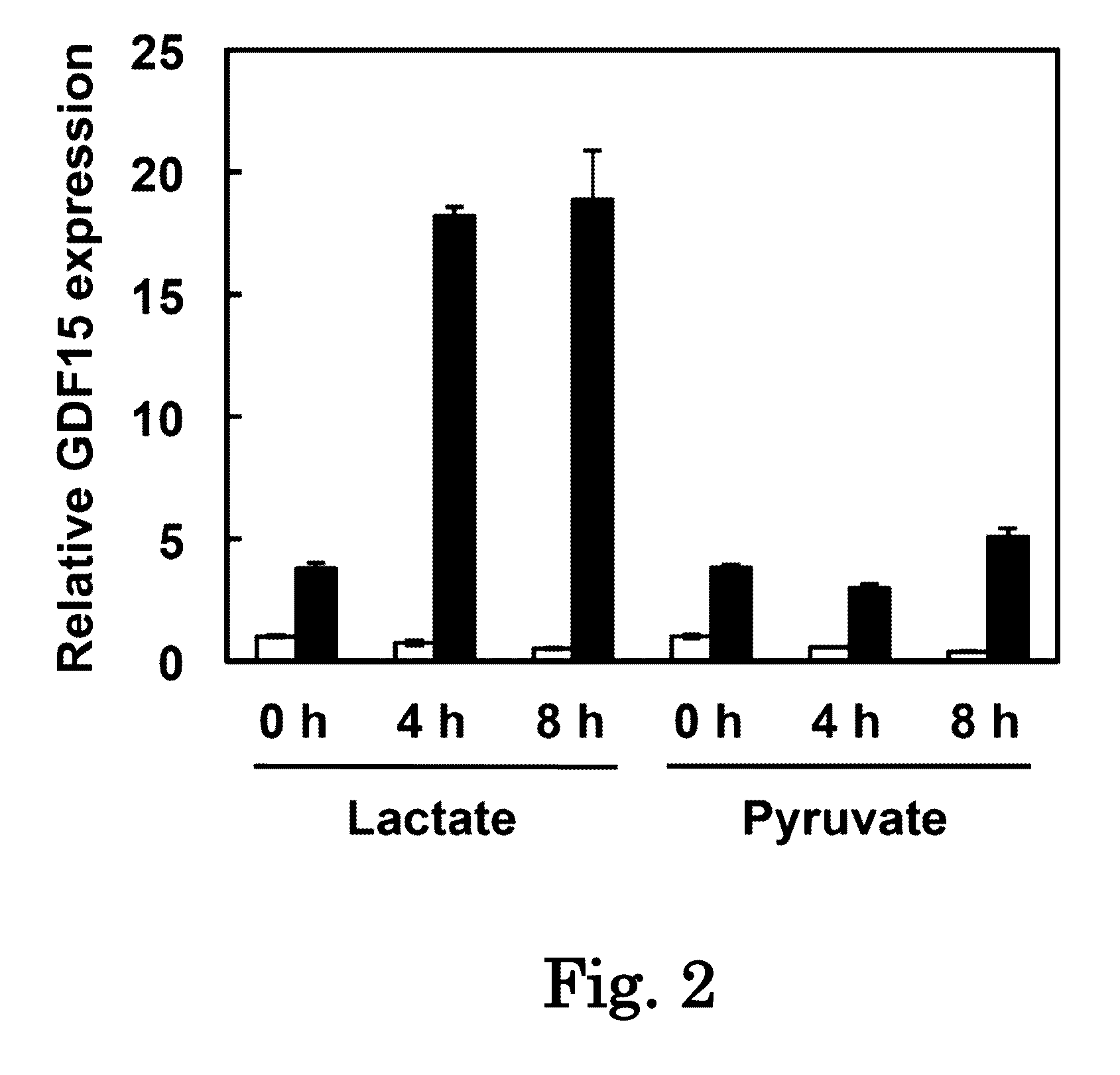
Gdf15 as biomarker for diagnosing mitochondrial diseases
InactiveUS20170010280A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against growth factorsDiseaseMitochondrial disease
To obtain data associated with a mitochondrial disease, a method includes measuring the level of at least one protein selected from the group consisting of GDF15 (growth differentiation factor 15), HGF (hepatocyte growth factor), MIG (gamma interferon induction monokine), SCF (stem cell factor) and SCGF-β (stem cell growth factor beta) in a biological sample collected from a subject. The measured protein level is compared to that of control subjects and then it is checked whether or not there is difference between the protein level of the subject and that of control subjects.
Owner:KURUME UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
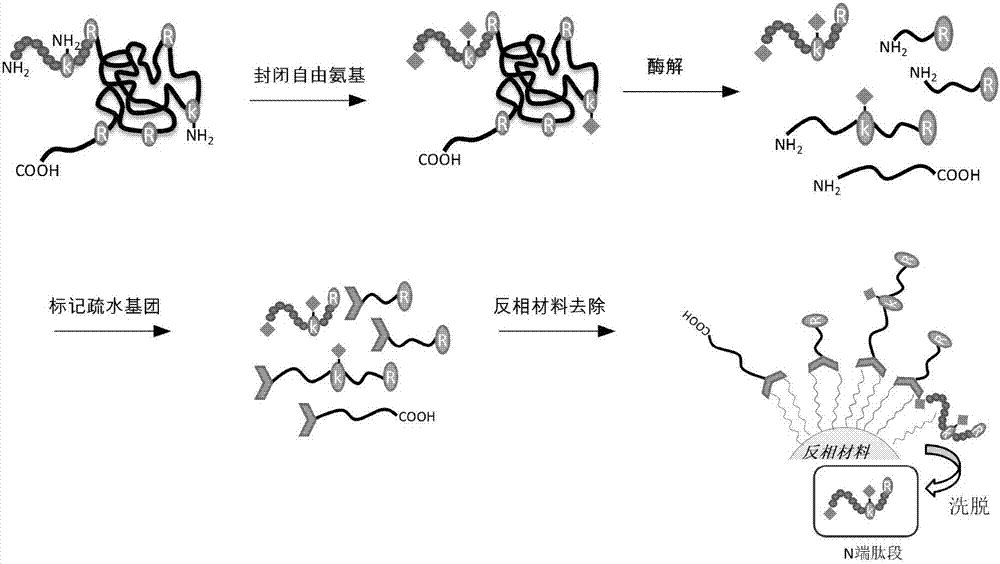
Hydrophobic group modification-based protein N-terminal enrichment method
ActiveCN107305172AAvoid co-removalHigh recovery ratePreparing sample for investigationBiological testingCrystallographySide chain
The invention relates to a hydrophobic group modification-based protein N-terminal enrichment method, which comprises the steps of sealing free amino groups in protein level, carrying out marking through a strong hydrophobic group, and carrying out affiliative trapping through a reverse phase material. Particularly, the method comprises the steps of firstly sealing free amino groups of an N terminal and a side chain in protein level by adopting chemical modification and carrying out enzymolysis on the protein; introducing the strong hydrophobic group to a non-N-terminal peptide segment through newly generated free amino groups; and finally removing the non-N-terminal peptide segment with the strong hydrophobic group by adopting the reverse phase material in an affiliative manner to obtain an N-terminal peptide segment of the protein. The hydrophobic group modification-based protein N-terminal enrichment method has the advantages of being high in mark efficiency, high in removal efficiency, high in selectivity and simple in processing step, and the sample loss and nonspecific adsorption are reduced.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Globin gene dual-expression lentivirus vector and application thereof
ActiveCN111363756AAchieve perfect cut and separationAchieve separationSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsGlobin genesViral vector
The present invention provides a globin gene dual-expression lentivirus vector and an application thereof. The lentiviral vector comprises optimized multiple globin genes connected by P2A-T2A connecting peptides. The efficient expression of globin is realized in protein level, the length of the vector is substantially reduced, the lentivirus packaging efficiency is remarkably improved, the complexity and quality control requirements of a production process are lowered, the problems of low efficiency and high energy consumption of the globin lentivirus vector are solved fundamentally, and an innovative scheme is provided for high-cost-performance large-scale stable production of gene therapeutic drugs.
Owner:INST OF HEMATOLOGY & BLOOD DISEASES HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
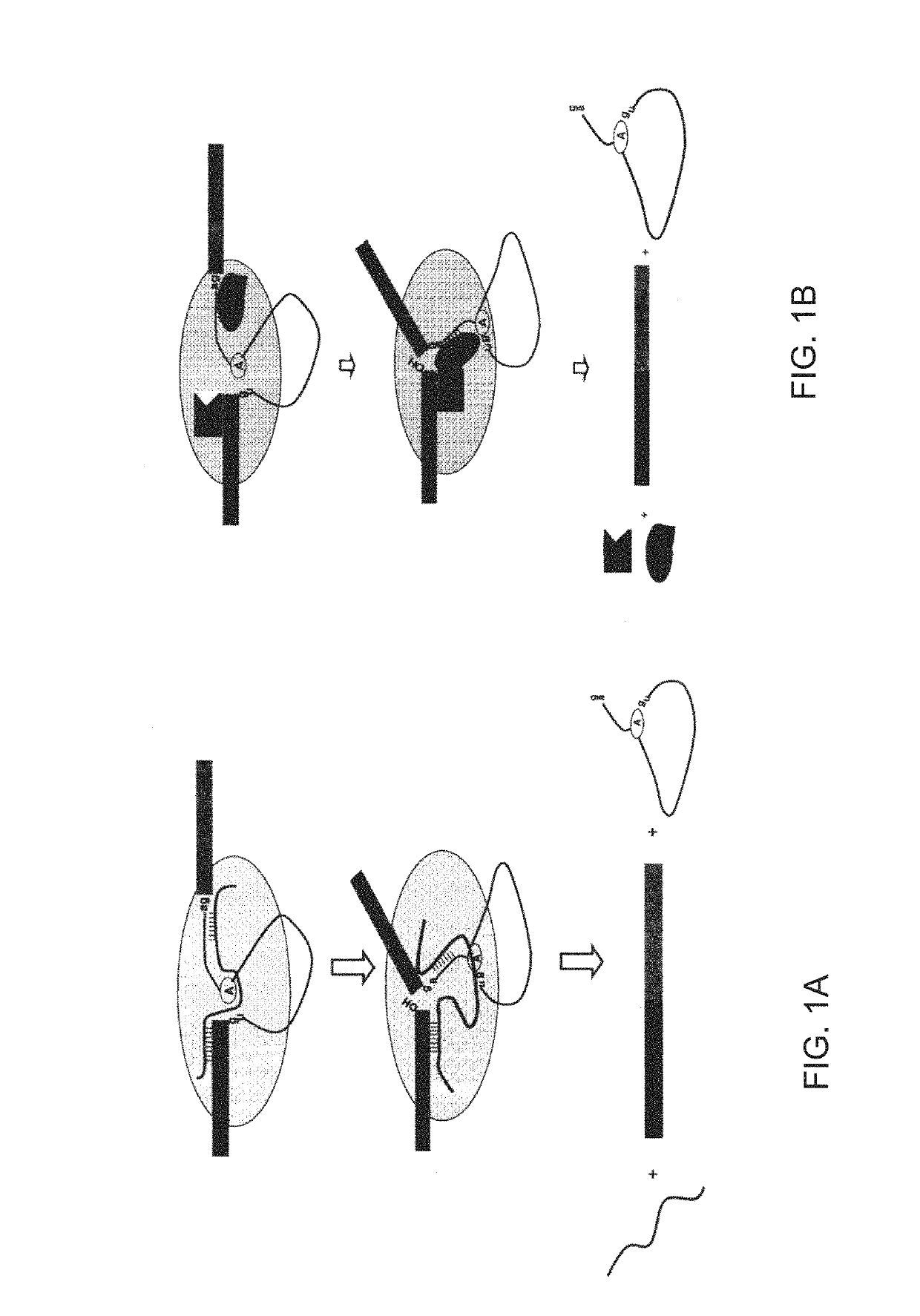
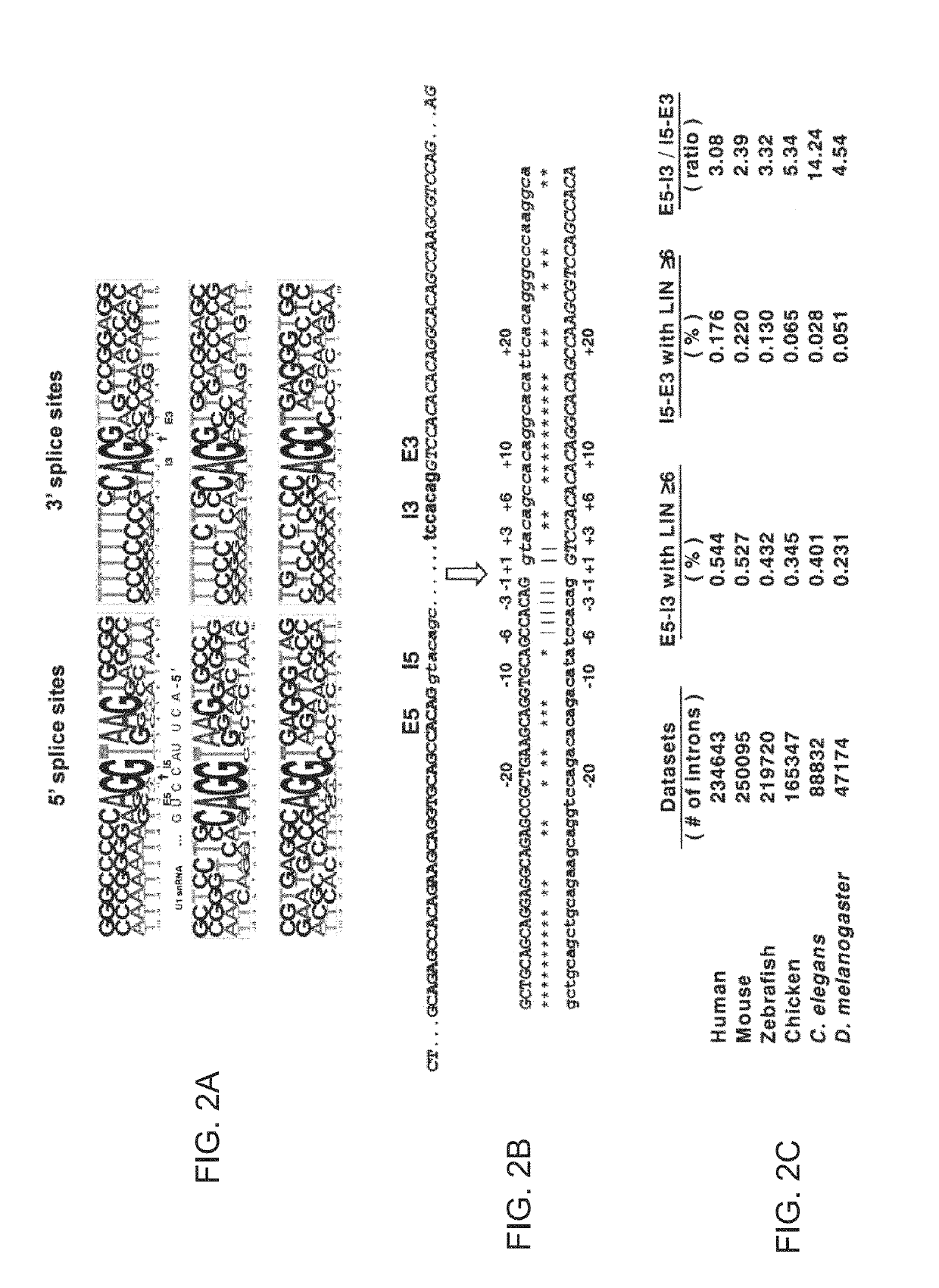
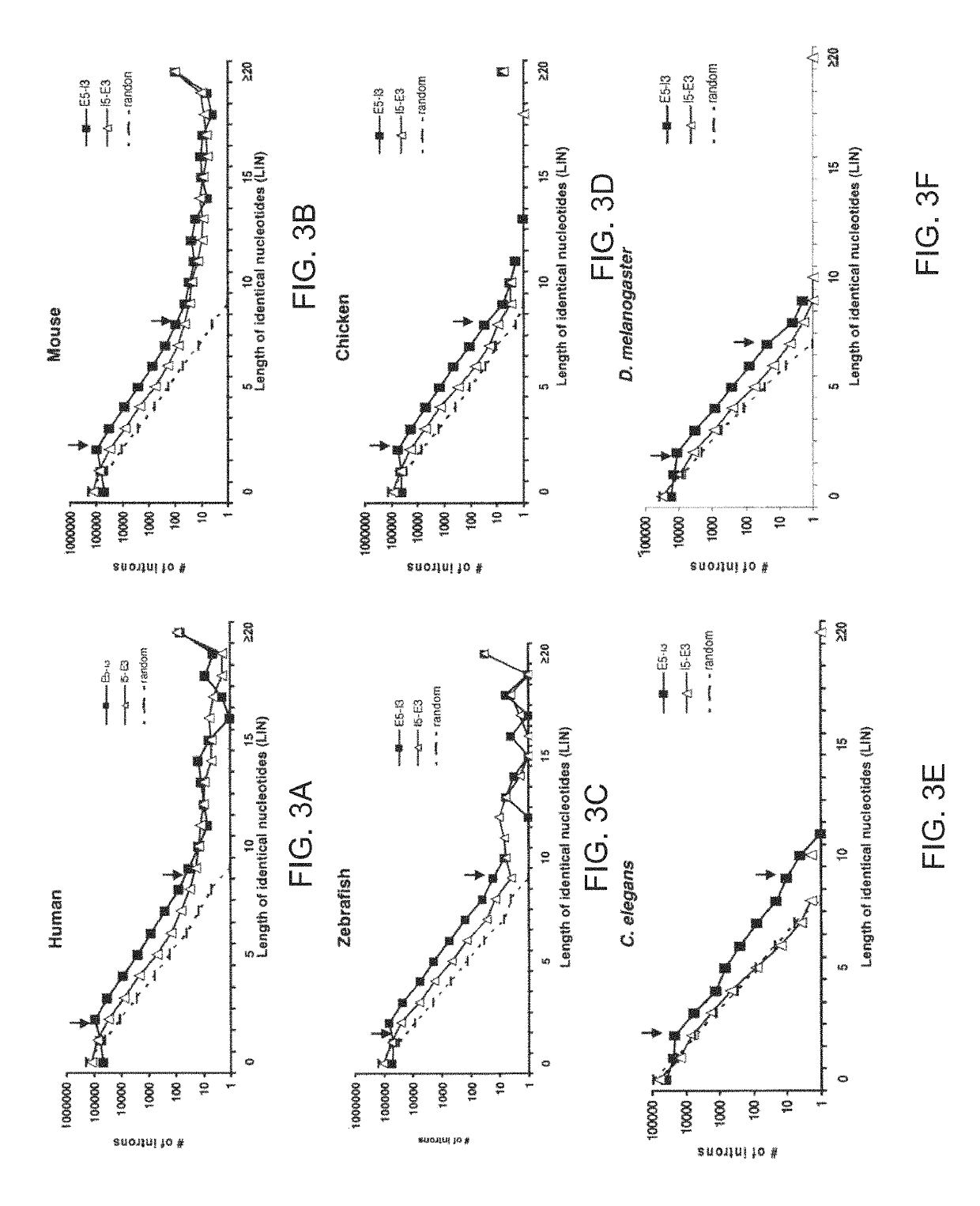
System and method for analyzing splicing codes of spliceosomal introns
ActiveUS10446261B1Lower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsDiseaseGenomic DNA
A system and method for analyzing splicing codes of spliceosomal introns is disclosed. One embodiment comprises methods of identifying introns and exons in genomic DNA or pre-mRNA sequences by locating characteristic markers in splicing junctions by computation and / or manually. Exon sequences predicted by computation can be verified and characterized by employing standard amplification methods, such as comparative genomic, RNA-seq, next-generation sequencing, RT-PCR. DNA / RNA / oligo, electrophoretic or protein chip technologies. If a given sample is verified, its polypeptide can be translated based on genetic codons. Its functions can be deduced based on its characteristics, computation predictions and related knowledge databases. These data can be used to compare databases which correlate the characterized intron or exon or gene to characterized diseases or genetic mutations. Isoforms can be detected and analyzed at mRNA and protein levels alone and with other isoforms predicted by computation, characterized by experiments and stored in existing databases.
Owner:BIOTAILOR
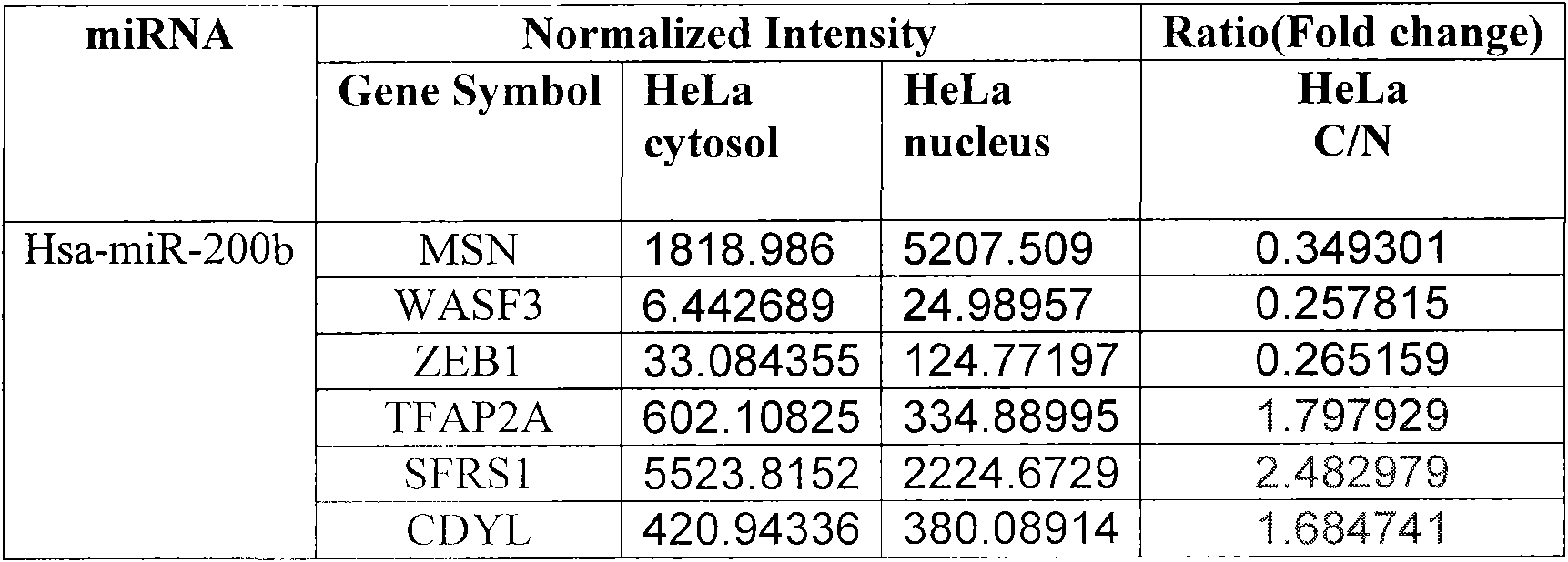
mRNA nucleoplasmic ratio variation-based method for identifying miRNA target gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a rapid and accuracy message Ribonucleic Acid (mRNA) nucleoplasmic ratio variation-based method for identifying a mirna Ribonucleic Acid (miRNA) target gene, and to application of the method in the biomedical field. The method is realized through the following technical scheme of: predicting possible target genes of a certain miRNA through the conventional miRNA target prediction bioinformatics software, such as Targetscan; measuring the mRNA nucleoplasmic ratio variation of the possible target genes in a cell by utilizing a biochip or real-time quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR); searching the possible target genes with an mRNA nucleoplasmic ratio of more than 1; and further confirming in the protein level through Western blot.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
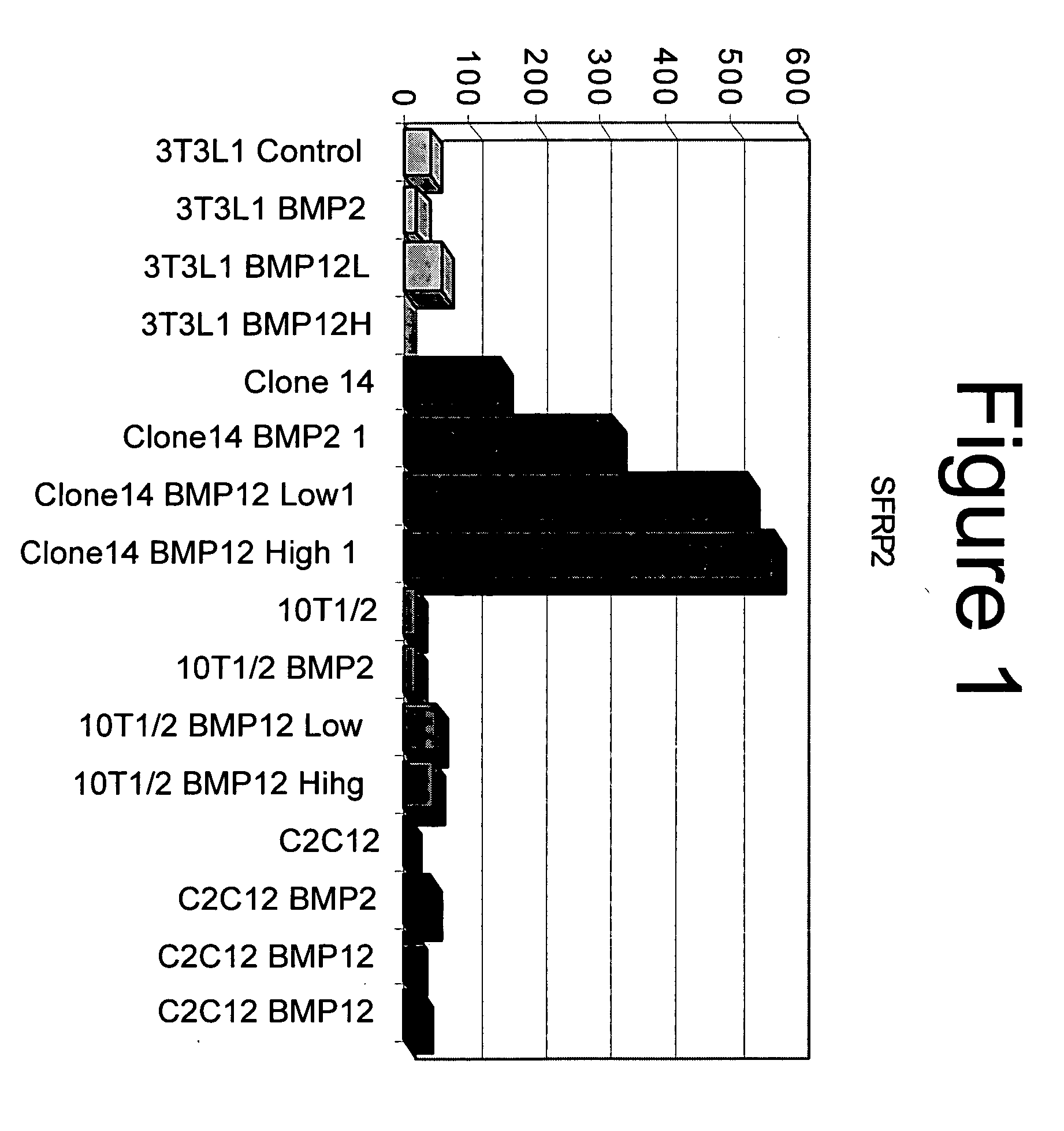
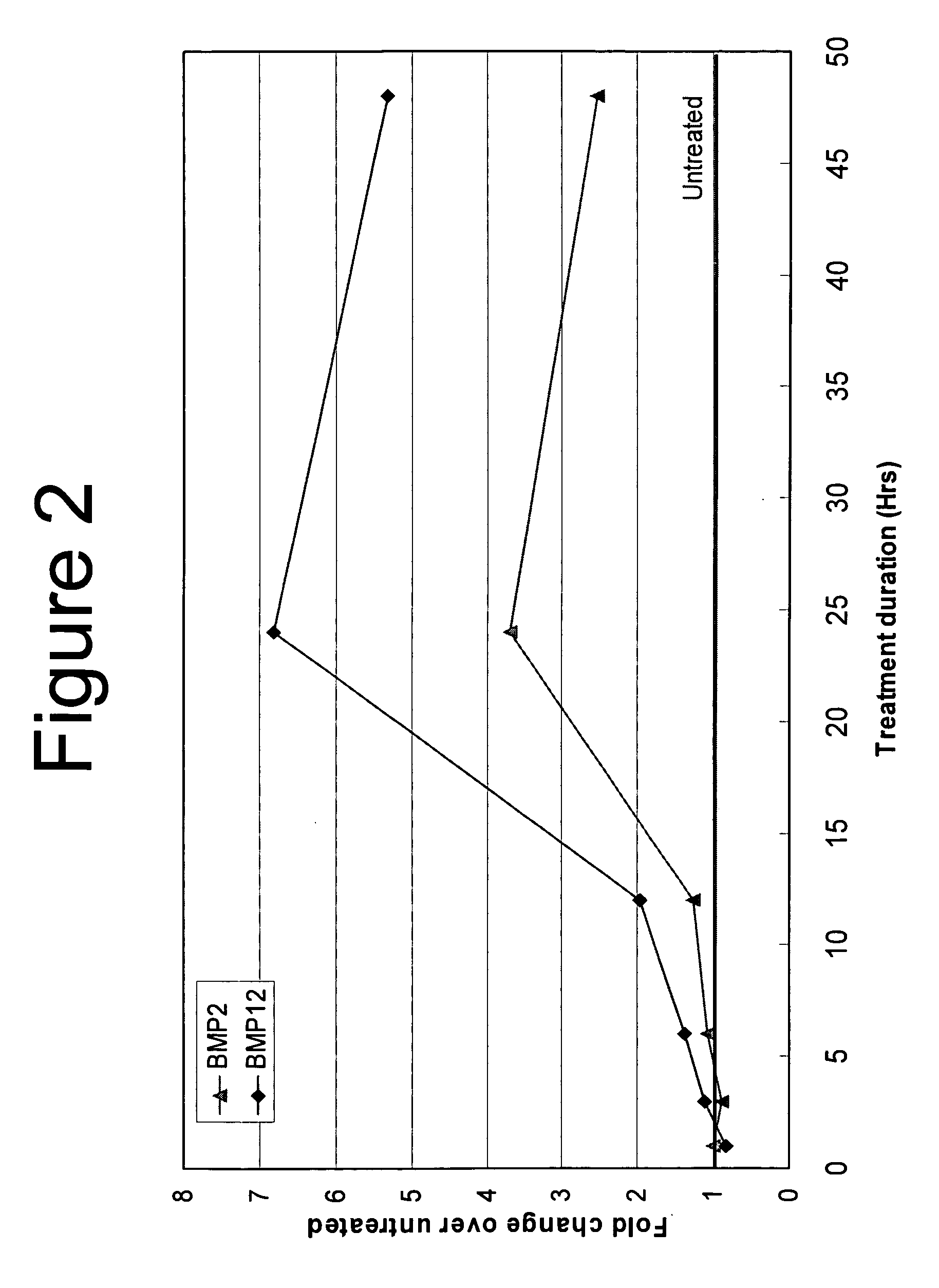
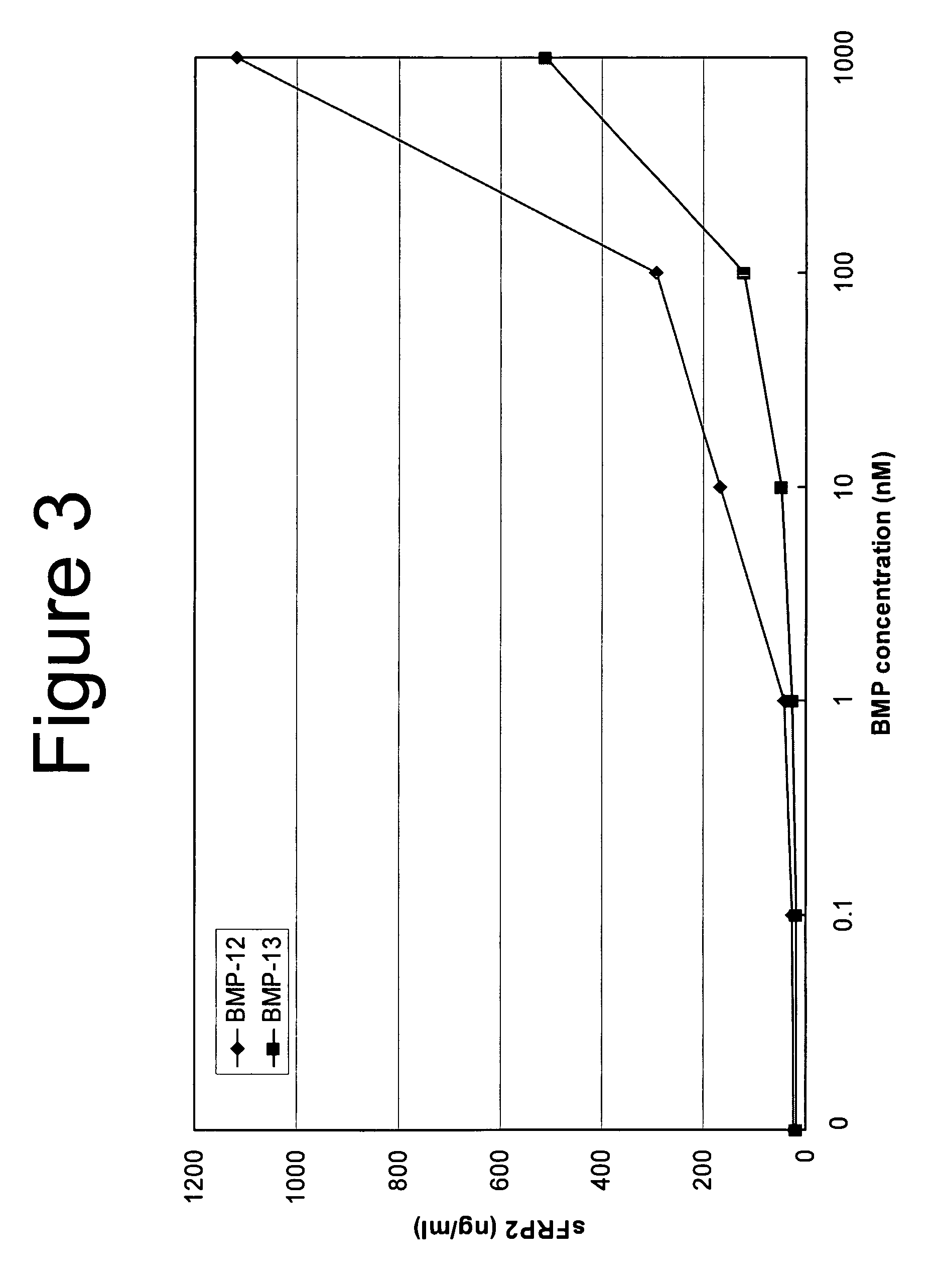
Use of sFRPs as markers of BMP activity
InactiveUS20060166251A1Improve the level ofMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisGene expressionBone morphogenetic protein
The disclosure provides assay systems for evaluating the presence of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) activity in a cell by evaluating the gene expression of secreted Frizzled Related Protein 2 and 3 (sFRP2 and sFRP3). The sFRP2 and sFRP3 gene expression may be detected at the RNA or protein levels. The methods include methods for evaluating exogenous and endogenous BMP expression and utilize both genomic sFRP2 and sFRP3 genes and reporter constructs.
Owner:WYETH
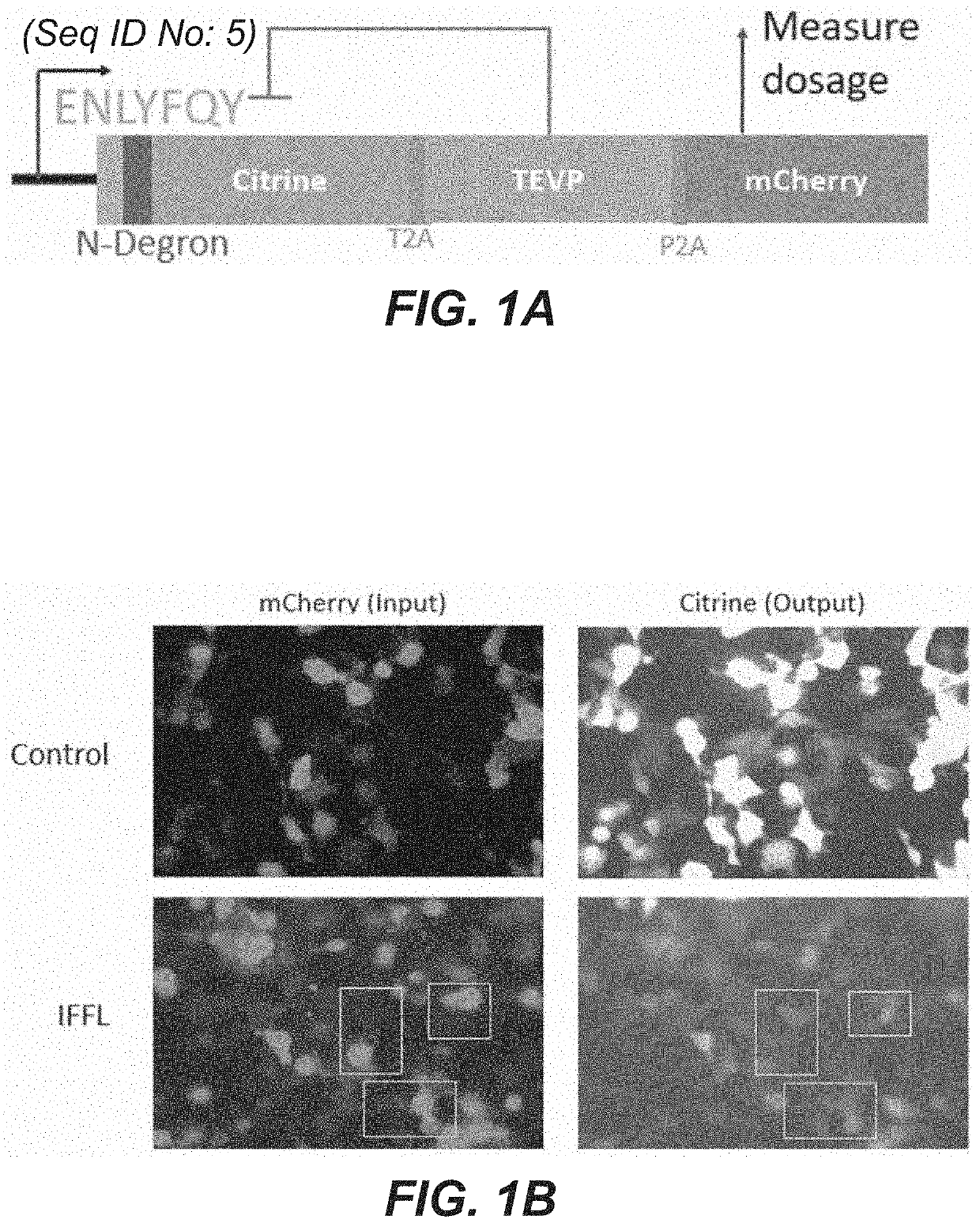
Method for robust control of gene expression
PendingUS20210171582A1Robust and tunable controlReduced stabilitySsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsPolynucleotidePromoter
Disclosed herein include methods, compositions, and kits suitable for robust and tunable control of payload gene expression. Some embodiments provide rationally designed circuits, including miRNA-level and / or protein-level incoherent feed-forward loop circuits, that maintain the expression of a payload at an efficacious level. The circuit can comprise a promoter operably linked to a polynucleotide encoding a fusion protein comprising a payload protein, a protease, and one or more self-cleaving peptide sequences. The payload protein can comprise a degron and a cut site the protease is capable of cutting to expose the degron. The circuit can comprise a promoter operably linked to a polynucleotide comprising a payload gene, a silencer effector cassette, and one or more silencer effector binding sequences.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for precisely and quantitatively detecting function effect of anti-prion medicament at protein level
ActiveCN101858910AShorten the timeOvercoming incomplete transferMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisImage analysisWestern blot
The invention relates to a method for precisely and quantitatively detecting function effect of an anti-prion medicament at a protein level. The invention adopts the technical scheme that the method comprises the following steps of: 1) activating saccharomyces cerevisiae cells; 2) primarily screening the anti-prion medicament, namely culturing the medicament to be detected, YPD liquid culture medium and prepared saccharomyces cerevisiae cell bacteria suspension for 1 to 5 days with shaking, and primarily judging the treatment effect of the medicament to be detected according to the change of the colony color; 3) quantitatively detecting the function effect of the anti-prion medicament by using an SDD-AGE / Western blot method; and 4) scanning and analyzing images by using a full-automatic image analysis system. The method can precisely evaluate the function effect of the medicament by detecting the soluble change of prion protein aggregates in the cells at the protein level, and judge the effect magnitude of the medicament on the prion at the protein level by quantitatively detecting the change of molecular weight of the prion protein aggregates.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for inactivating target transcription factor using artificial small interfering peptide and use thereof
ActiveUS20160138036A1High precision and efficiencyInhibitory activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTranscription factor activityProtein level
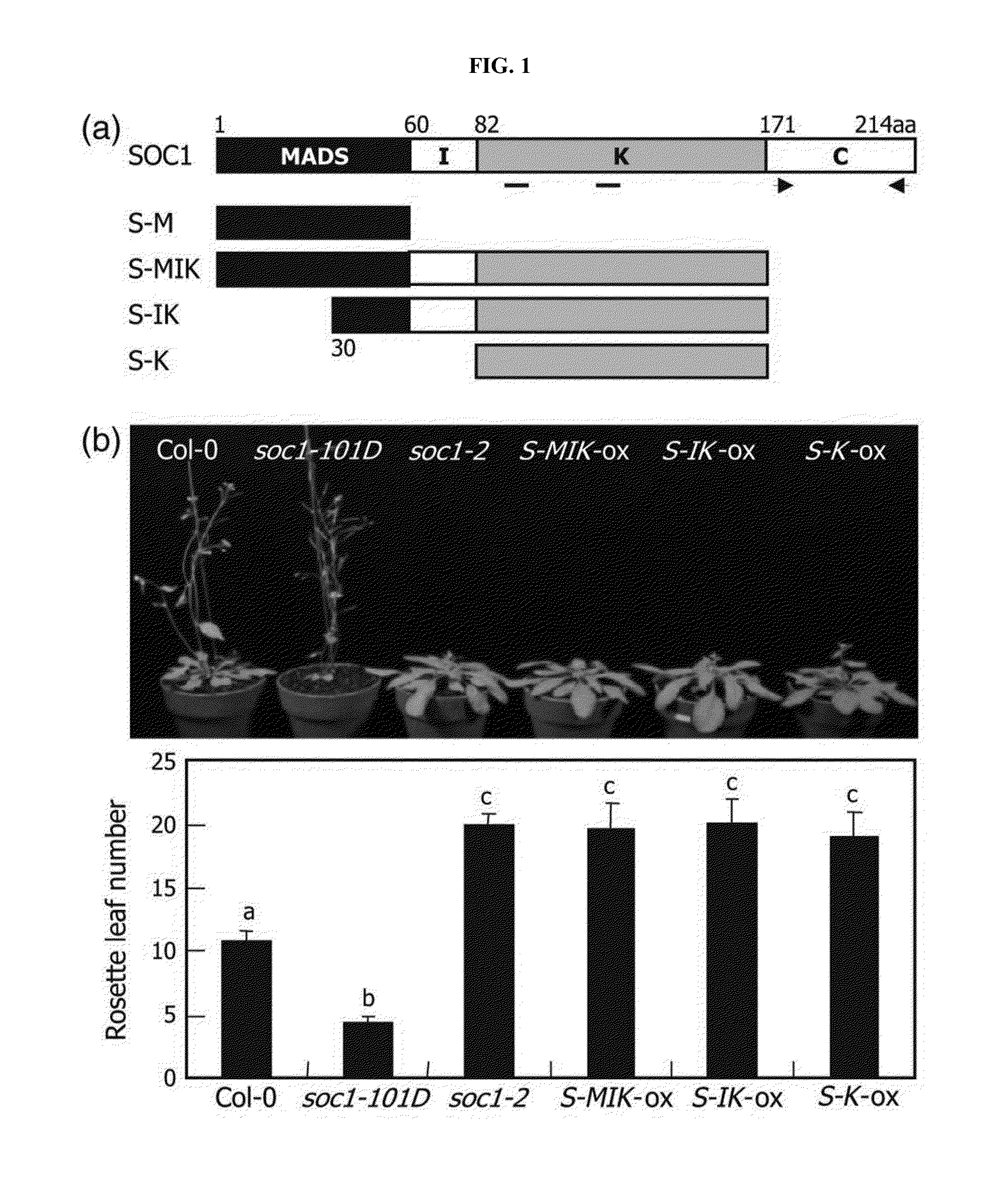
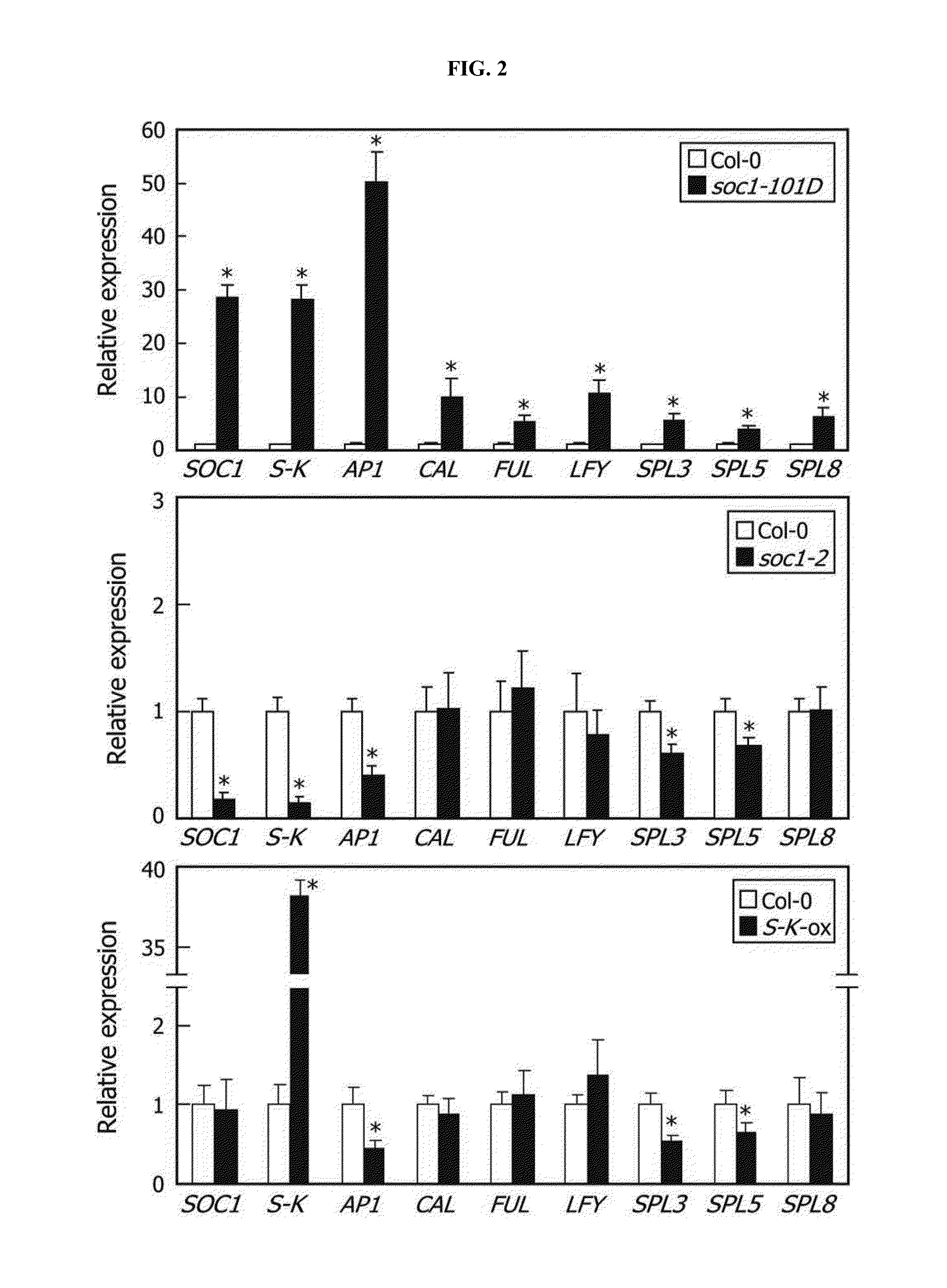
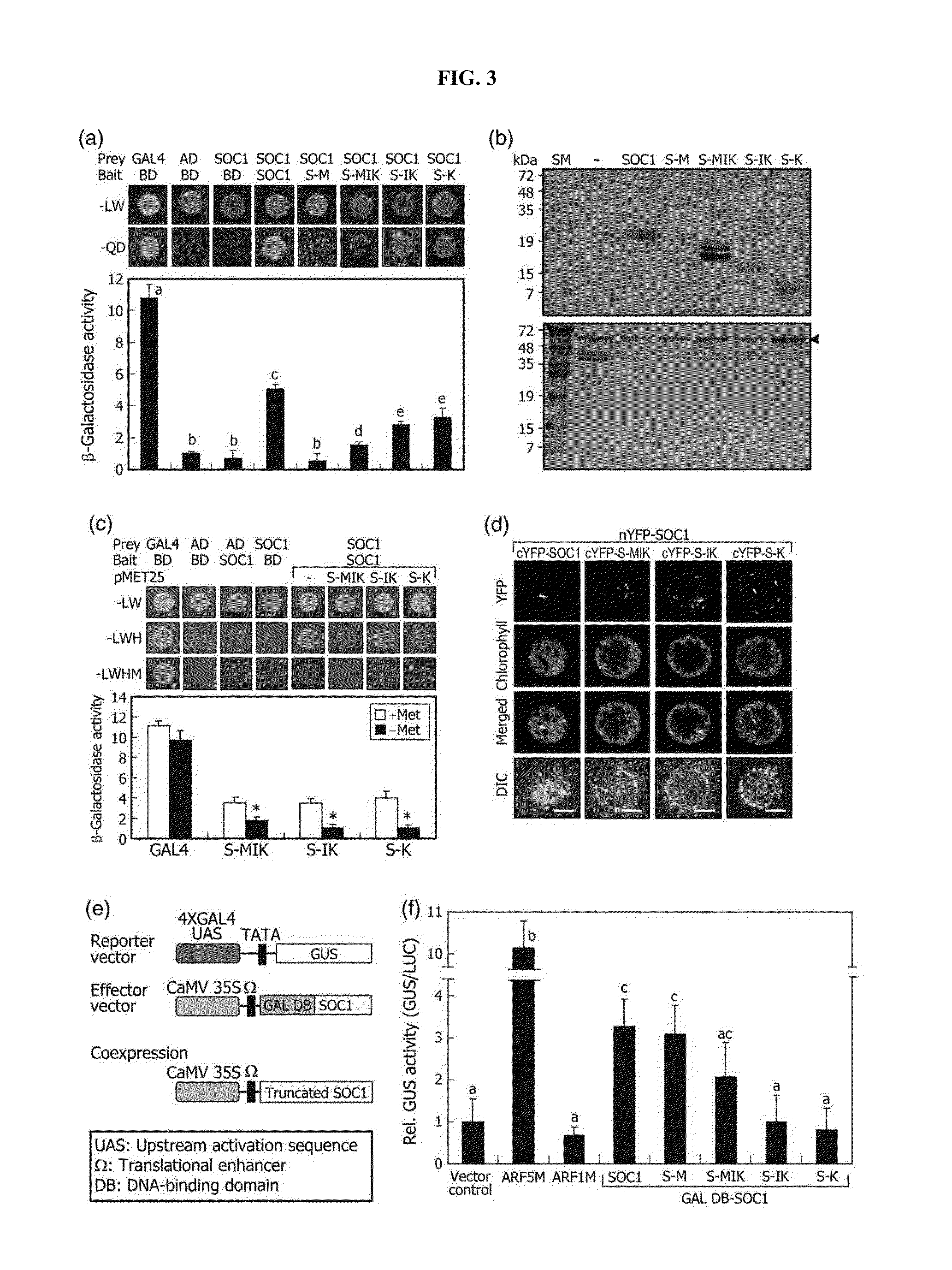
The present invention relates to a method for targeted inactivation of transcription factor using an artificial small interfering peptide and a use thereof. According to the present invention, an artificial small interfering peptide (a-siPEP) as a truncated from of the transcription factor for regulating transcription by dimerization was produced. It was also confirmed that, as a-siPEP forms a heterodimer with a transcription factor, DNA binding and transport into a nucleus of the transcription factor are inhibited, so that inactivation of the transcription factor is achieved at protein level. The method for inhibiting transcription factor activity using a-siPEP can replace a gene knock-out method and it allows protein-level inhibition of a transcription factor. Also, it is a transcription regulation method with high precision and high efficiency that can be applied for both monocot and dicot plants.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Determination of glycosylation signature
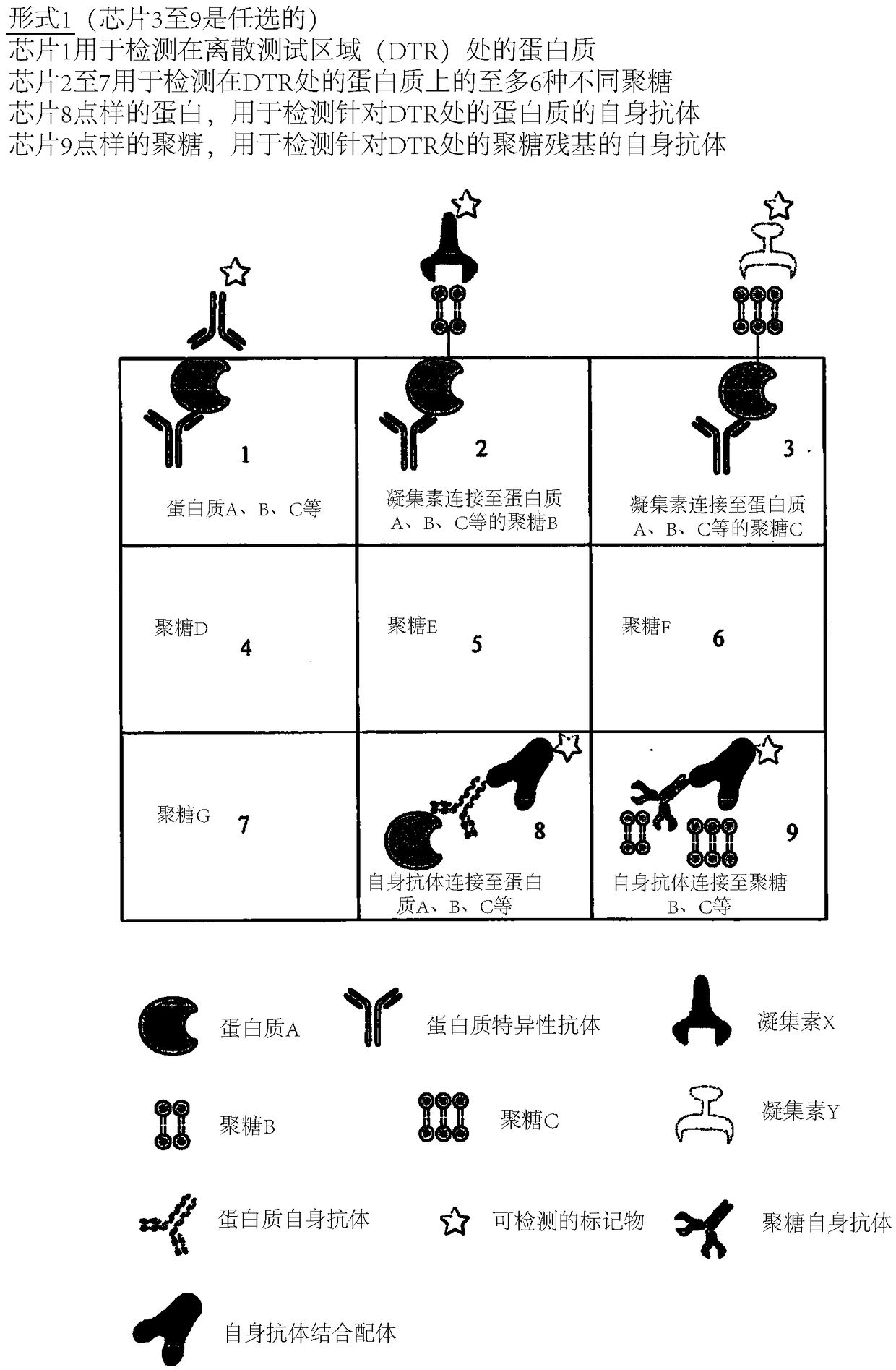
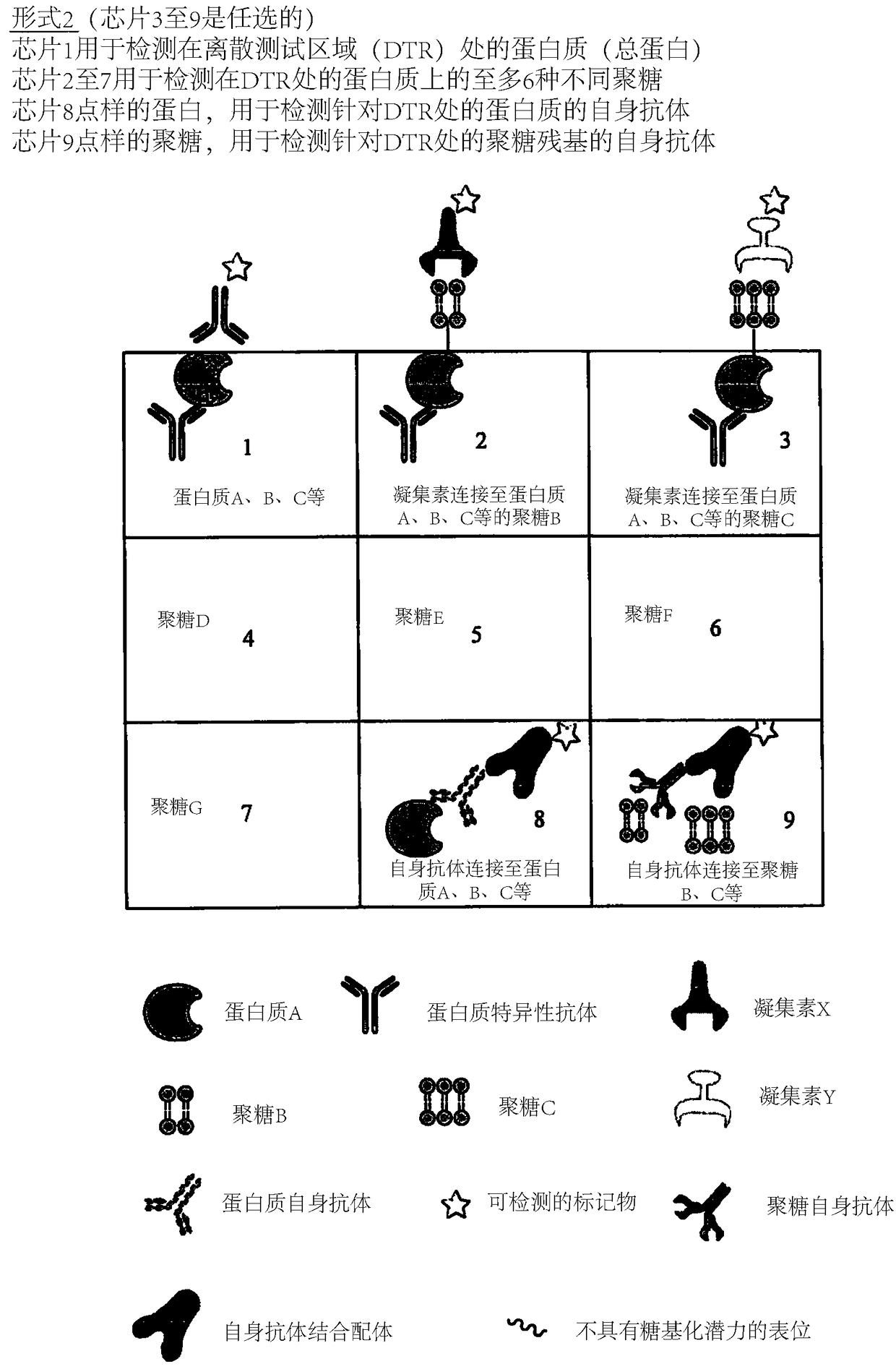
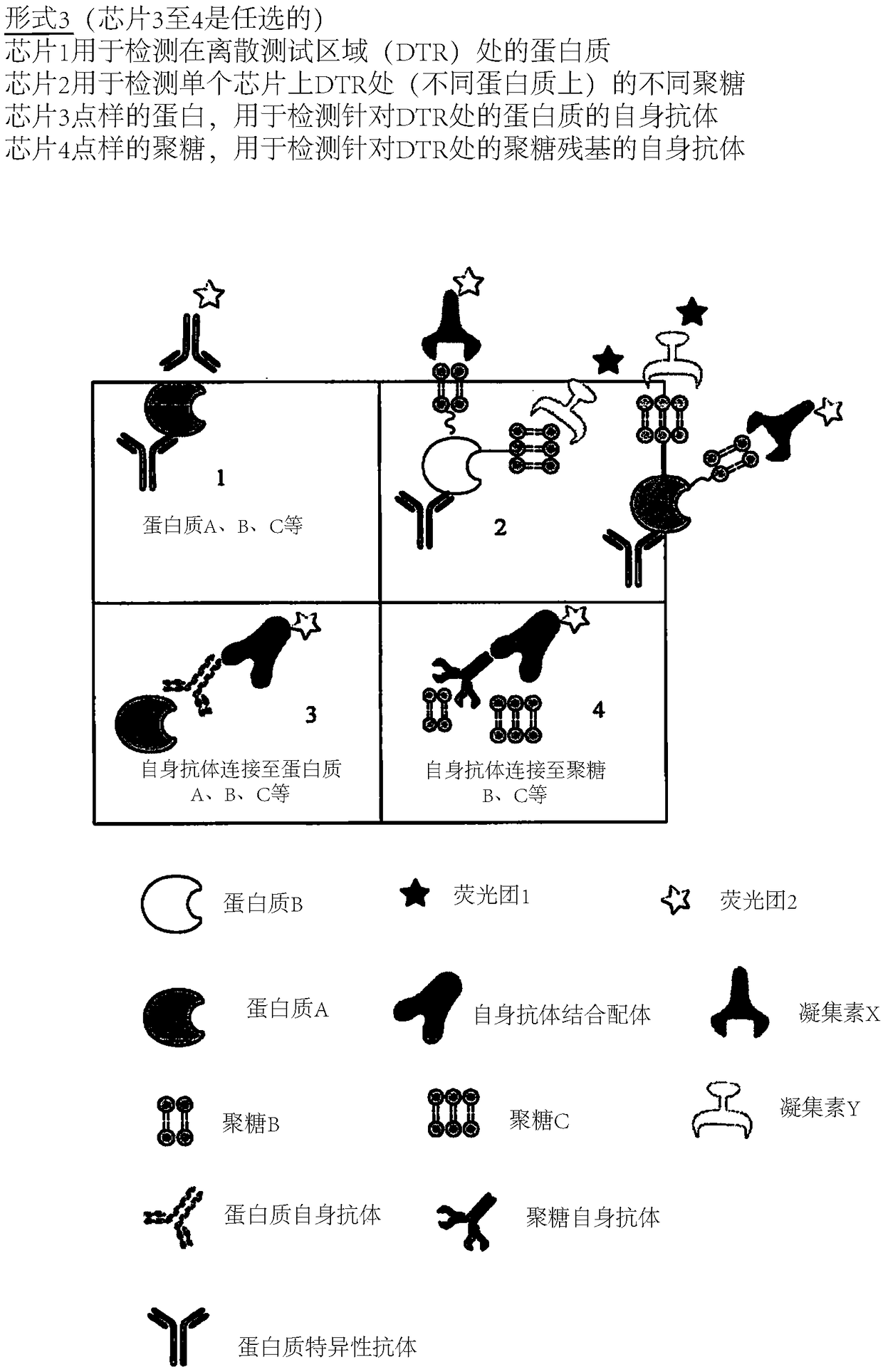
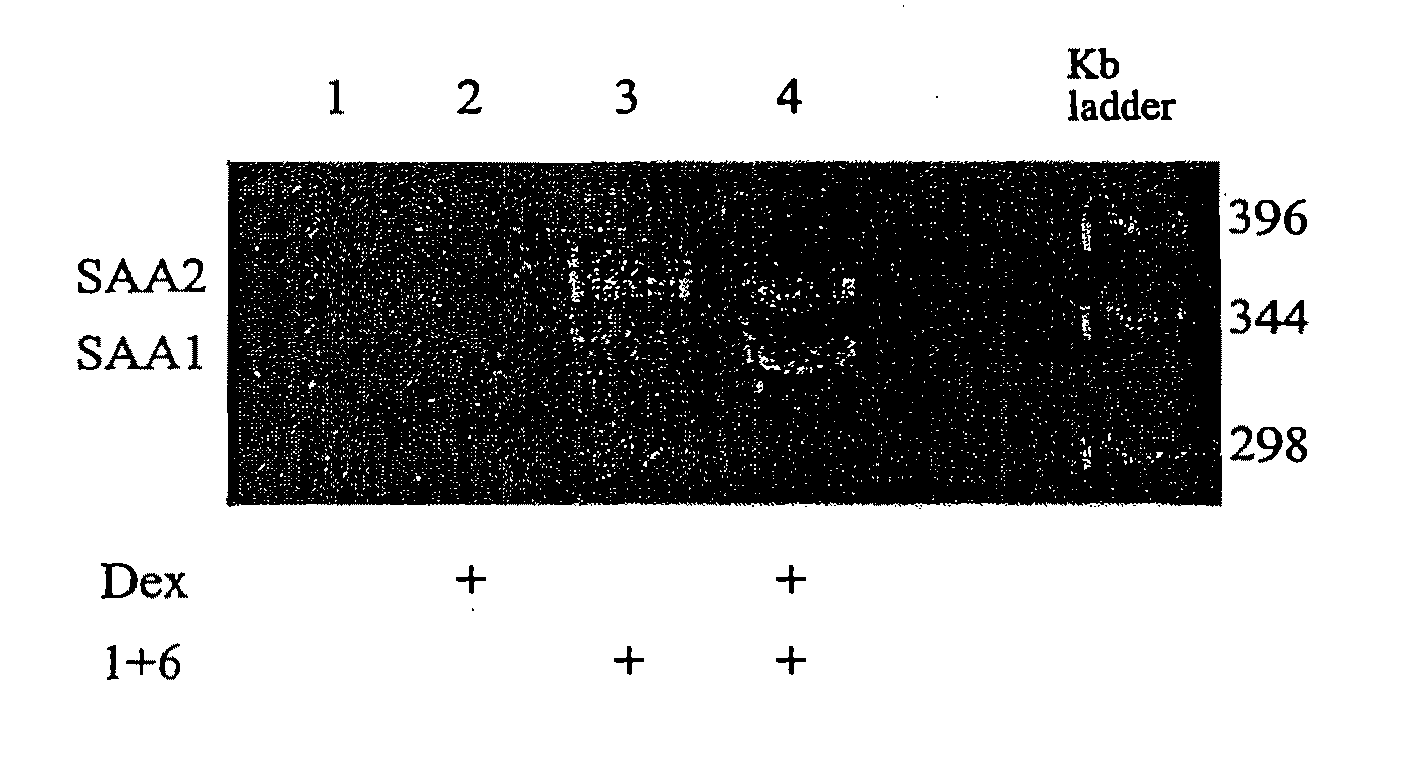
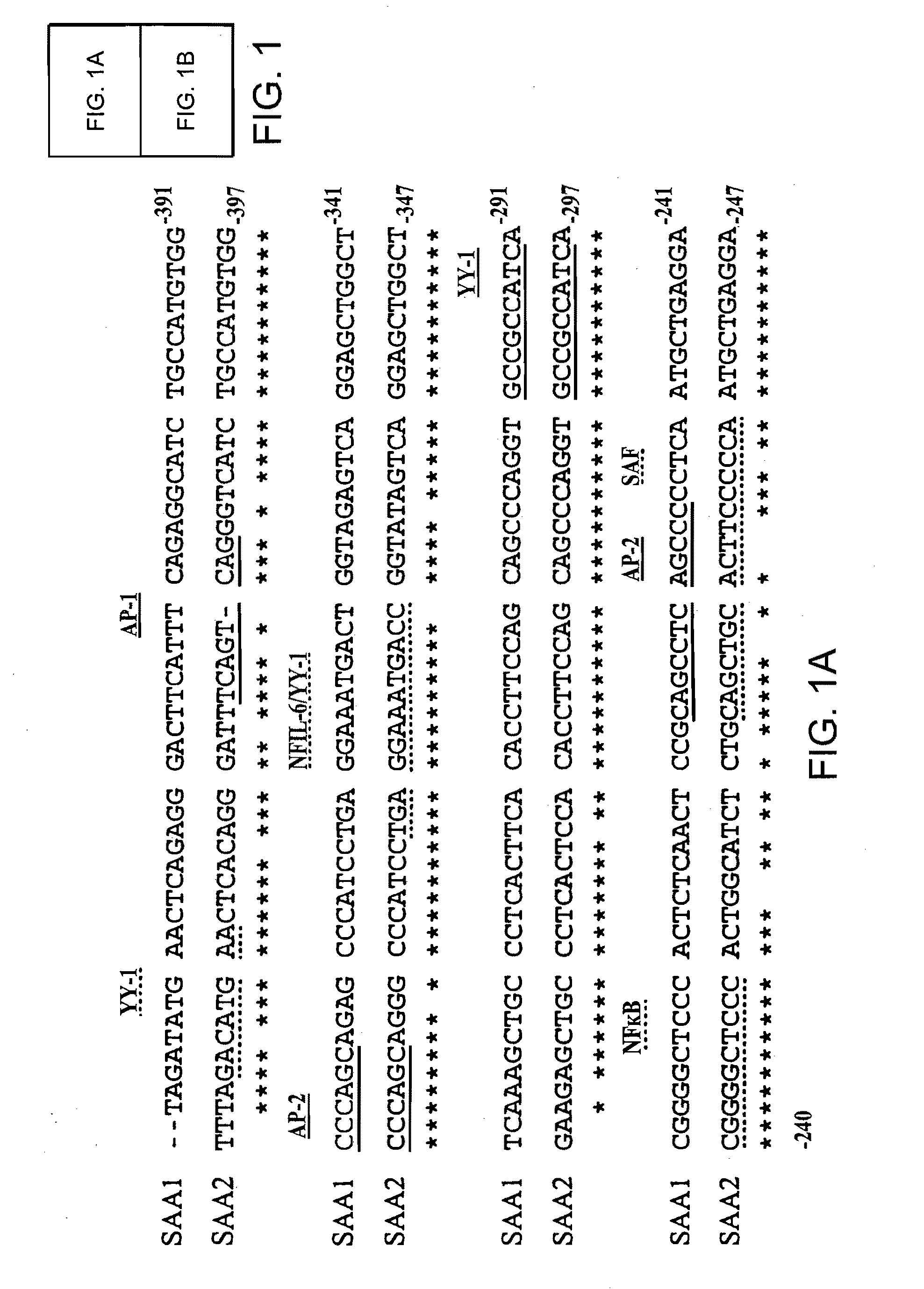
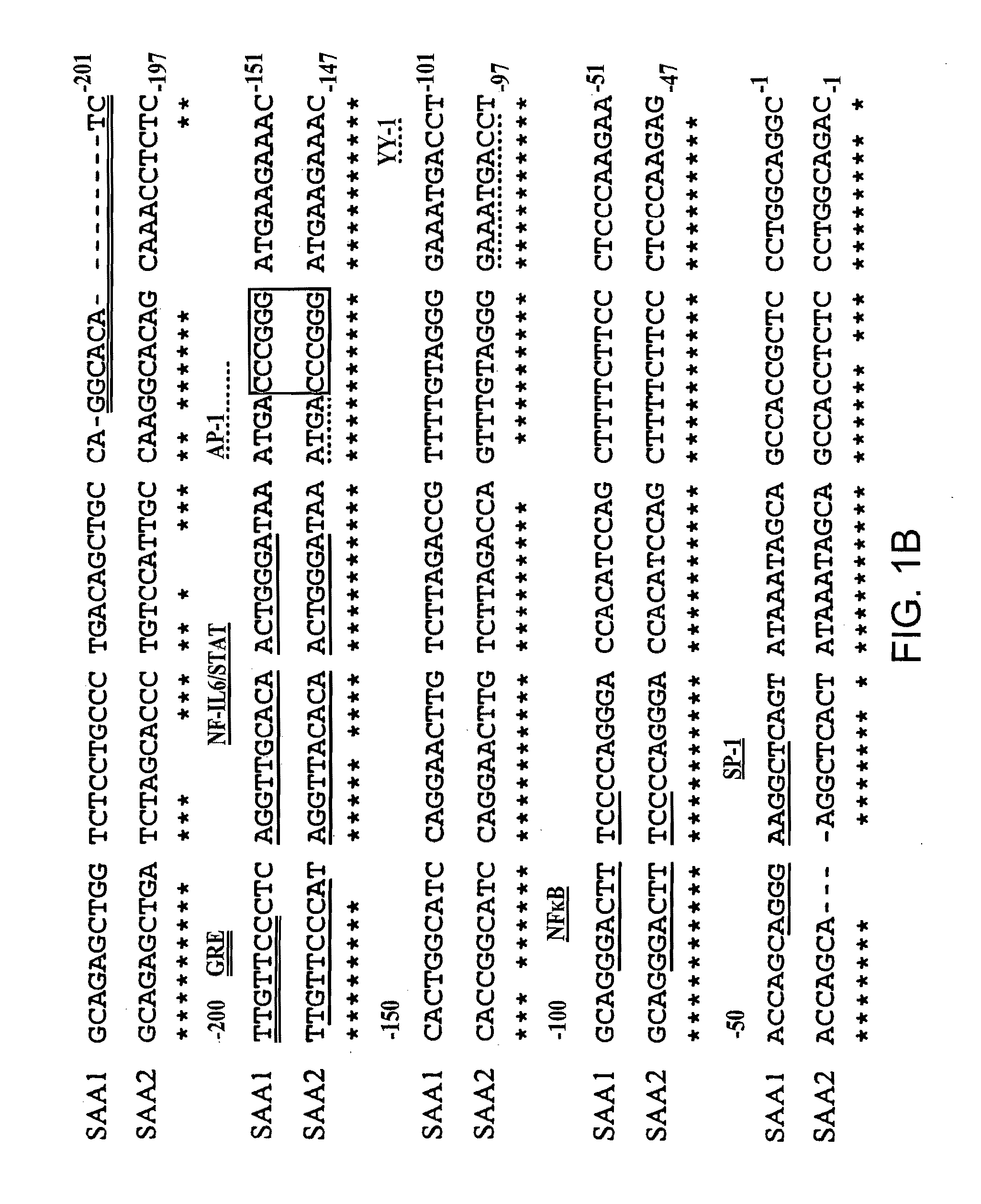
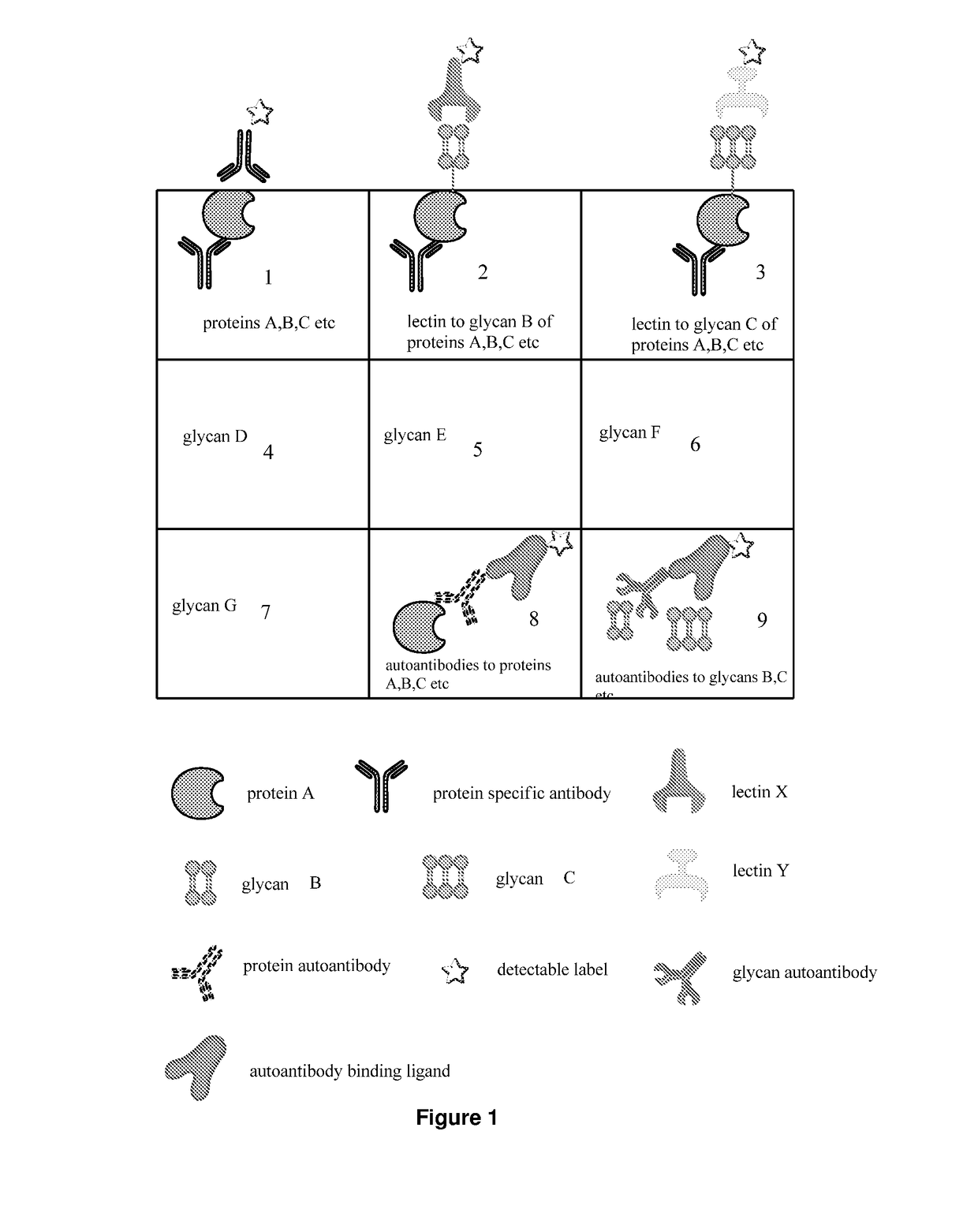
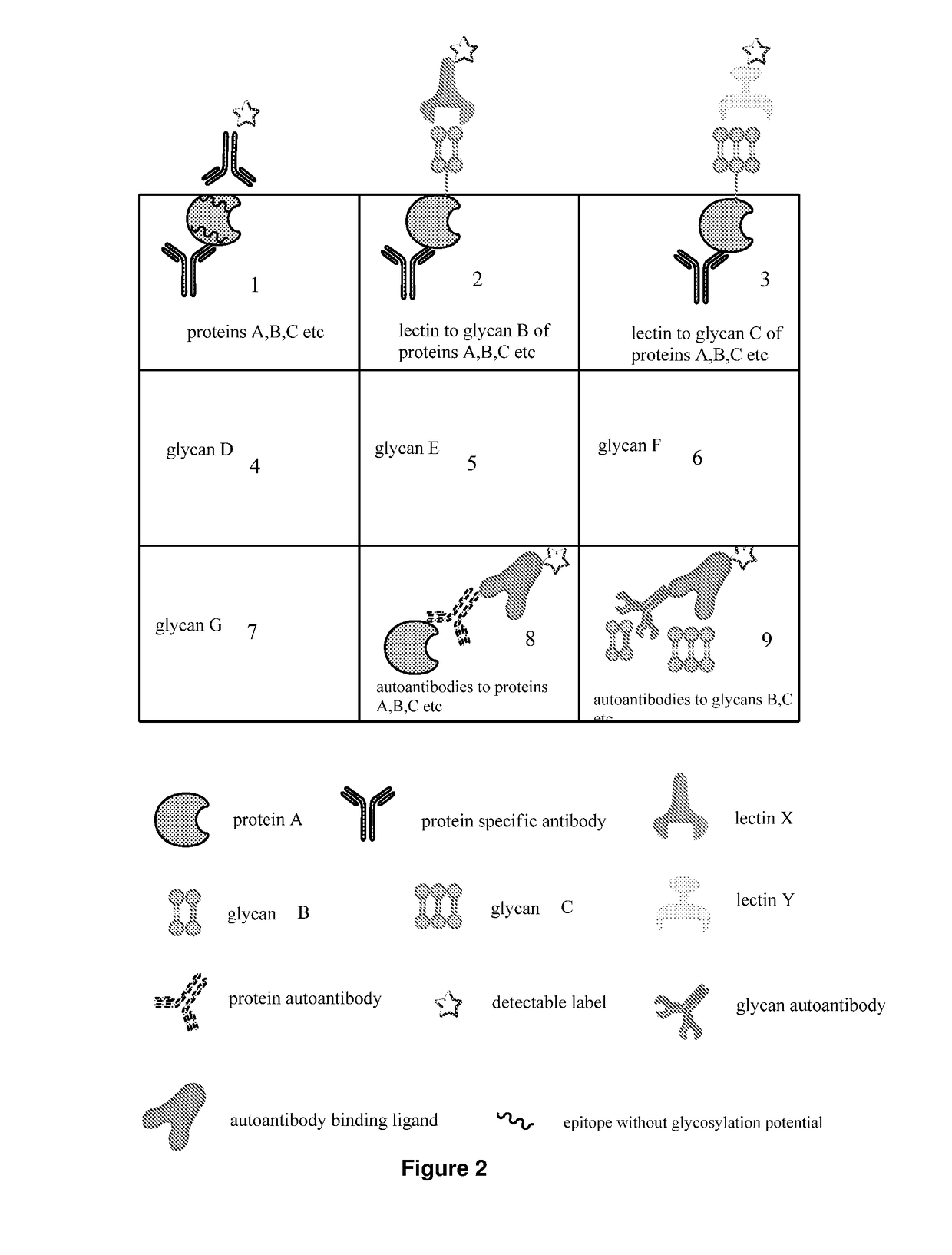
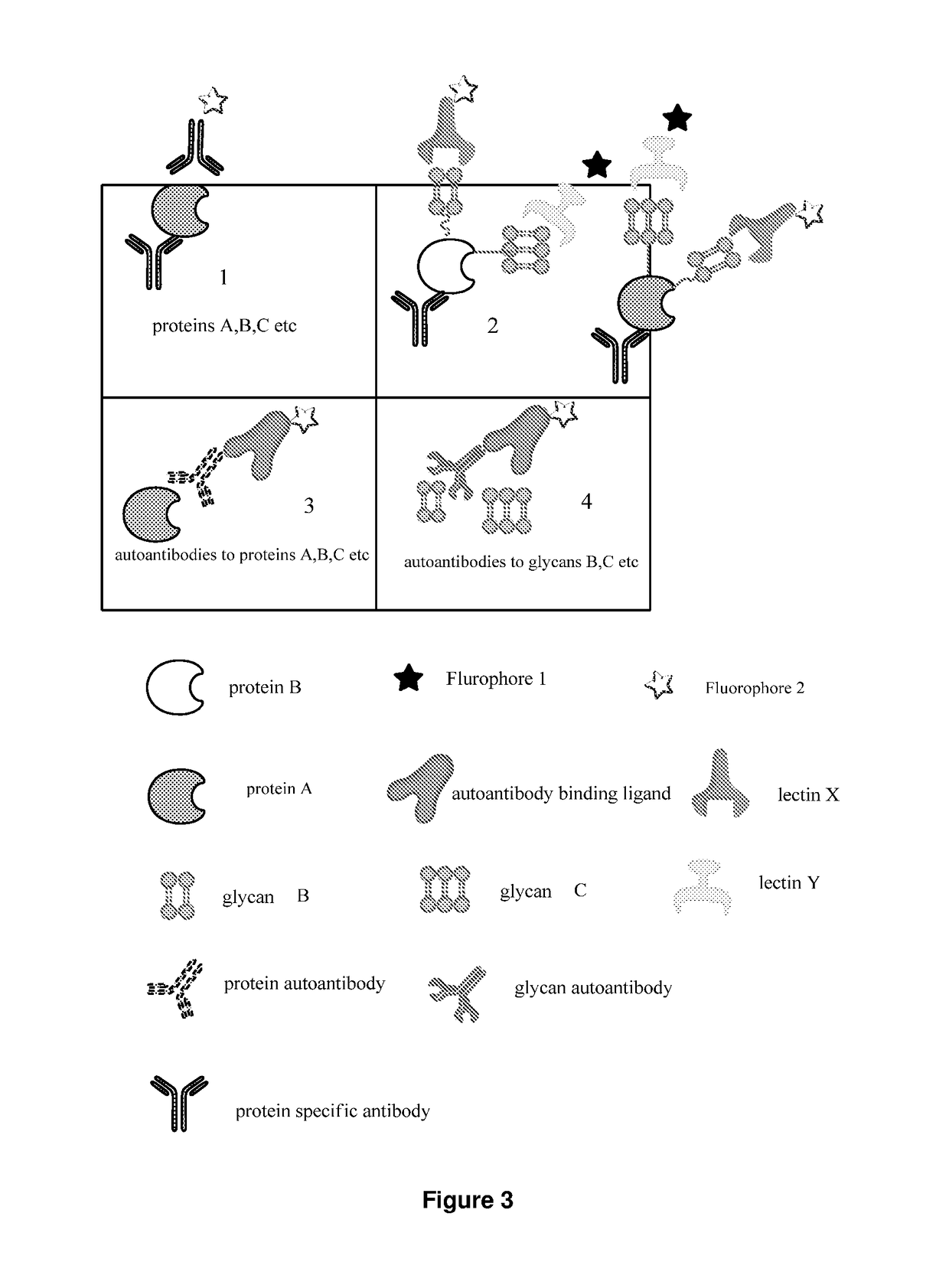
The present invention describes methods of determining the glycosylation signature and determining the level of a protein in a sample obtained from a patient. The present invention also describes useof a patient protein glycosylation profile to identify the presence or absence of a disease in subjects.
Owner:RANDOX LAB LTD +1
Method of treating bone metastasis diseases, medicaments therefore, and a method of predicting the clinical outcome of treating bone metastasis diseases
A method is used for treating bone metastasis diseases in subjects. The method preferably depends on whether the subject shows certain specific proteins levels in one or more body fluids prior to or during treatment. The treatment includes the administration of at least one pan αv integrin inhibitor to a subject, a medicament for use in said new methods, and a method of predicting the outcome of a treatment with at least one pan αv integrin inhibitor based on the specific protein levels in one or more body fluids of the subject.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Methods for determining drug responsiveness
InactiveUS7666608B2Minimize RNA and protein degradationEvaluate steroid responsivenessSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein levelBody fluid
The invention provides a diagnostics assay for measuring the responsiveness to a drug by comparing the protein levels of a gene that responds to the drug, such as a steroid, to the protein levels of a gene that does not respond to the drug. Methods according to the invention are useful for predicting the ability of a patient (or a tissue, body fluid or cell sample in vitro) to respond to a drug or steroid at any stage of their treatment (i.e., before, during or after), and to monitor the patient (or a tissue, body fluid or cell) over time to assess continued responsiveness to the drug or steroid.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for Determining Drug Responsiveness
InactiveUS20090286267A1Minimize degradationMinimize RNA and protein degradationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBody fluidProtein level
The invention provides a diagnostics assay for measuring the responsiveness to a drug by comparing the protein levels of a gene that responds to the drug, such as a steroid, to the protein levels of a gene that does not respond to the drug. Methods according to the invention are useful for predicting the ability of a patient (or a tissue, body fluid or cell sample in vitro) to respond to a drug or steroid at any stage of their treatment (i.e., before, during or after), and to monitor the patient (or a tissue, body fluid or cell) over time to assess continued responsiveness to the drug or steroid.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Determination of glycosylation signature
ActiveUS20190004050A1Effective judgmentDetection of post translational modificationsDiseaseBioinformatics
The present invention describes methods of determining the glycosylation signature and determining the level of a protein in a sample obtained from a patient.The present invention also describes use of a patient protein glycosylation profile to identify the presence or absence of a disease in subjects.
Owner:RANDOX TEORANTA +1
Method for enhancing streptomyces genome editing efficiency and application of method
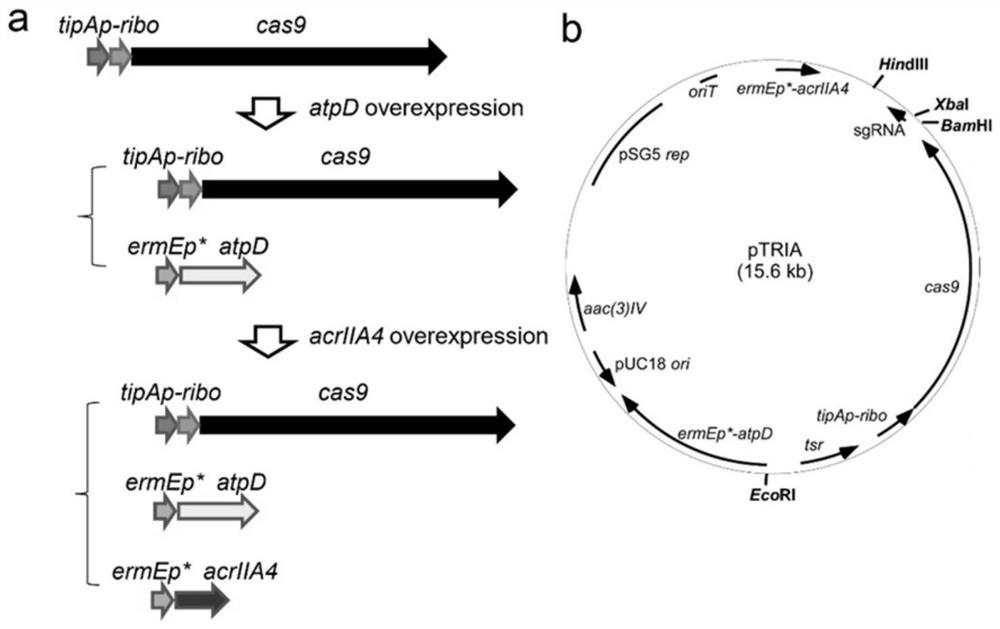
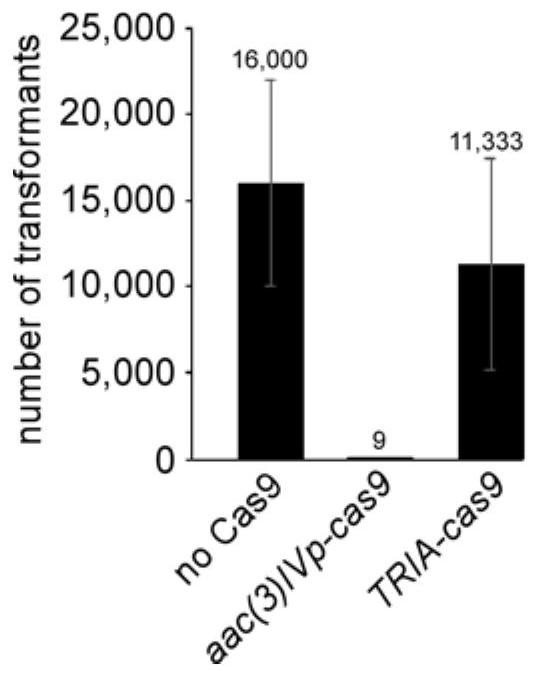
ActiveCN113278645AControl activityAchieve inhibitionVectorsHydrolasesTransformation efficiencyProtein activity
The invention provides a method for enhancing streptomyces genome editing efficiency and application of the method. By adding an element for controlling Cas9 activity, triple control of Cas9 protein activity on transcription, translation and protein levels is realized, cytotoxicity of Cas9 protein to streptomycete is inhibited, transformation efficiency of plasmids in streptomycete is improved, and efficient gene editing can be realized under induction conditions. According to the invention, a gene editing system which is induced by chemical small molecules and regulated and controlled by inhibitory proteins is established, in-vivo toxicity of Cas9 is inhibited, and efficient introduction of genetic elements and efficient editing of subsequent genes are realized on the premise of not influencing transformation efficiency of editing plasmids and growth and metabolism of host cells. The small molecule chemical inducer is convenient to add, and efficient and accurate genome editing based on double-strand breakage and directional repair can be achieved. The method of the inventioon can be applied to gene engineering and genetic modification transformation of streptomycetes including mode or industrial streptomycetes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A protein-binding product, a device containing said protein-binding product and a method for extracorporeal reduction of the level of protein in blood plasma
PendingUS20200406230A1Overcome disadvantagesOther chemical processesHaemofiltrationBlood plasmaLactose binding
A protein-binding product comprising one or more porous polymer beads, wherein at least one ligand is bound to the surfaces of said polymer beads via a spacer (R), and wherein said at least one ligand is Galβ1-3HexNAcβ—O—, Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ—O— and / or a derivative thereof, is disclosed as well as a device containing said protein-binding product and a method for reduction of the level of at least one galactose-binding protein and optionally at least one other protein in human blood plasma.
Owner:GLYCOREX TRANSPLANTATION
Application of rps9 protein in prediction of good response to superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys
ActiveCN113341152BImproved Prediction of Superovulation OutcomesPractical application valueDisease diagnosisBiological testingPhysiologySignalling pathways
The invention relates to the application of RPS9 protein in the prediction of good response to superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys, belonging to the technical field of superovulation. The method of proteomics is used to analyze the first day of superovulation success group and the fifth day of superovulation success group. , Superovulation failure group on day 1 and superovulation failure group on day 5 for bioinformatics analysis to obtain the differential protein among the groups. From the study of protein level, the changes of protein expression revealed in the blood of superovulated monkeys were explored. In superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys, RPS9 protein was expressed on day 5 in the superovulation success group, but not in the superovulation failure group on day 5. It is suggested that the down-regulation of PRS9 expression in the superovulation failure group affects the activation of MAPK signaling pathway and NK-κB pathway, thereby leading to cell apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and inhibition of proliferation. The down-regulation of PRS9 expression may lead to the activation of p53, resulting in the inhibition of cell proliferation, thereby affecting the formation of follicles and leading to the failure of superovulation response. Therefore, RPS9 protein has become a new molecule to predict the good response to superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys, and has practical application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Automatic sample workflow for lc-ms based hba1c measurement on intact protein level
The present invention refers to a method for determining intact glycated hemoglobin A (HbA1c) by mass spectrometry (MS), a kit and a diagnostic system adapted for performing the method.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Application of RPL26 protein in predicting good response of cynomolgus monkeys to superovulation
ActiveCN113358876AImproved Prediction of Superovulation OutcomesGrowth and development are smoothBiological testingProteomics methodsPhysiology
The invention relates to application of RPL26 protein in predicting good response of cynomolgus monkeys to superovulation, and belongs to the technical field of superovulation. Biological information analysis is carried out on blood sample protein on the first day of a superovulation success group, the fifth day of the superovulation success group, the first day of a superovulation failure group and the fifth day of the superovulation failure group through adopting a proteomics method, and differential proteins among the groups are obtained. The protein expression change of the blood of the superovulation monkeys is discussed from protein level research. In superovulation of cynomolgus monkeys, RPL26 protein exists on the fifth day in a superovulation failure group and is not expressed on the fifth day in a superovulation success group, the fact possibly prompts that ribosome stress occurs in cynomolgus monkeys with poor response in the superovulation process, and accordingly the cell cycle progress is affected, the growth and development of oocytes in the superovulation process are affected, and superovulation is not facilitated. Therefore, the RPL26 protein becomes a new molecule for predicting good response of the cynomolgus monkey to superovulation, and has practical application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
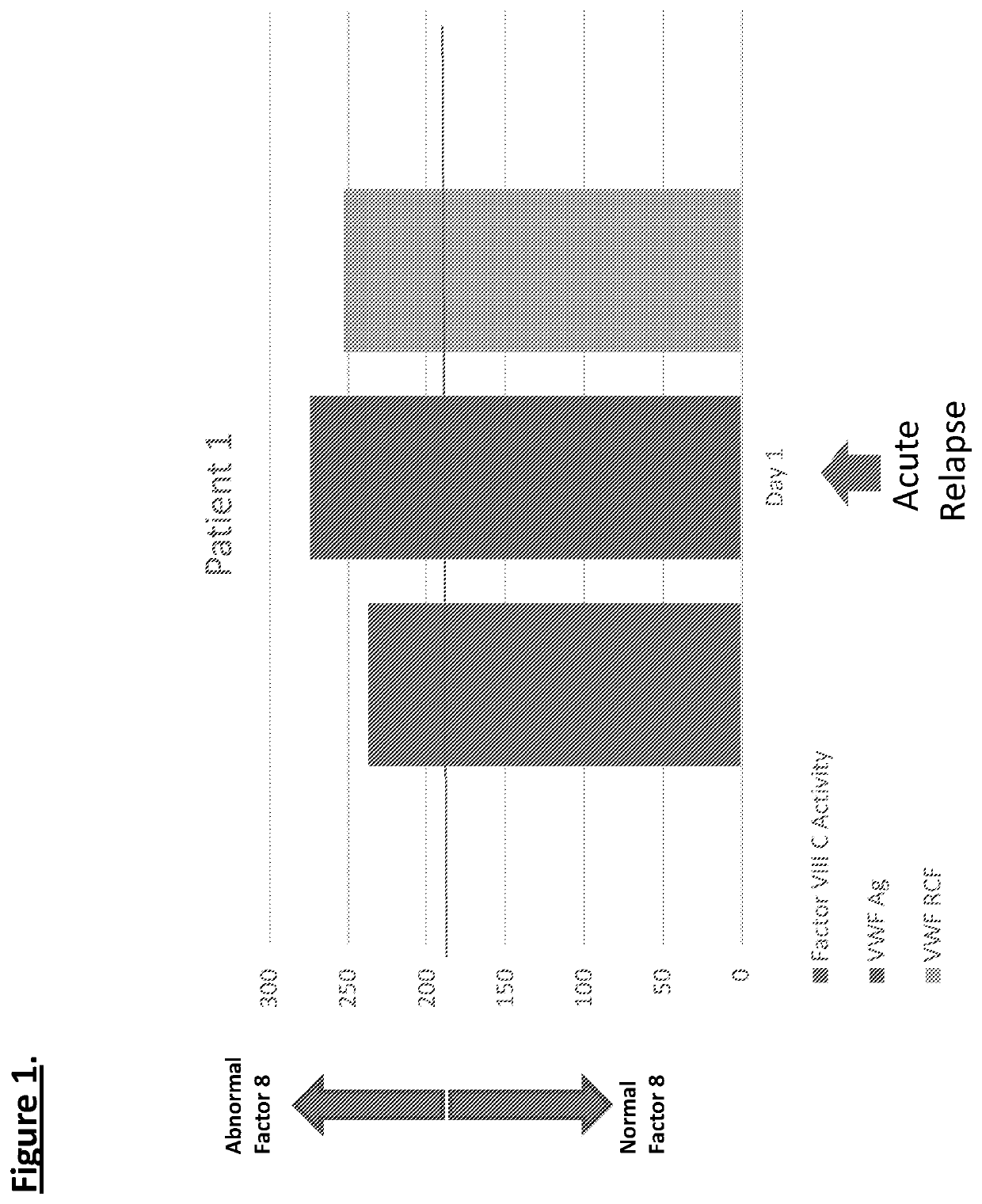
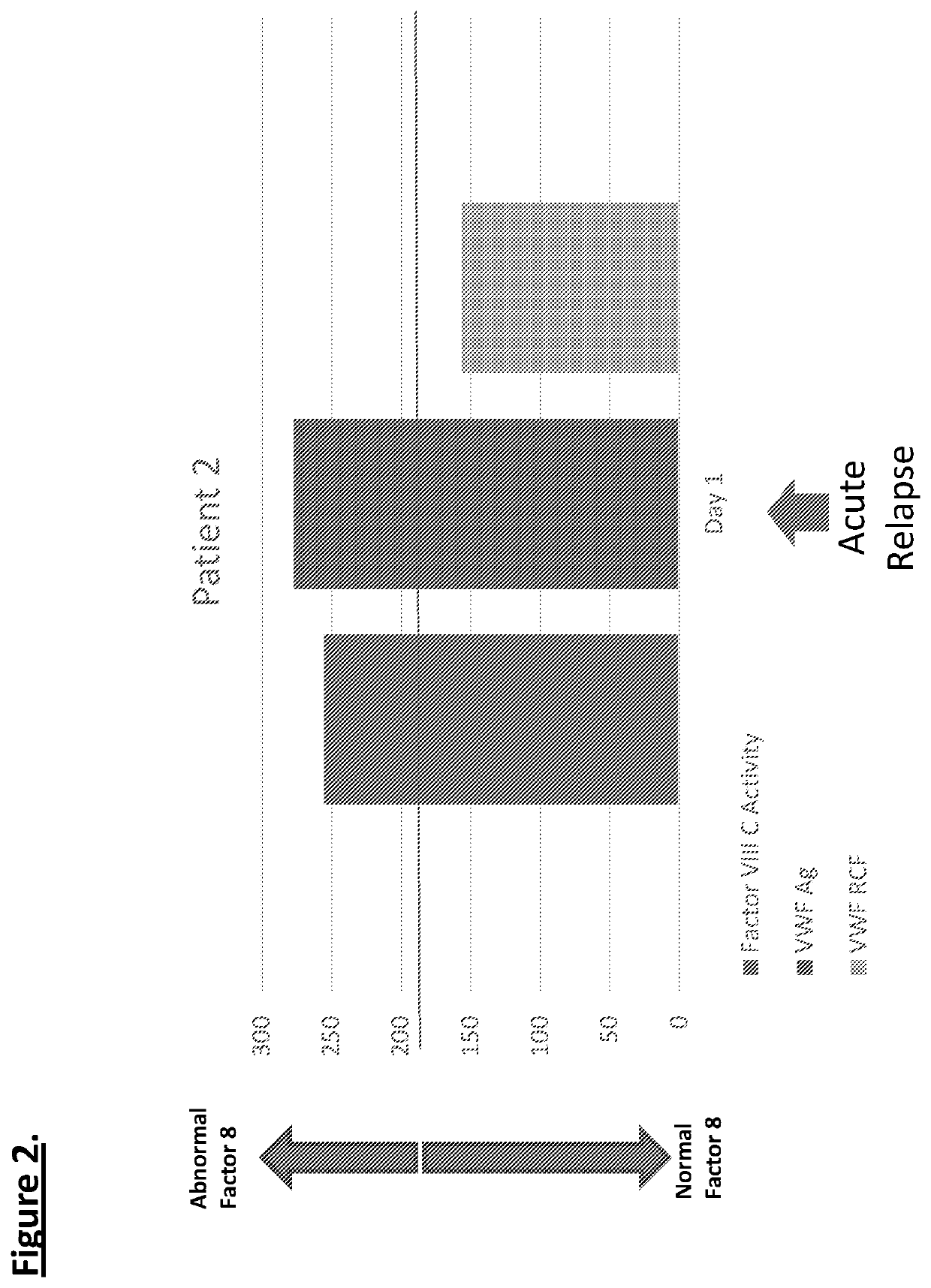
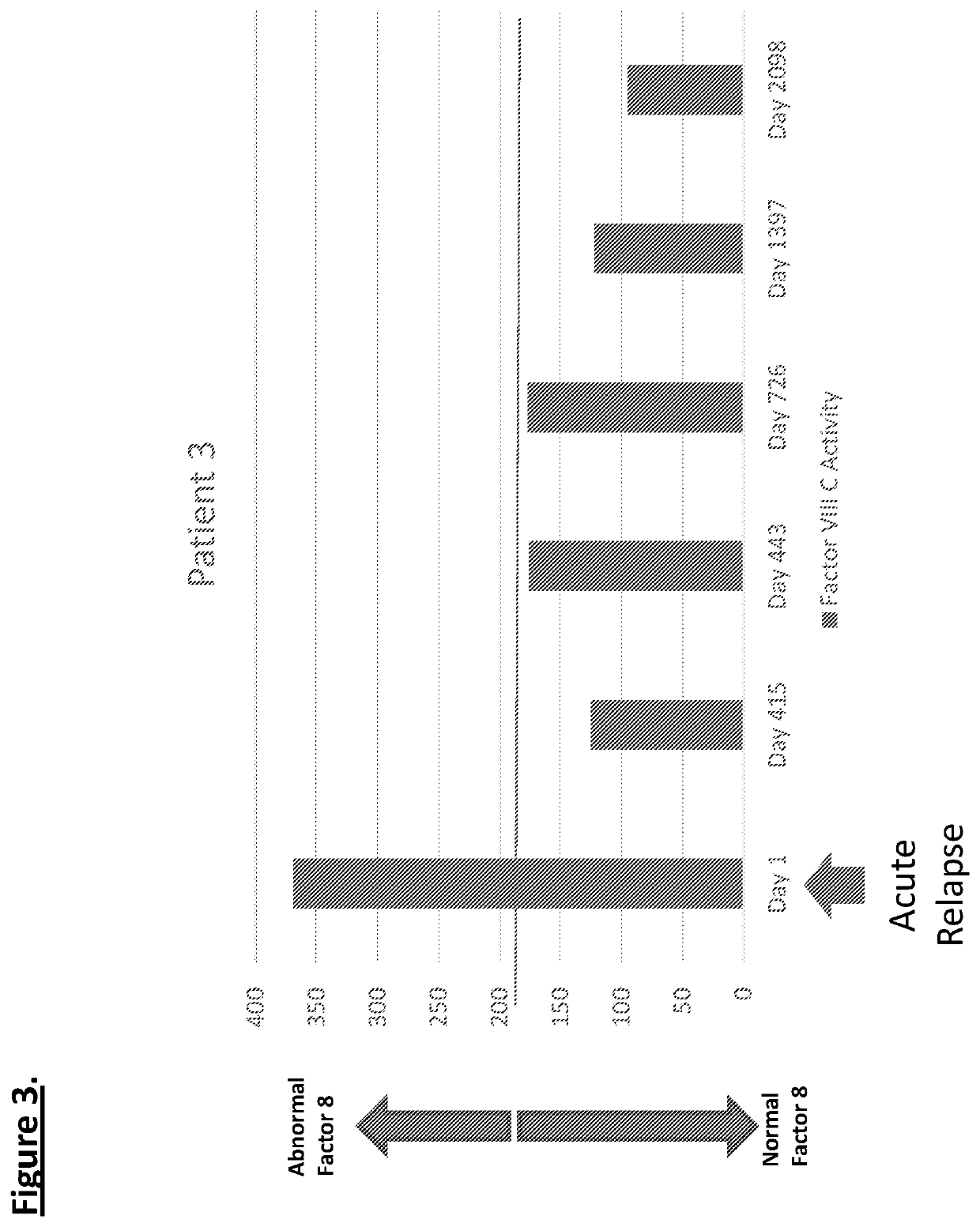
Diagnostic or predictor of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis
Provided herein is a method of detecting or predicting a relapse of multiple sclerosis in an individual afflicted with a form of multiple sclerosis, comprising: (a) providing a blood sample of the individual; (b) testing the blood sample to determine a protein activity or protein level, wherein the protein is Factor VIII, von Willebrand factor, or Protein C; and (c) detecting or predicting a relapse of multiple sclerosis in the individual if the protein activity or protein level is elevated compared to the protein activity or protein level in an individual not afflicted with the form of multiple sclerosis and patients' own baseline values. Also provided herein is a method of treating an individual afflicted with multiple sclerosis, who is experiencing a relapse or predicted to experience a relapse, comprising treating the individual by administering a dose of a steroid or anti-coagulation compound effective to alleviate the symptom of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
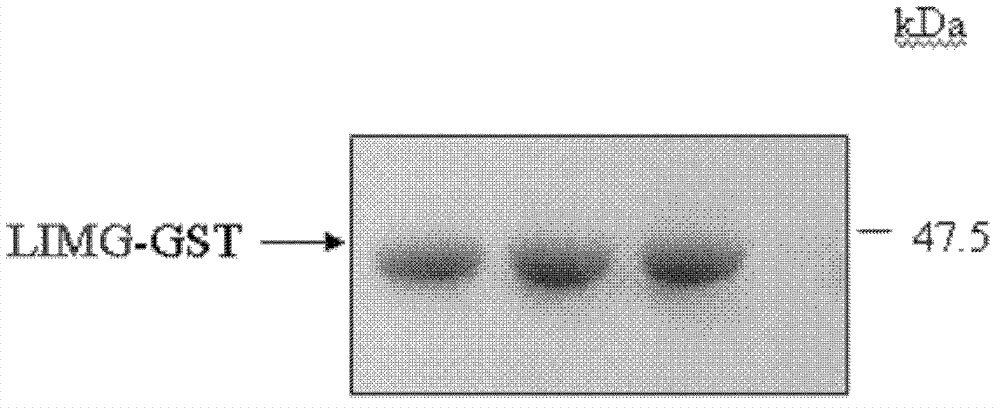
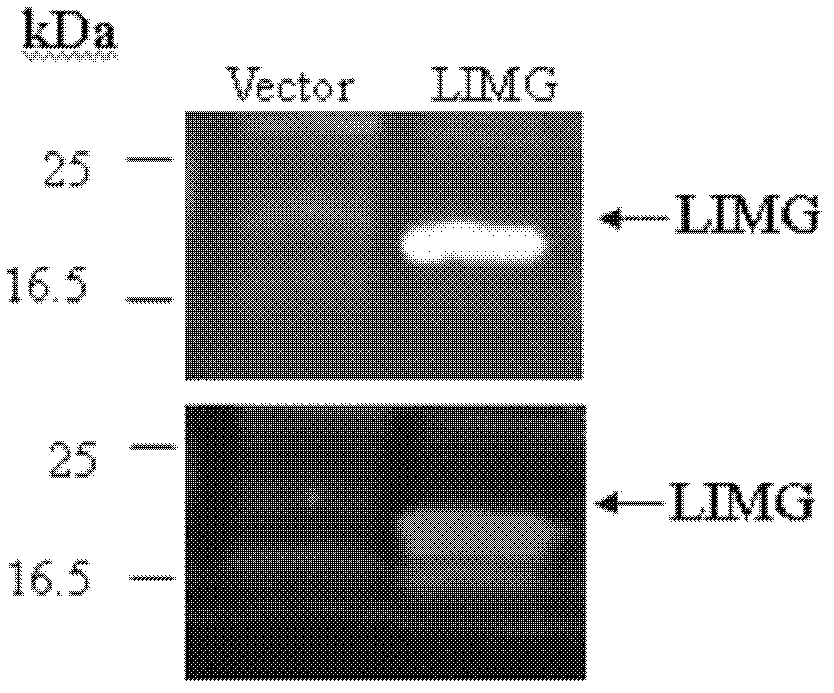
Application of protein coded by gene LIMG and antibody thereof in breast cancer diagnosis and/or treatment
InactiveCN102952849AThe detection method is simplePeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein proteinAntibody
The invention relates to a protein coded by gene LIMG and an antibody thereof, and specifically relates to an application of the protein coded by gene LIMG and the antibody thereof in mammary gland diagnosis and / or treatment. According to the invention, gene LIMG expression is detected by using a quantitative PCR method, and detection is carried out by using a quantitative PCR instrument. When a gene LIMG level to be detected is higher by 1.95-2.05 times that of a normal reference group gene LIMG level, it is determined as positive. When the protein coded by LIMG is detected by using an ELISA immunoassay method, when the level of the gene-LIMG-coded protein to be detected is higher by 1.95-2.05 times that of a normal reference group gene LIMG level, it is determined as positive. The invention also relates to applications of the gene LIMG, the protein coded by the gene, and the antibody thereof in breast enhancement and in mammary gland development detection.
Owner:北京艾吉生物科技有限公司
Application of rpl26 protein in prediction of good response to superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys
ActiveCN113358876BImproved Prediction of Superovulation OutcomesGrowth and development are smoothBiological testingPhysiologyRibosome
The invention relates to the application of RPL26 protein in the prediction of good response to superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys, and belongs to the technical field of superovulation. The first day of the successful superovulation group and the fifth day of the successful superovulation group are analyzed by the method of proteomics. , Superovulation failure group on day 1 and superovulation failure group on day 5 for bioinformatics analysis to obtain the differential protein among the groups. From the study of protein level, the changes of protein expression revealed in the blood of superovulated monkeys were explored. In superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys, the presence of RPL26 protein on day 5 in the failed superovulation group but not in the successful superovulation group may suggest poor response during superovulation Ribosome stress occurs in cynomolgus monkeys, which affects the cell cycle process, resulting in the growth and development of oocytes being affected during superovulation, which is not conducive to superovulation. Therefore, the RPL26 protein has become a new molecule for predicting a good response to superovulation in cynomolgus monkeys, and has practical application value.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Application of RPS9 protein in predicting good response of cynomolgus monkey to superovulation
ActiveCN113341152AImproved Prediction of Superovulation OutcomesPractical application valueDisease diagnosisBiological testingProteomics methodsPhysiology
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
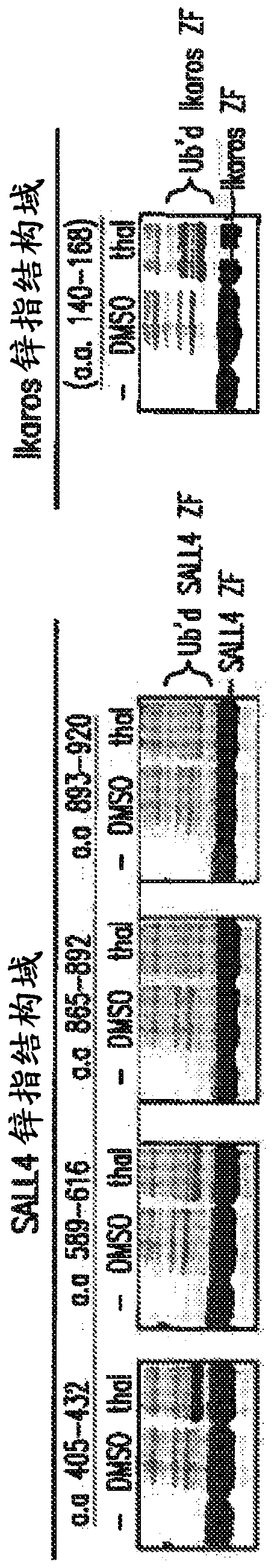
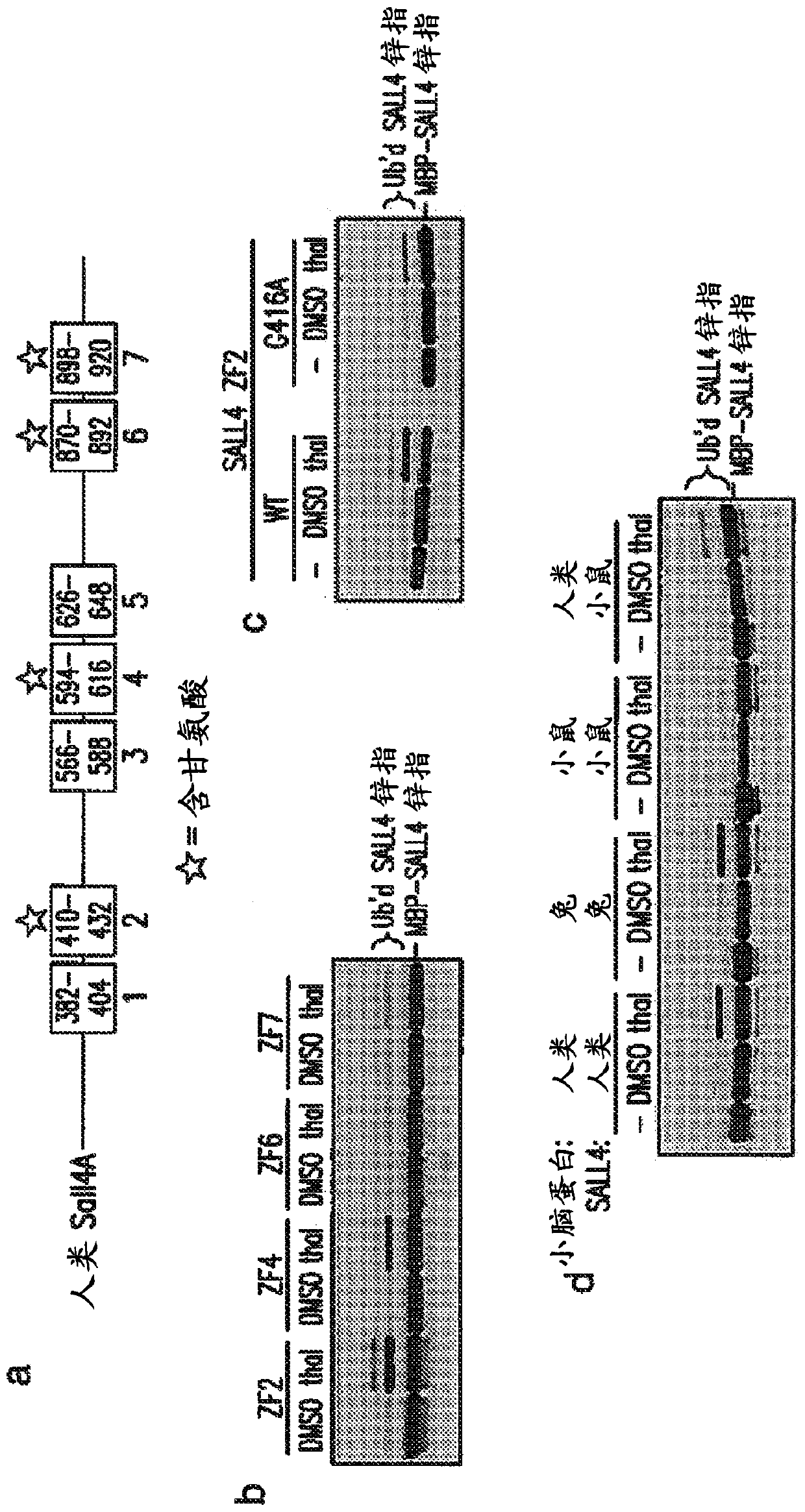
Methods for screening cereblon modifying compounds
A method of screening a cereblon modifying compound for treating a disease or disorder, comprising: obtaining a sample; determining a first protein level of SALL4; administering the cereblon modifyingcompound to the sample; determining a second protein level of SALL4; comparing the first level and the second protein level of SALL4 to determine if the cereblon modifying compound induces degradation of SALL4; and selecting the cereblon modifying compound that does not induce degradation of SALL4.
Owner:CELGENE CORP
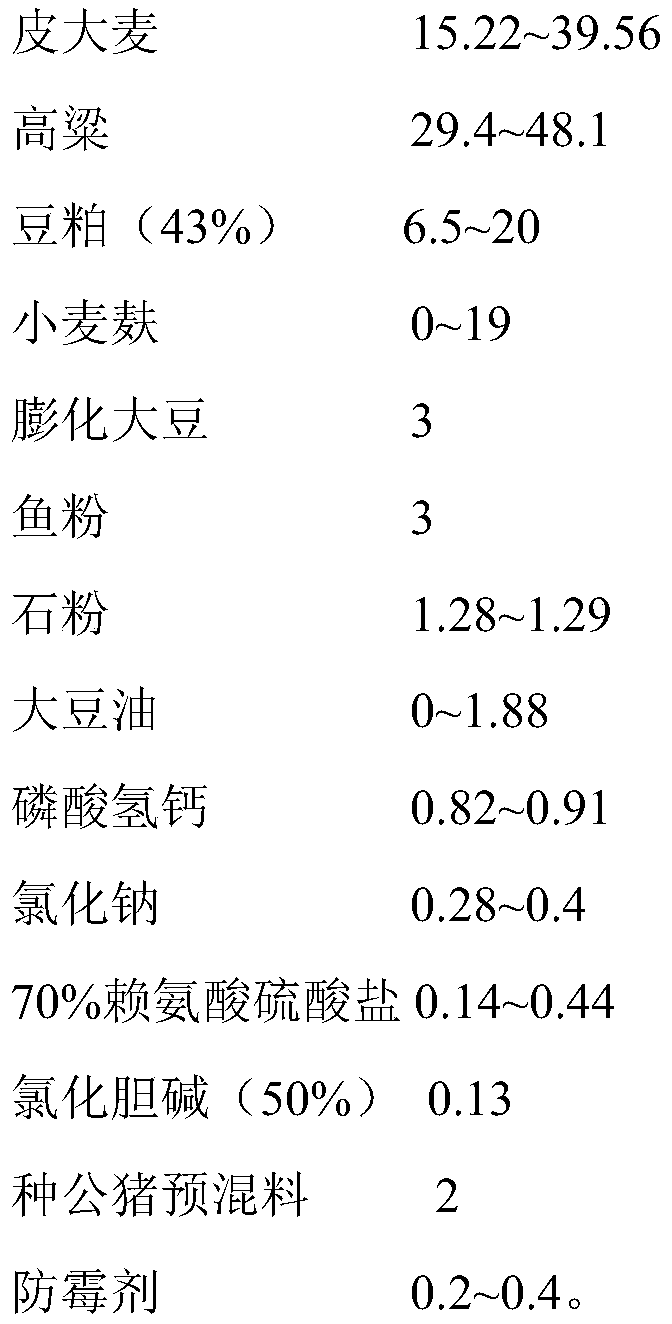
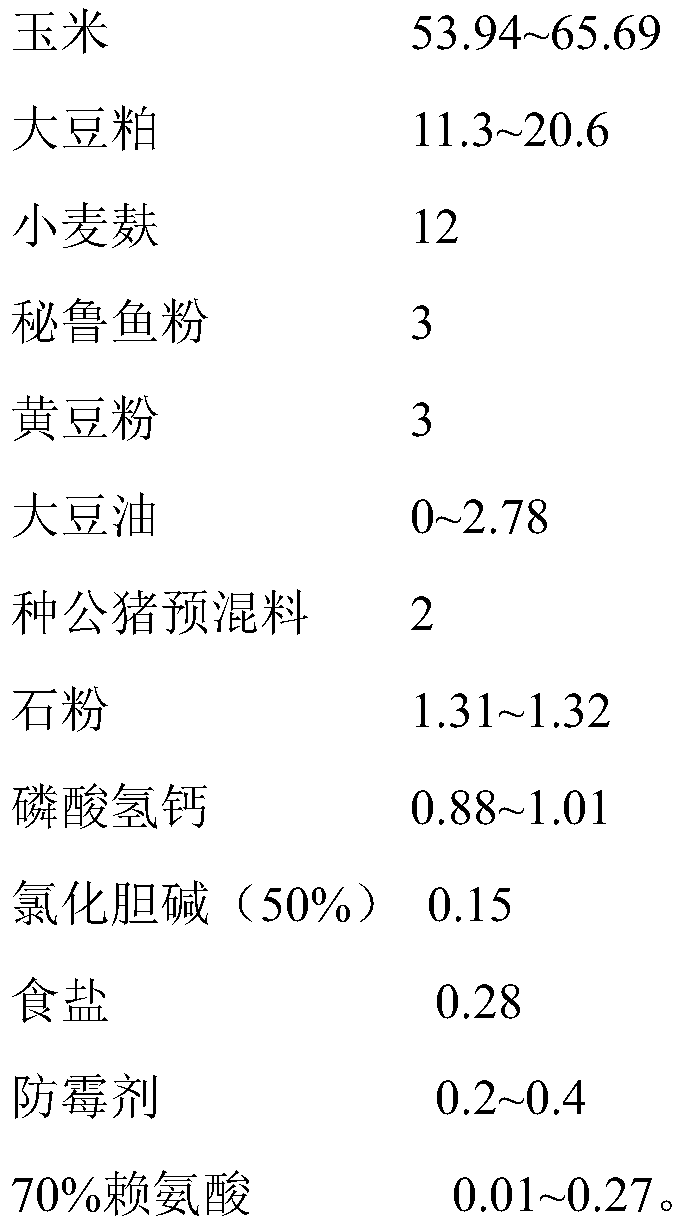
Special feed for improving boar semen quality
Owner:WENS FOOD GRP CO LTD
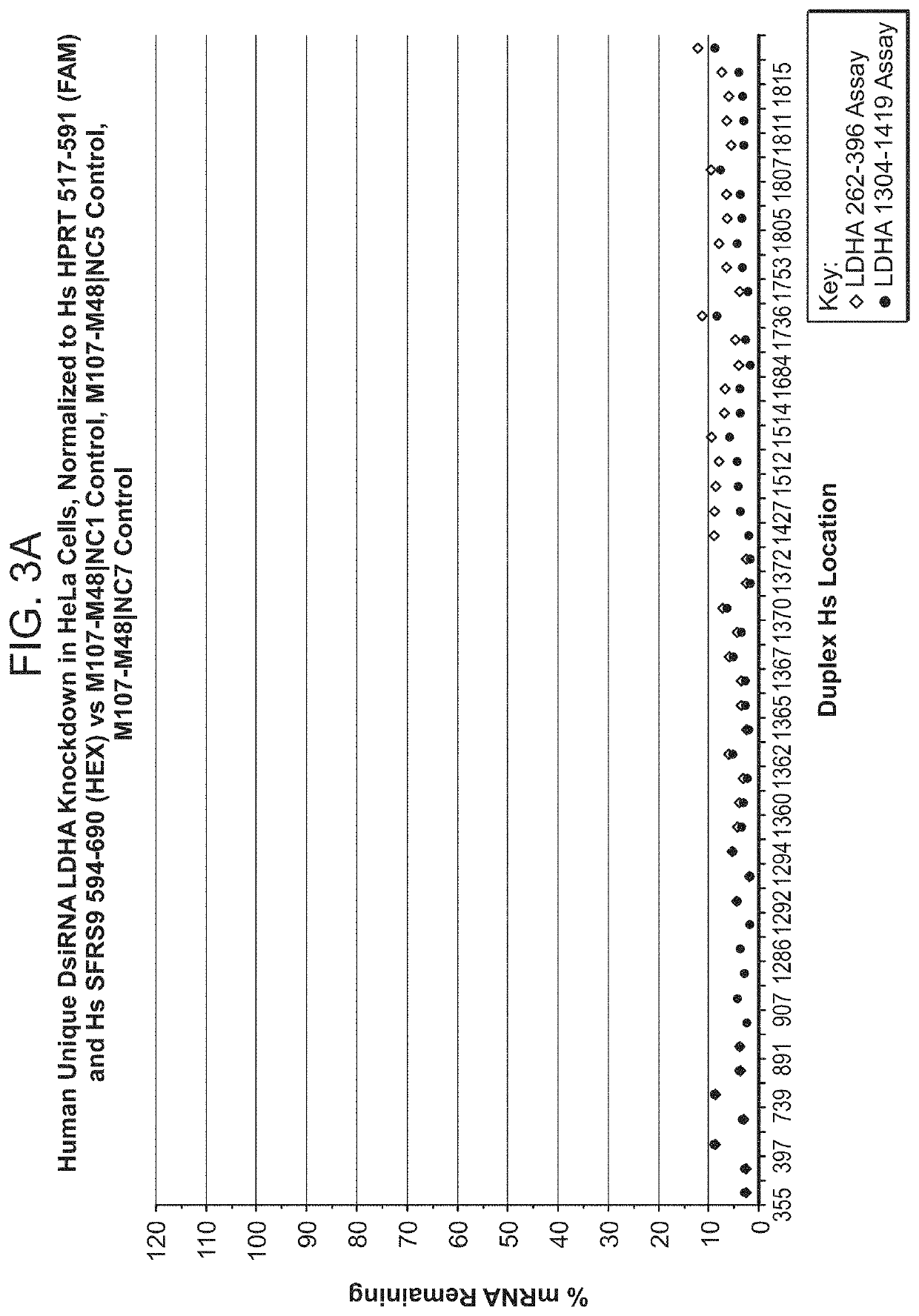
Therapeutic inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase and agents therefor
ActiveUS11359203B2Inhibitory activityHighly attractiveOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryDicerLactate dehydrogenases
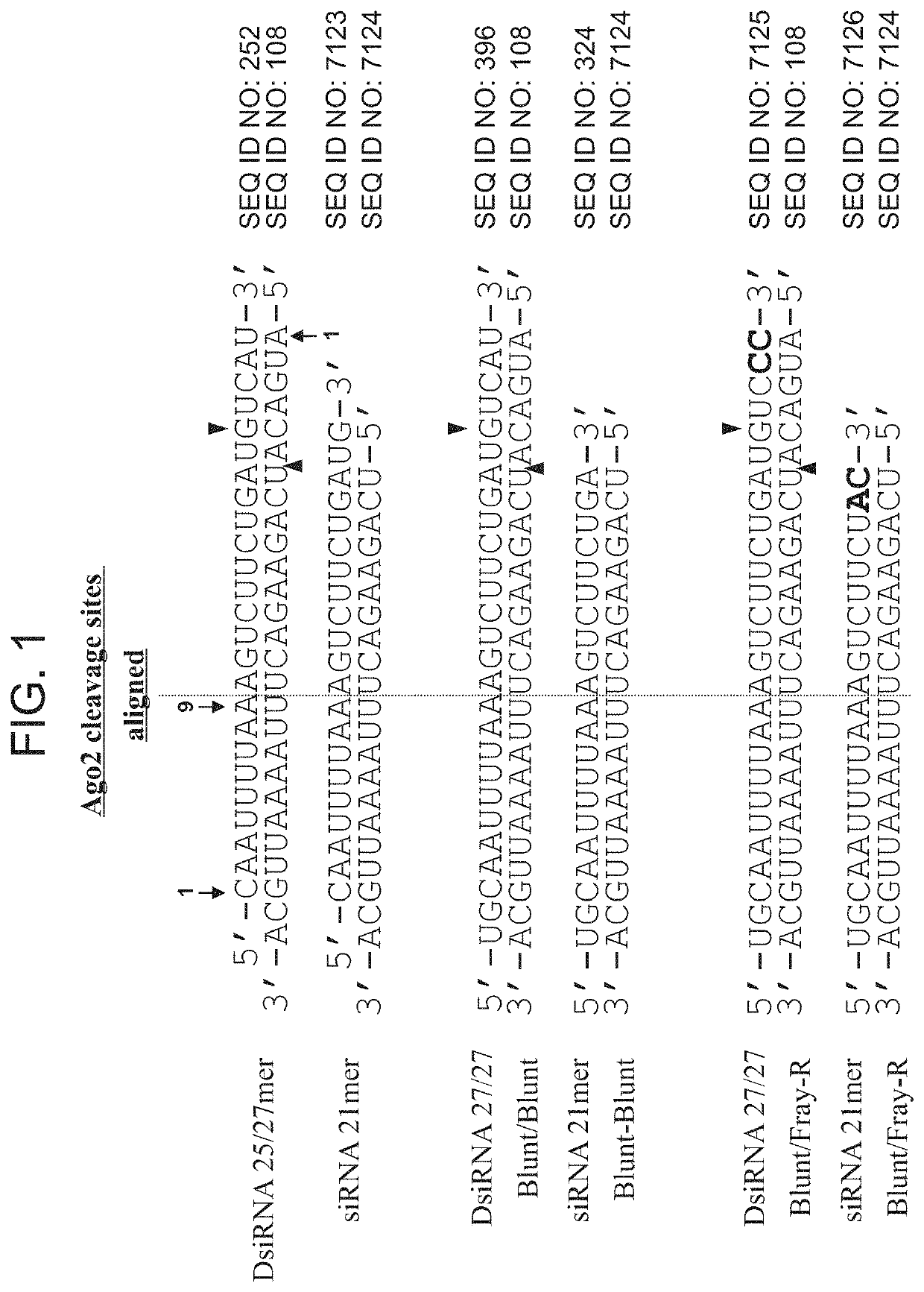
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for reducing lactate dehydrogenase target RNA and protein levels via use of ds RNAs, e.g., Dicer substrate siRNA (DsiRNA) agents.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK HEALTH CARE AG
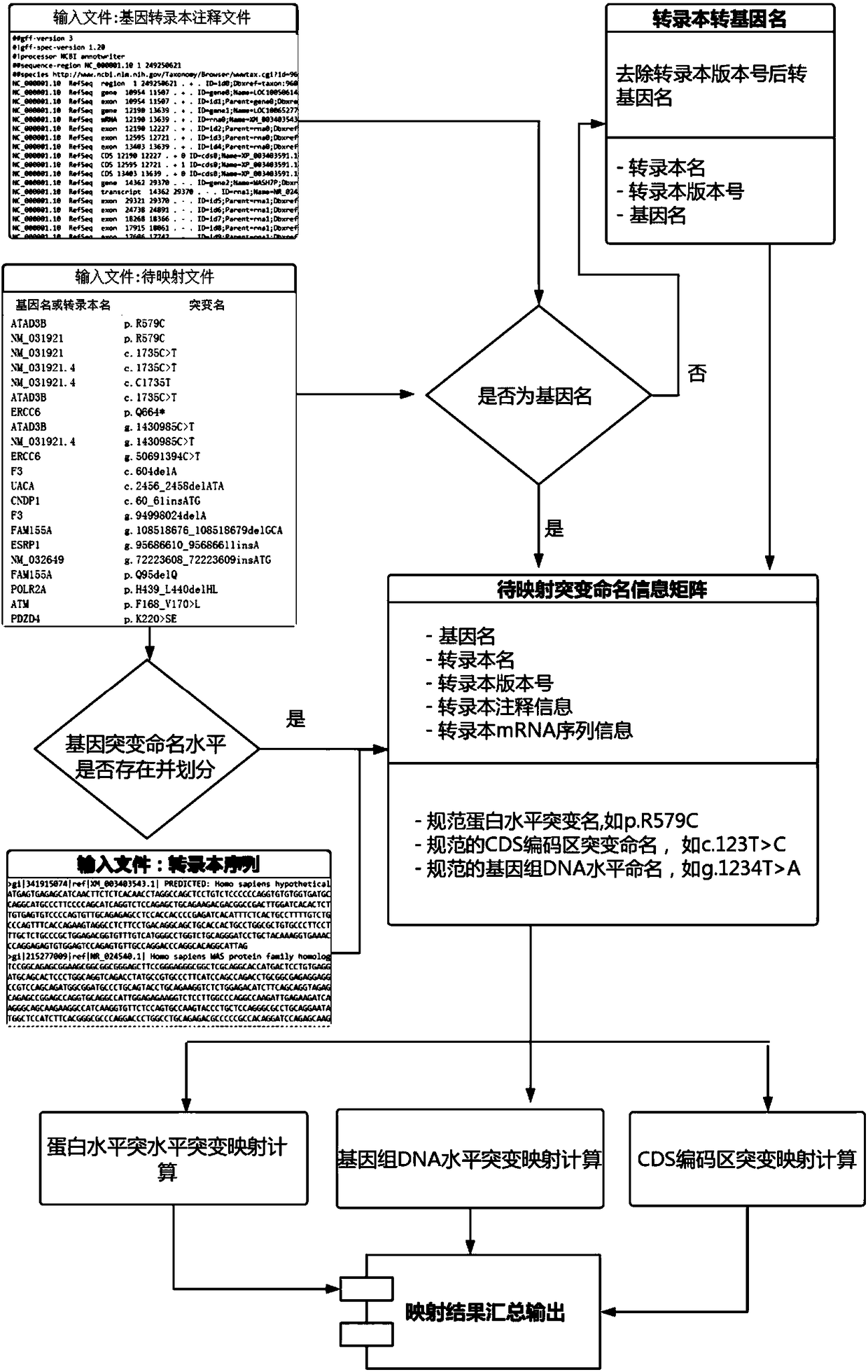
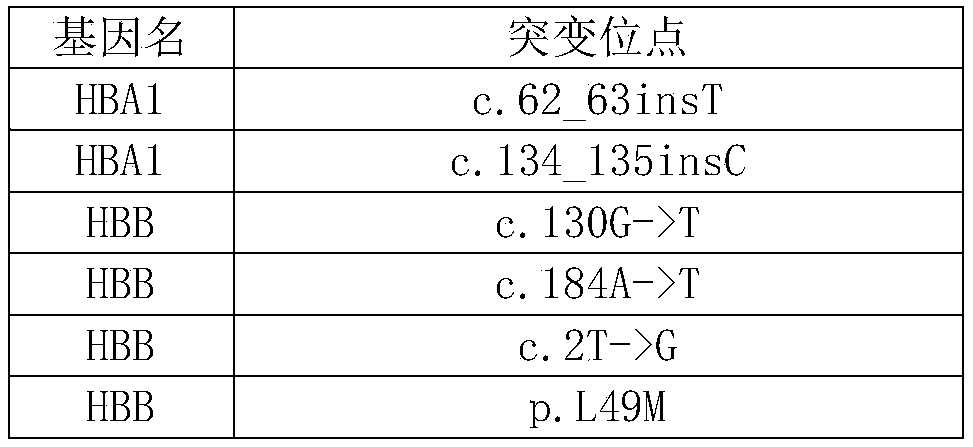
A DNA and protein level mutation analysis method
The invention discloses a DNA and protein level mutation analysis method. The method comprises the steps of 1, reading a gene mutation file, and formatting the file into a standard name; 2, indexing a transcript sequence, gene information and gene transcript annotation information, thereby forming an amino acid codon corresponding relationship table; judging a mutation level and a mutation mode, and judging whether a mutation name is protein level mutation, genome DNA level mutation or CDS code area mutation; and 4, entering different level mutation mapping processes according to a judging result of the step 3, thereby obtaining mapping relationships of three mutation names. According to the method, the mapping relationships of various mutation names are output by carrying on phenotypic correlation gene mutation and polymorphic sites mined from literatures, thereby finishing annotating correspondence between pathogenic variation mined from the literatures, and gene mutation and polymorphic sites identified by sequencing.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Methods and Compositions for the Detection of Host Protein Cleavage by Group IV Viral Proteases
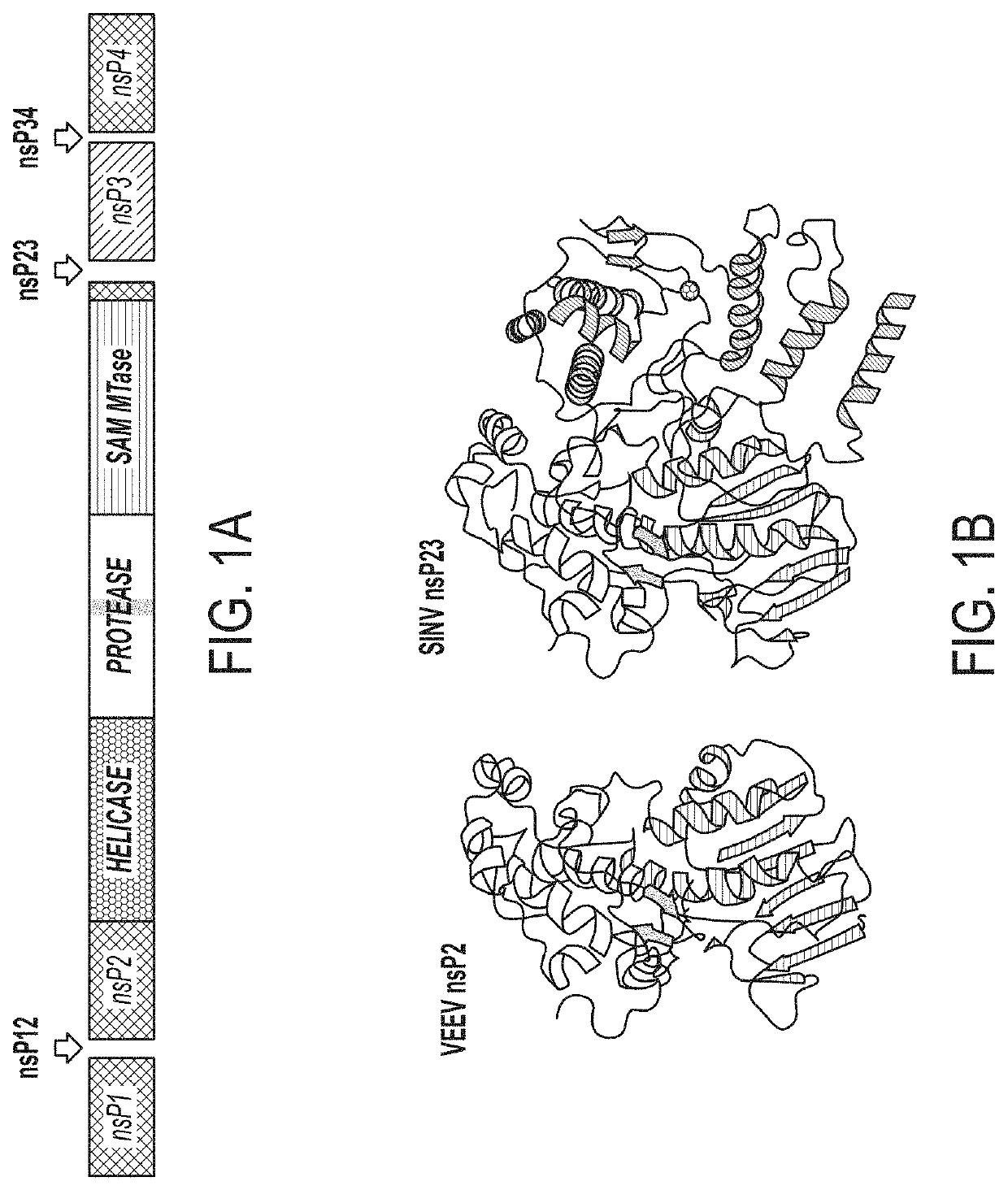
PendingUS20210389324A1Loss of functionSsRNA viruses positive-senseHydrolasesPost translationalProtein
Proteases of Group IV (+)ssRNA viruses were found to act on a human sequences in addition to the viral sequences. The identity of the cleavable human sequences is disclosed. Detection of these sequences can act as a diagnostic of infection. It is contemplated that these findings could be employed to facilitate post-translational silencing at the level of protein (e.g., removal of existing proteins), thus serving as a protein analog to CRISPR / Cas9 and RNAi / RISC, and further to enable sequence-specific silencing of host functions without the modification of the host genome.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com