Method for prediction of flutter in numerical-control milling of mold cavities
A CNC milling and cavity technology, applied in milling machine equipment, manufacturing tools, details of milling machine equipment, etc., can solve the problems affecting the processing quality of mold cavity, low accuracy of milling chatter prediction, and speed up tool failure, etc., to achieve the prediction process Convenience and quickness, accurate chatter prediction, and guaranteed processing quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0031] Specific implementation mode 1: A method for predicting flutter in CNC milling of mold cavity in this implementation mode The specific process is as follows:
[0032] Step 1. Establishing the relative transfer function of the tool-workpiece system;
[0033] Obtaining the dynamic characteristics of the tool-workpiece system, that is, the transfer function matrix, is an important prerequisite for predicting the stability of the milling process. Most of the previous studies only considered the dynamic characteristics of the tool system, while ignoring the influence of the workpiece system on the dynamic characteristics of the overall machining system. The present invention comprehensively considers the dynamic characteristics of the tool subsystem and the workpiece subsystem, and establishes The overall dynamics model of the tool-workpiece system.
[0034] Obtain the transfer functions of the tool subsystem and workpiece subsystem separately
[0035] G ci (jω)=X ci (jω...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0042] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in Step 2, the relative transfer function of the tool-workpiece system obtained in Step 1 is introduced into the three-dimensional milling stability model to obtain the milling chatter frequency of the milling cutter The critical axial depth of cut at ; the specific process is:
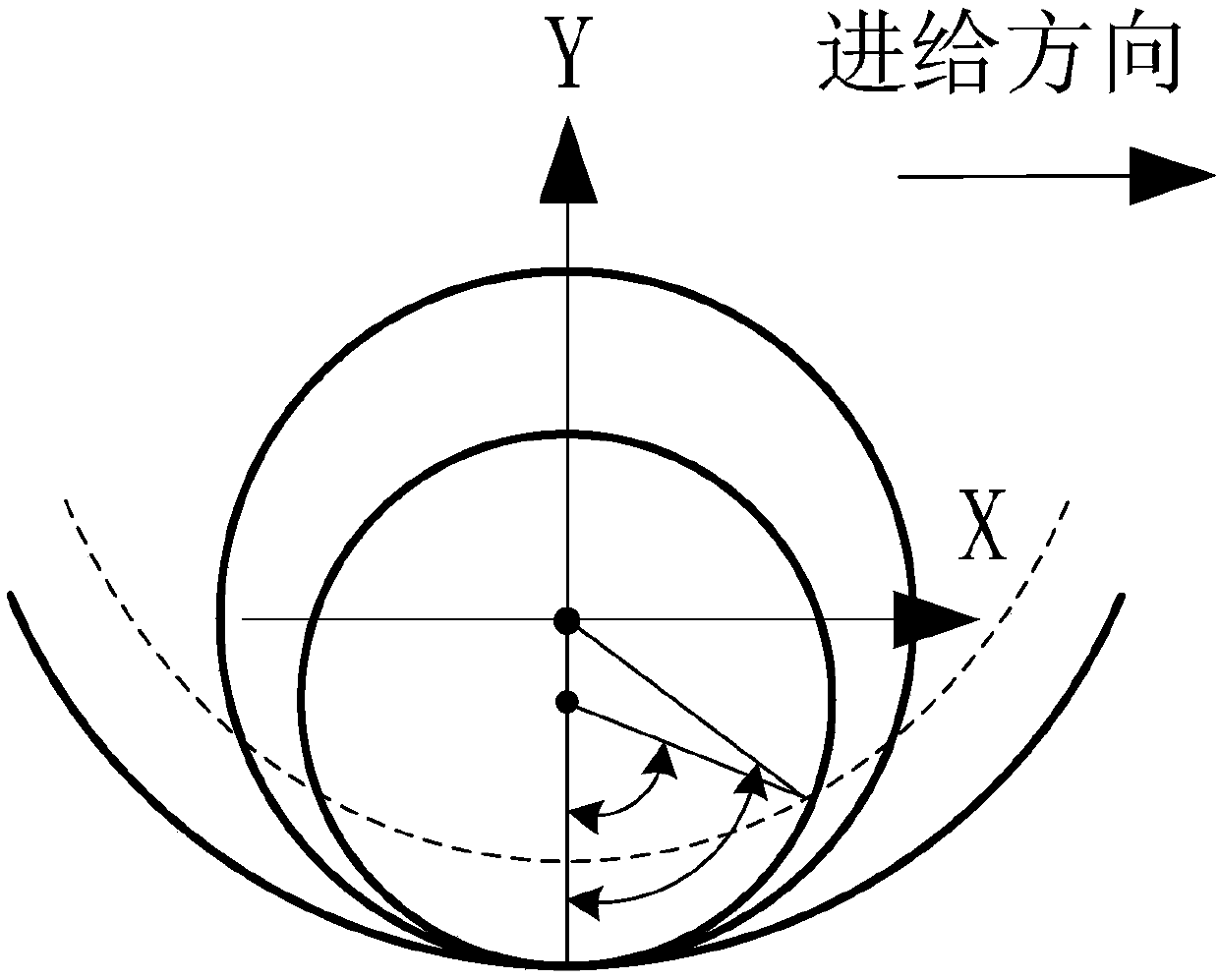
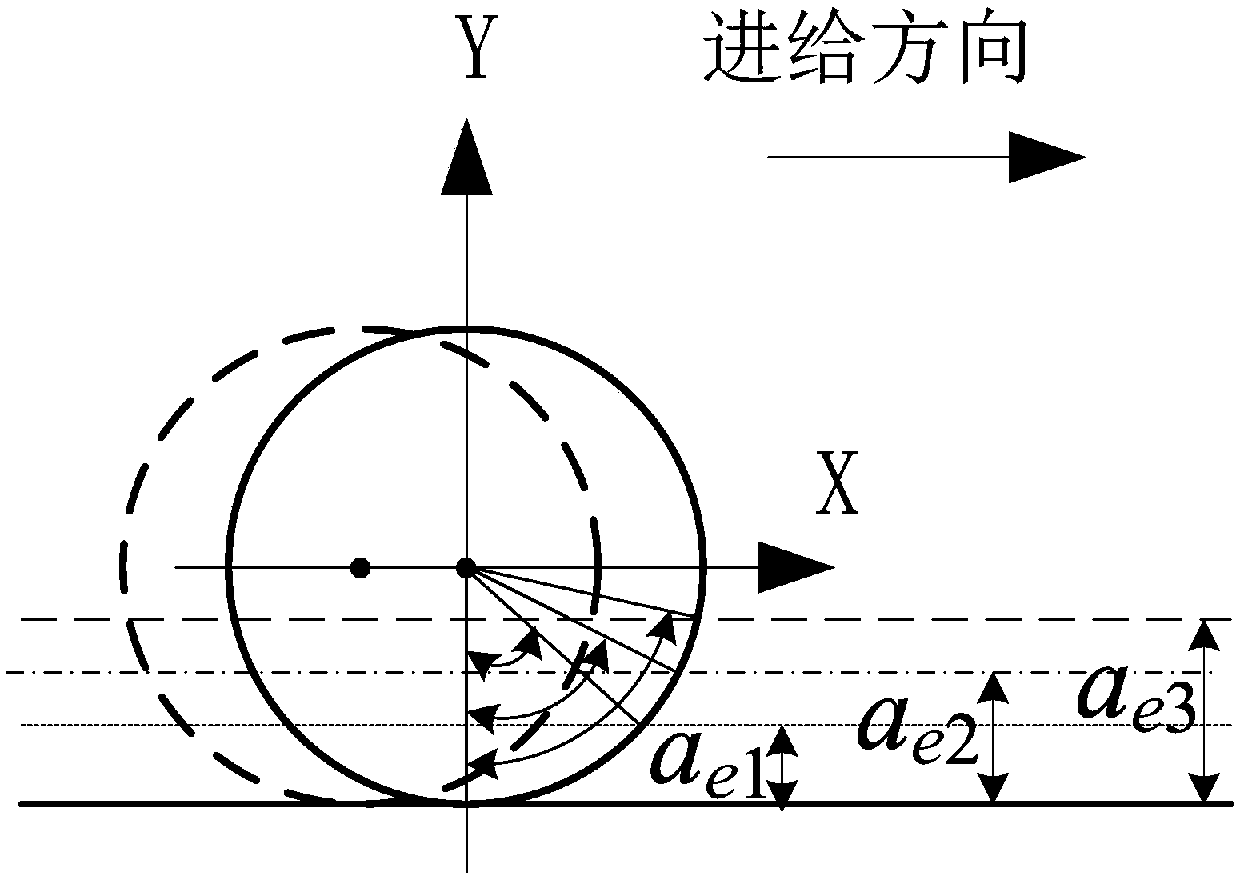
[0043] Three-dimensional milling stability model based on the frequency domain method. During the process of milling the side of the mold cavity by the milling cutter, the tangential force F t Distribution along the direction of milling speed along the milling edge of the milling cutter, the radial force F r is the radial direction of the milling cutter feed, the axial force F aActing in the axial direction of the milling cutter; in order to consider the general case, in the milling edge line, the milling edge is divided into a finite number of small differential units. The chip loads and corresponding differential ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
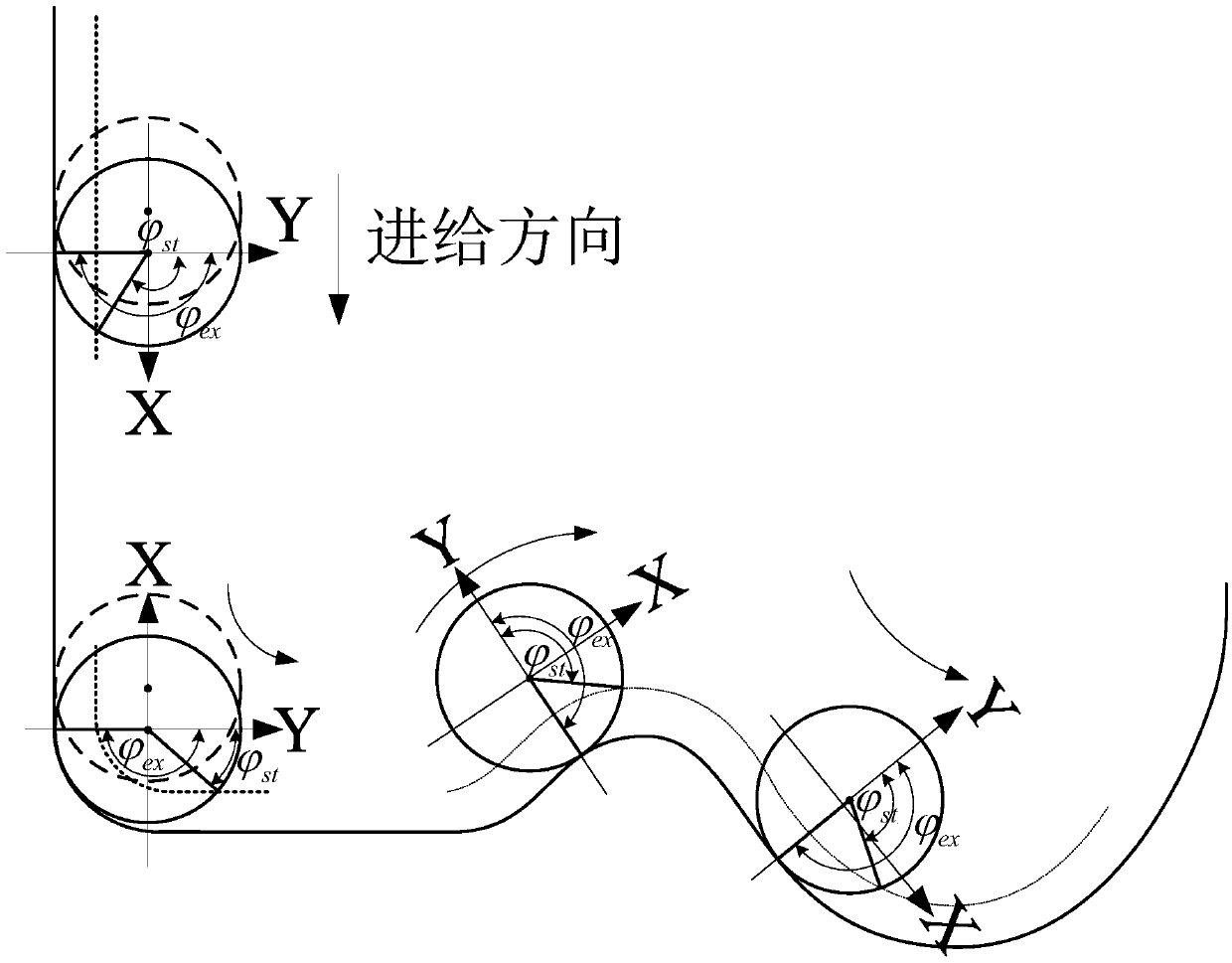
[0100] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that: when the tool is down milling, the horizontal cutting angle and cutting angle of the cutter tooth are respectively and The formula is:
[0101]
[0102] In the formula, R c is the tool radius, a e is the radial depth of cut;
[0103] When the tool is up milling, the horizontal entry angle and exit angle of the cutter tooth are respectively and The formula is:
[0104]
[0105] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com