Pre-service thermodynamic training process simulation method for shape memory alloy wave spring drivers
A memory alloy and process simulation technology, applied in design optimization/simulation, instruments, special data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as low training efficiency, inability to realize pre-service training of complex SMA components, and achieve the effect of overcoming low efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, and the embodiments are exemplary and intended to explain the present invention, but should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
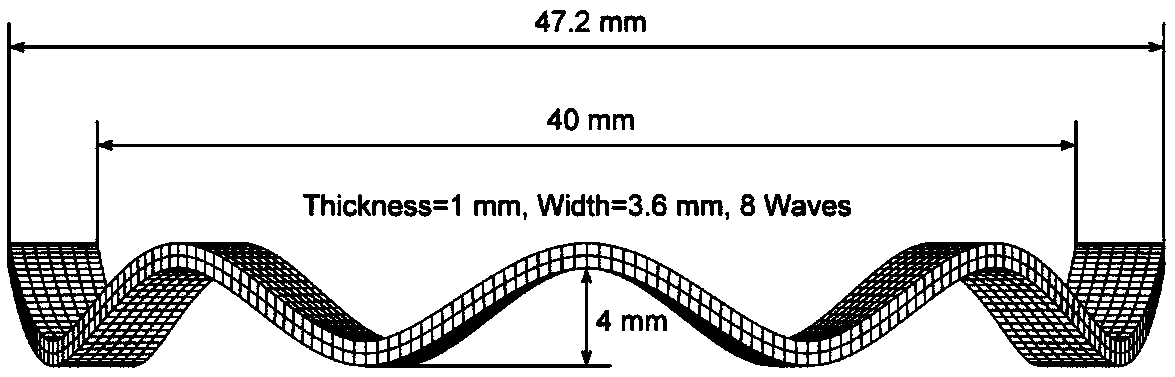
[0032] The simulation method for the pre-service thermodynamic training process of the shape memory alloy wave spring driver in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0033] Step 1: Determine the mechanical properties of the material:
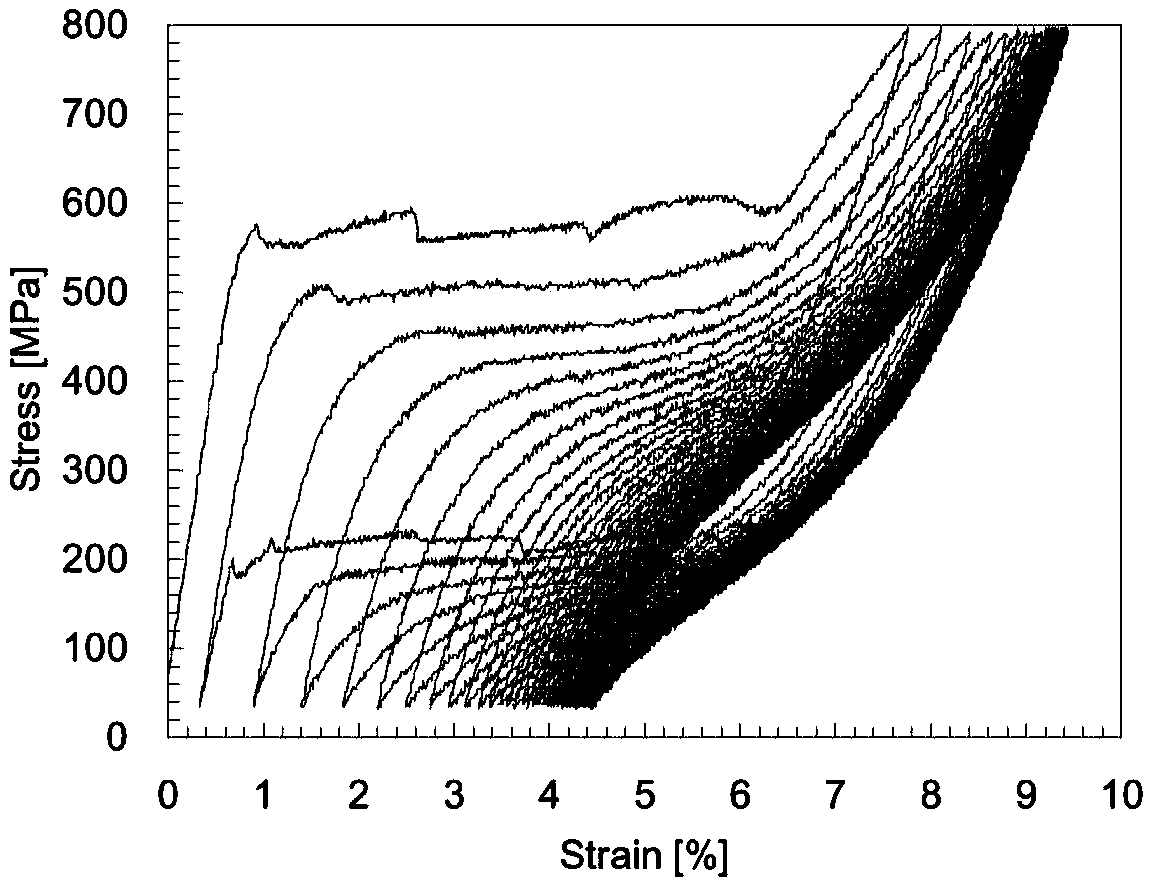
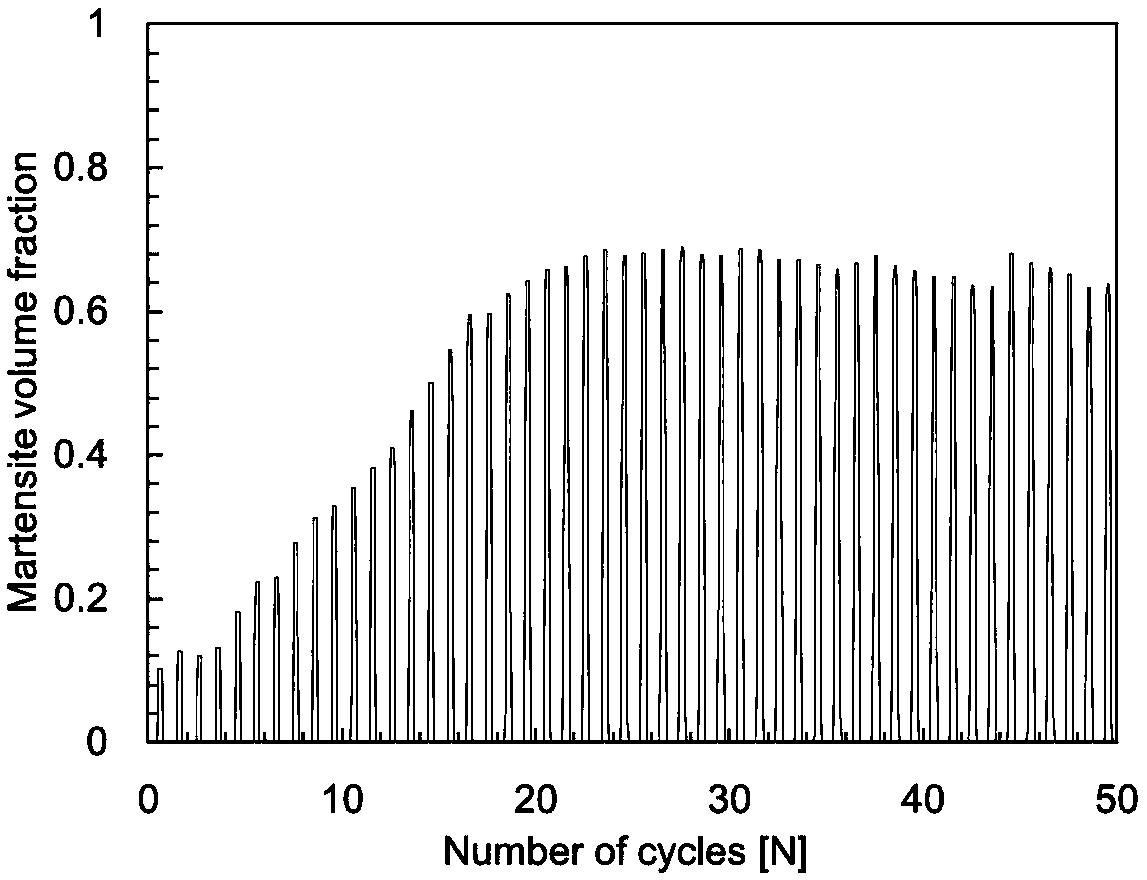
[0034] Select the SMA wire made of the same material as the wave spring driver to carry out uniaxial cycle loading and unloading experiments, measure the influence of strain rate, ambient temperature and maximum stress on the mechanical response of SMA materials, and obtain the thermodynamic properties of SMA materials under different load conditions, including Stress-strain relationship, maximum residual deformation, maximum recoverable deformation, and number of stabilization cycles.
[0035] In this example, the ex...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com