Quasi-resonance converter synchronous rectification circuit
A technology of synchronous rectification and converter, which is applied in the direction of DC power input conversion to DC power output, AC power input conversion to DC power output, instruments, etc. Self-driving mode and other problems, to overcome the effect of large conduction loss, small switching loss, low conduction resistance and conduction loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
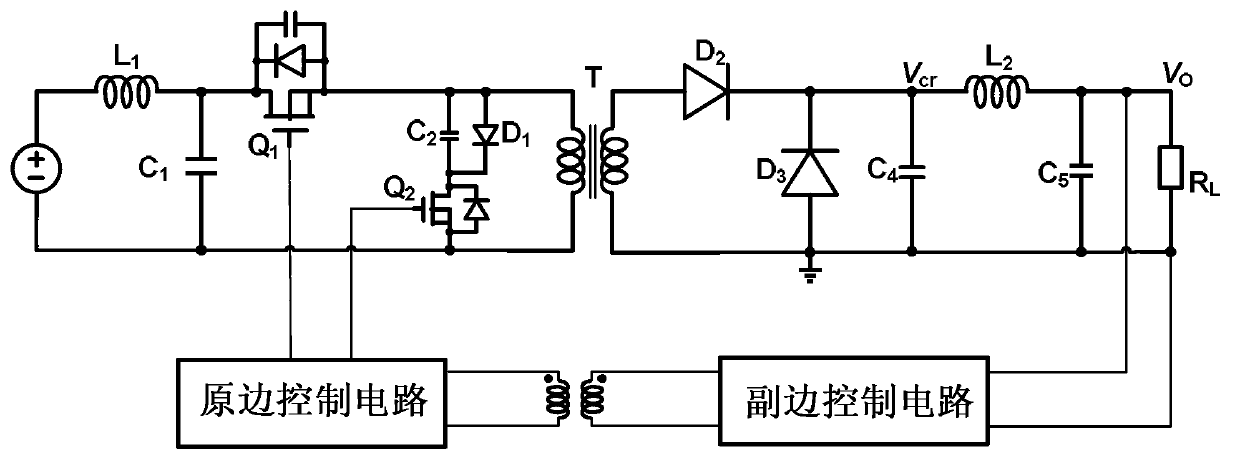
[0056] figure 1 It is a circuit diagram of a traditional quasi-resonant forward converter. The secondary circuit of the transformer T is rectified by a diode. Due to the conduction voltage drop of the diode (U D ) is usually large, generally above 0.5V, especially in the output current (I F ) is larger (tens of amperes or even nearly a hundred amperes), the on-state voltage drop is greater, and the diode conduction loss is
[0057] P DLoss =U D ×I F …………………………………………………………(1)
[0058] It can be seen from the above formula that the conduction loss of the diode is proportional to the forward current, the greater the output current, the greater the loss; and the parallel connection of multiple diodes cannot reduce the conduction loss; therefore, figure 1 The conventional quasi-resonant converter shown is not efficient enough for high power applications, especially for low voltage / high current output.
[0059] figure 2 is the synchronous rectification circuit diagram of th...
Embodiment 2
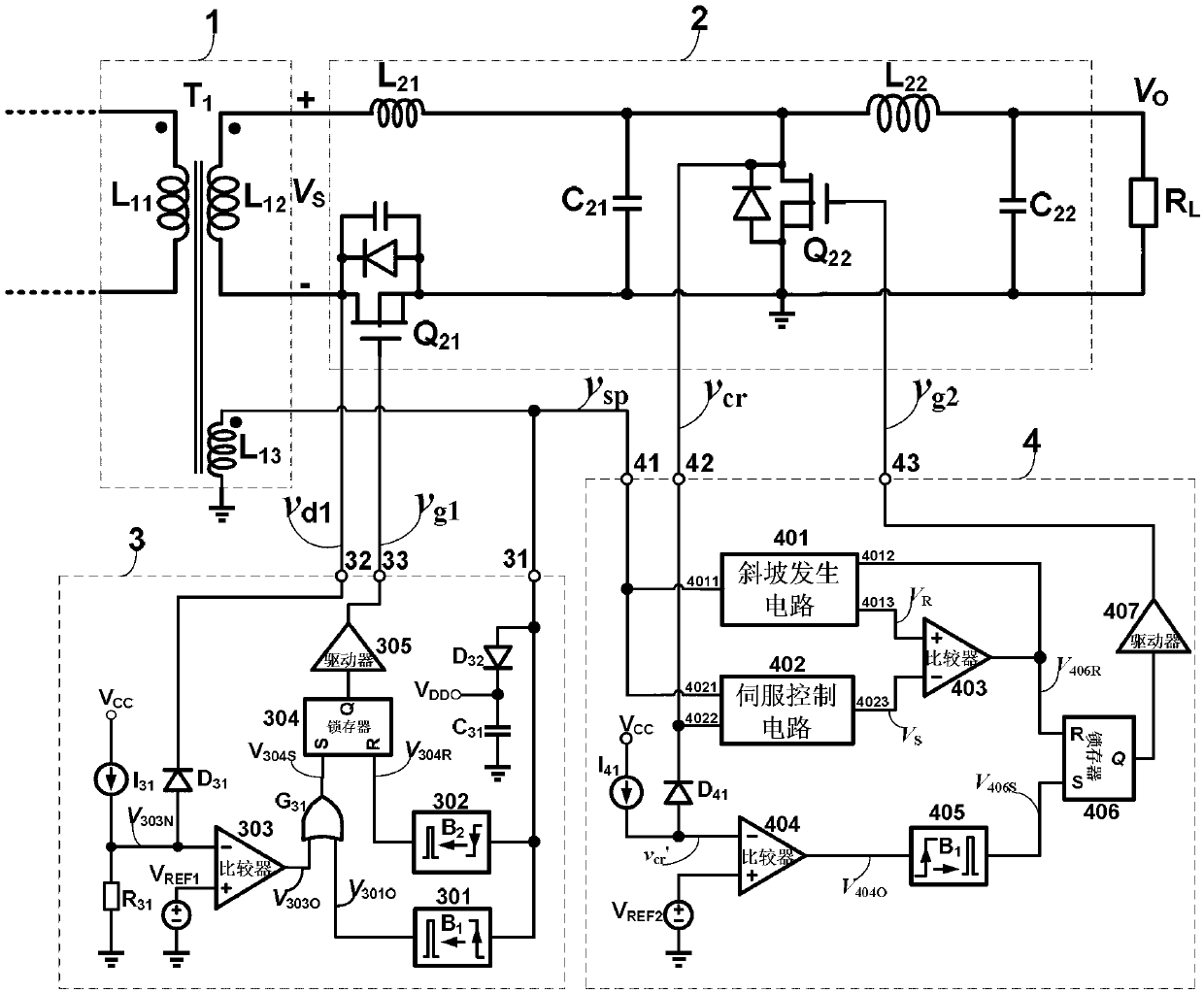
[0084] This embodiment describes in detail the principle of the quasi-resonant converter synchronous rectification circuit:
[0085] The power transformer T1 includes at least the primary winding L 11 , Secondary winding L 12 and auxiliary winding L 13 ;Primary winding L 11 and the secondary winding L 12 Realize input / output electrical isolation and voltage conversion, auxiliary winding L 13 Provide DC bias voltage and synchronous signal for the control circuit (ie rectifier tube control circuit 3 and freewheel tube control circuit 4).
[0086] The secondary switch circuit 2 includes a resonant inductor L 21 , Resonant capacitance C 21 , filter inductance L 22 , filter capacitor C 22 , rectifier tube Q 21 and freewheel Q 22 ; where the rectifier tube Q 21 and freewheel Q 22 It is not limited to the use of MOSFET type controllable switches, and other types of controllable switches, such as BJT, IGBTS, etc., can also be used. The on-resistance of the controllable sw...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com