A method for preparing ingots by layer-by-layer pouring based on slag protection
An ingot and slag technology, applied in the fields of metallurgy and foundry, can solve the problems of difficult one-hundred-ton steel ingots and high production costs, and achieve the effects of realizing metallurgical bonding, solving interface oxidation, and avoiding oxidation of molten steel surface.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] In this embodiment, a 1 ton low-alloy steel ingot is prepared, and its casting method includes the following steps:
[0020] (1) Determine the required amount of molten steel according to the specifications of the cast large ingot, and divide the amount of molten steel into 4 parts, each 0.25 tons, and melt the molten steel one by one according to the casting sequence and time;
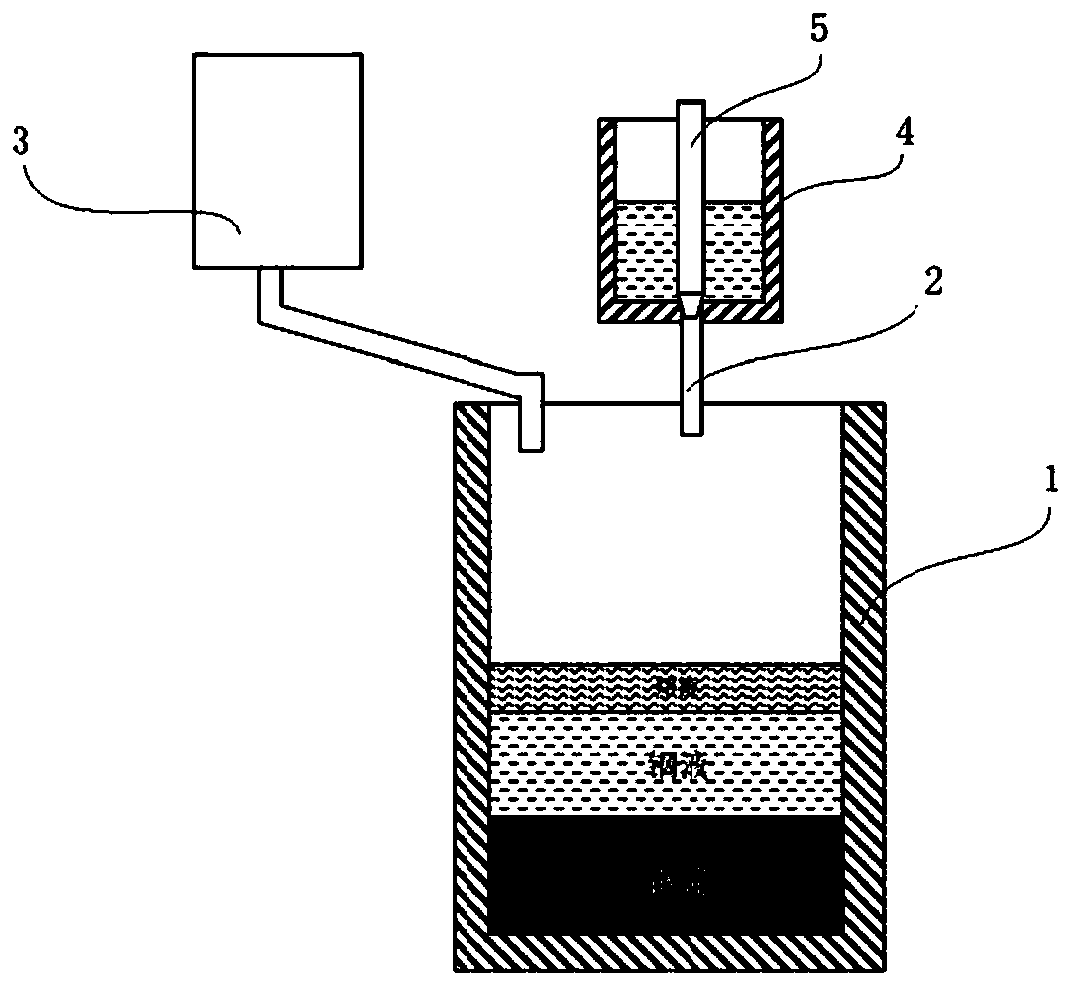
[0021] (2) The 0.25 tons of molten steel in the tundish 4 is poured into the steel ingot mold 1 through the stopper 5 along the nozzle 2. The superheating temperature of the molten steel during pouring is 50 ℃, and the pouring speed is 0.1 ton / min; The slag feeder 3 adds 2Kg (volume ratio with molten steel about 0.016:1) of TLC-32 domestic glass mold flux slag to the steel ingot mold 1, so that the slag evenly covers the entire surface of the molten steel;
[0022] (3) When the remaining volume fraction of molten steel in the ingot mold 1 is 5%, that is, the molten steel has solidified 95%, move anoth...
Embodiment 2
[0025] In this embodiment, 18 tons of low alloy steel ingots are prepared, and the pouring method includes the following steps:
[0026] (1) Determine the required amount of molten steel according to the specifications of the large cast ingots, and divide the amount of molten steel into 9 parts, 2 tons each, and melt the molten steel one by one according to the casting sequence and time;
[0027] (2) The 2 tons of molten steel in the tundish 4 are poured into the steel ingot mold 1 along the nozzle 2 through the stopper 5, where the molten steel overheating temperature is 35°C during pouring, and the pouring speed is 3 tons / min; The slag feeder 3 adds 15Kg (volume ratio with molten steel about 0.015:1) TLC-32 domestic glass mold flux slag to the steel ingot mold 1, so that the slag evenly covers the entire surface of the molten steel;
[0028] (3) When the remaining volume fraction of molten steel in the ingot mold 1 is 15%, that is, the molten steel has solidified 85%, move another ...
Embodiment 3
[0031] In this embodiment, 50 tons of low-alloy steel ingots are prepared, and the casting method includes the following steps:
[0032] (1) Determine the required amount of molten steel according to the specifications of the cast large ingot, and divide the amount of molten steel into 25 parts, 2 tons each, and melt the molten steel one by one according to the casting sequence and time;
[0033] (2) The 2 tons of molten steel in the tundish 4 are poured into the steel ingot mold 1 through the stopper 5 along the nozzle 2. The superheating temperature of the molten steel during pouring is 70 ℃, and the pouring speed is 4 tons / min; The slag feeder 3 adds 15Kg (volume ratio with molten steel about 0.015:1) TLC-32 domestic glass mold flux slag to the steel ingot mold 1, so that the slag evenly covers the entire surface of the molten steel;
[0034] (3) When the remaining volume fraction of molten steel in the ingot mold 1 is 0%, that is, the molten steel is completely solidified, move a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com