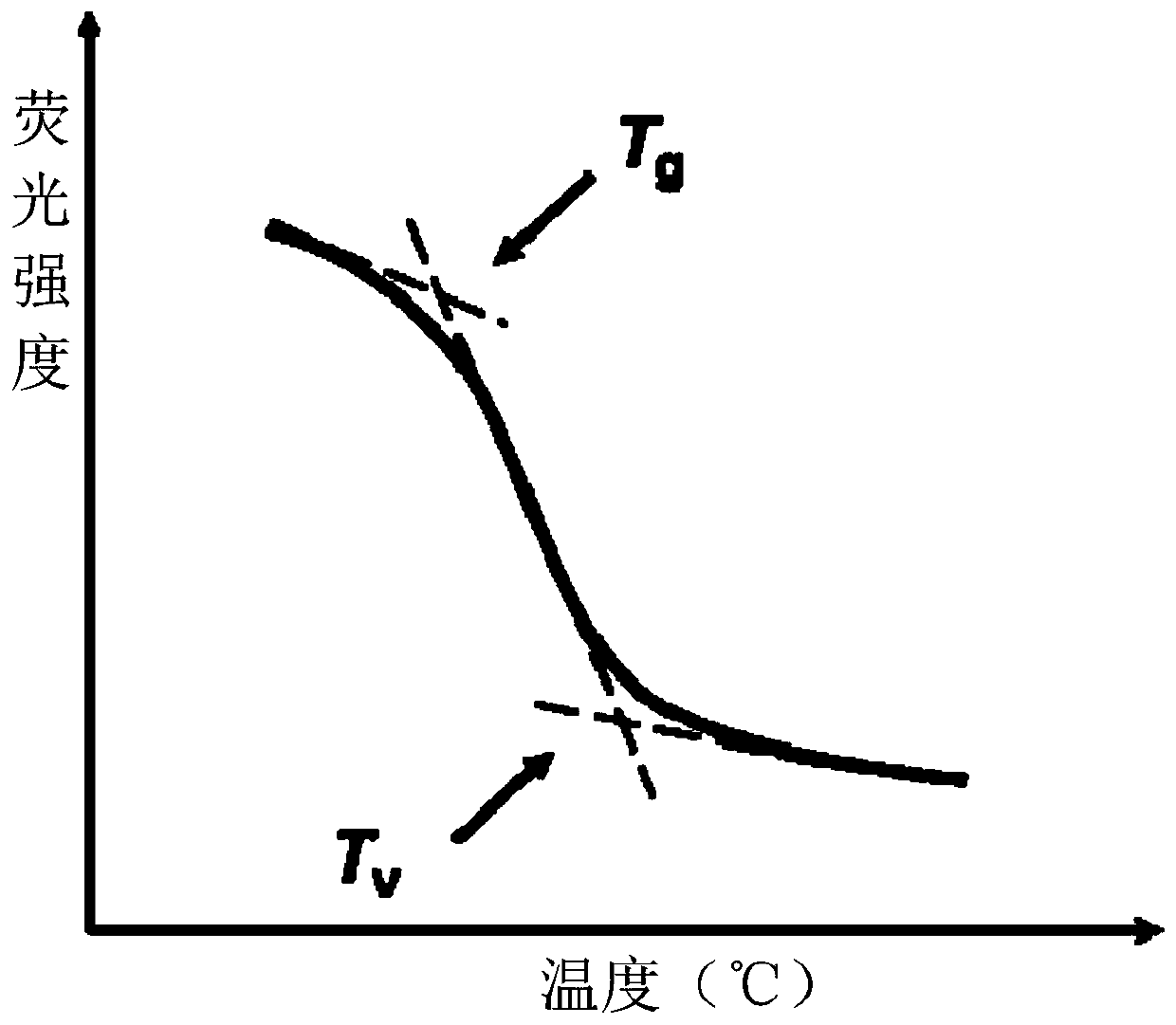
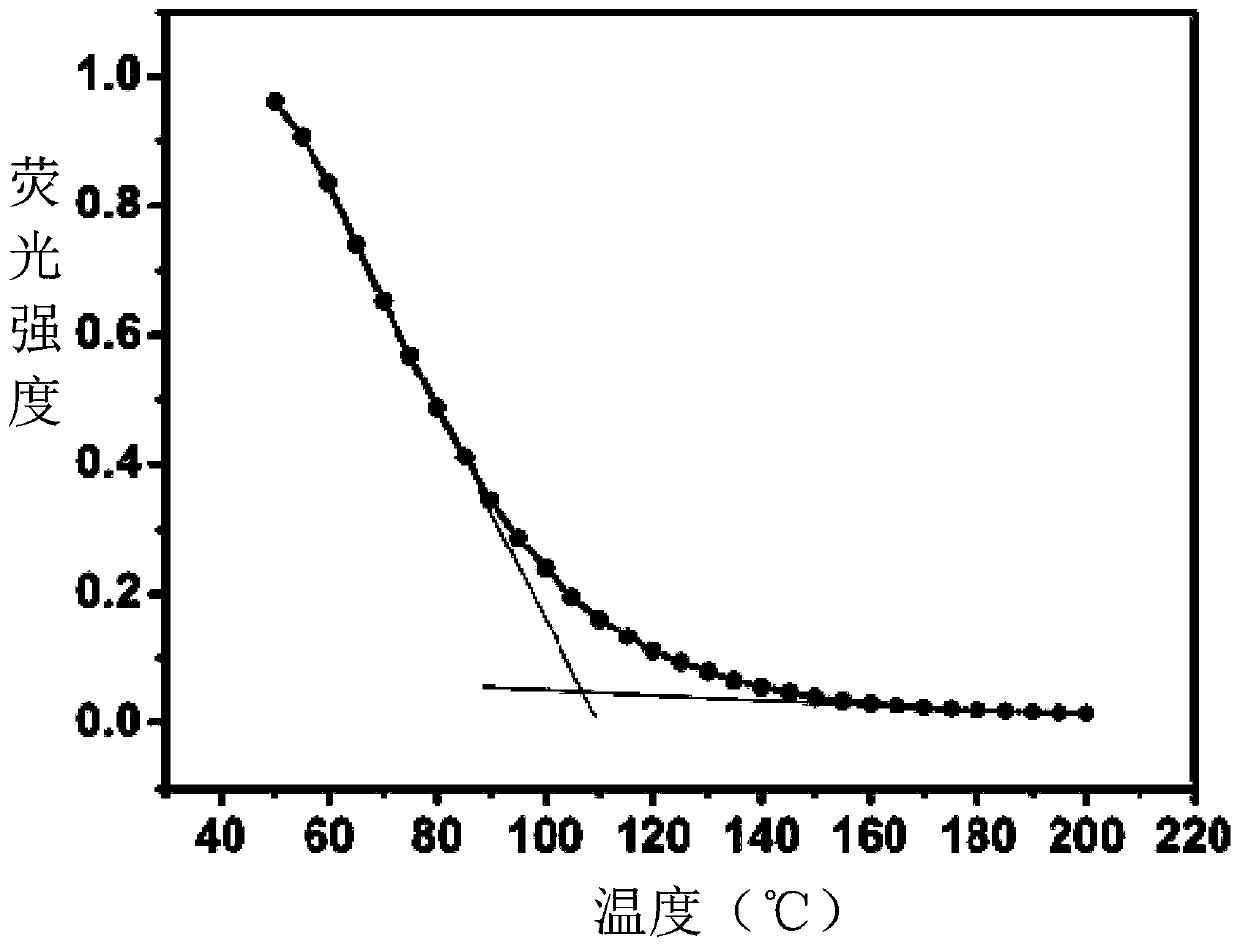
Determination method of topological network structure transition temperature of glass-like polymer materials
A technology of polymer materials and network structure, applied in the field of measurement of transition temperature of topological network structure, can solve problems such as insignificant expansion change, difficulty in accurately determining Tv temperature, and large difference in results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] A mixture of bisphenol A diglycidyl ether, adipic acid and transesterification catalyst 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene (TBD) in molar ratio of 1:1:0.1 was prepared ;
[0055] Melt the mixture at 180°C and stir to mix evenly;
[0056] The melted mixture was placed in a mold, and the temperature was kept constant until the system began to condense, and then the system was placed under 5 MPa for hot pressing, and continued to cure for 4 hours to obtain a modified thermosetting epoxy resin material.
[0057]The fluorescence intensity of the thermosetting epoxy resin material at a series of temperatures during the heating process was measured by a temperature-rising fluorescence spectrometer. The decomposition temperature of the thermosetting epoxy resin material is 200°C. The temperature measurement range of the topological network structure transition temperature is 25°C to 200°C, and the fluorescence intensity is measured once every 5°C of temperature increase.
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com