Method of arranging structure health monitor sensors
A health monitoring and layout method technology, applied in the direction of instruments, special data processing applications, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve the problems of complex calculation process, densely arranged sensors, not very suitable for health monitoring, etc., to achieve less consumption and better calculation process Simple and convenient operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
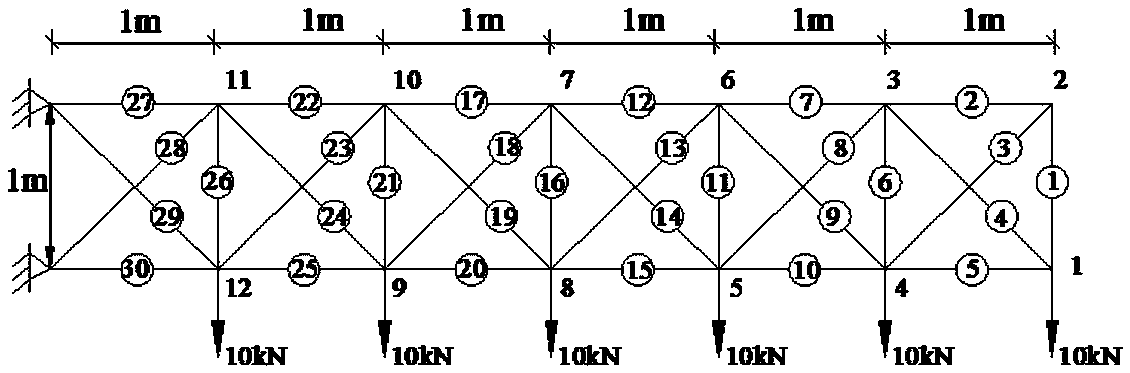
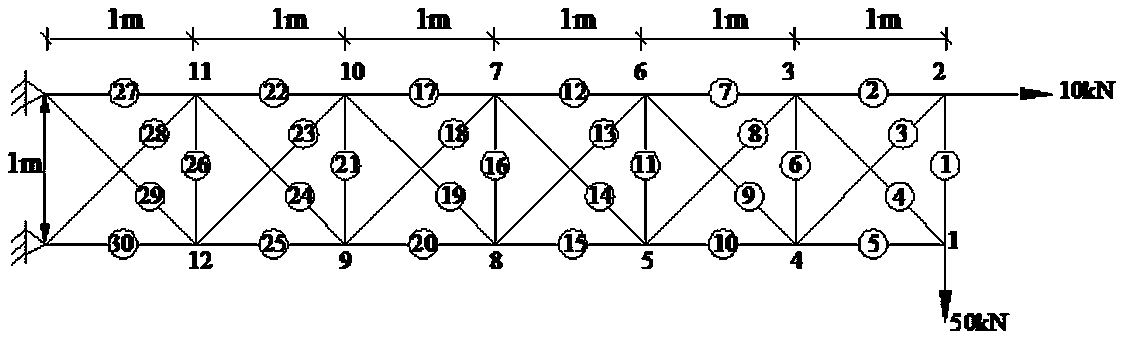
[0032] The following takes the same steel truss structure as the object to elaborate the technical scheme. The basic physical parameters of the selected steel truss structure are: elastic modulus E=200GPa, density ρ=7.8×10 3 kg / m 3 , the bar cross-sectional area A=7.85×10 -5 m.
[0033] External forces are mainly divided into two types: horizontal force and vertical force. For steel truss structures, the force can be divided into one-way force and two-way force. The following two types of one-way force and two-way force For the mode of action, analyze the transverse load action on the same steel truss respectively, see figure 1 with figure 2 , analyze the arrangement of sensors on it under the action of transverse load, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0034] (1) Establish a structural finite element model to obtain the structural stiffness matrix K;
[0035] (2) Decompose the stiffness matrix K, and decompose it into the product form of the degree of f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com