Twelve-phase permanent magnetic synchronous motor fault tolerance control method based on output maximum torque
A technology of permanent magnet synchronous motor and maximum torque, which is applied in motor control, motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, etc. It can solve the problems of unbalanced current amplitude and inability to guarantee maximum torque output, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] A fault-tolerant control method for a twelve-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor based on the maximum output torque, the method includes the following steps: (1) Considering the n-phase motor as a whole, dividing each variable in the motor into α that participates in electromechanical energy conversion The model of the twelve-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor is established in the -β plane and in other planes that have nothing to do with electromechanical energy conversion; (2) According to the principle of constant total magnetic potential, keep the system decoupling transformation matrix unchanged, and obtain the twelve-phase motor The expressions of the remaining phase currents in the maximum torque output mode during open-phase operation; (3) The expressions of the currents of each phase are After the static coordinate transformation, the size of the current that needs to be injected into the corresponding harmonic sub-plane can be calculated.
Embodiment 2
[0058] According to the fault-tolerant control method of the twelve-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor based on the maximum output torque described in embodiment 1, the n-phase motor is regarded as a whole, and each variable in the motor is divided into α- The specific process in the β plane and other planes that have nothing to do with electromechanical energy conversion is as follows: The Clark transformation matrix of n-phase symmetric polyphase motor is given:
[0059]
[0060] in: is the electrical angle between every two sets of windings;
[0061] The value of m is related to the phase number of the motor, when is an even number, ,when is an odd number, , and the last row of vectors shown in formula (1) will not exist;
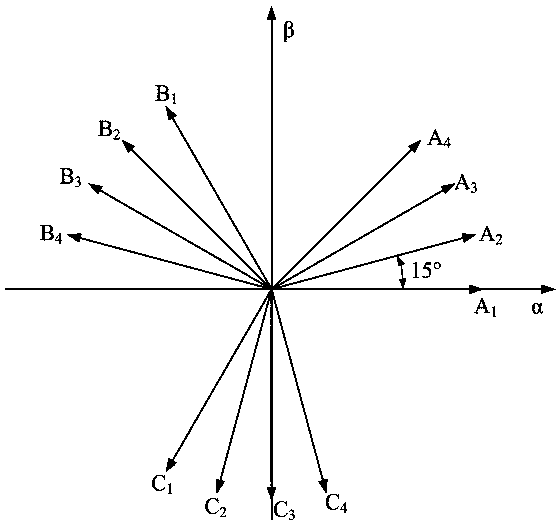
[0062] When the stator and rotor magnetic potentials are sinusoidally distributed, the first two rows of vectors correspond to the α-β subspace, which corresponds to the fundamental flux linkage and torque components, which are the sam...
Embodiment 3
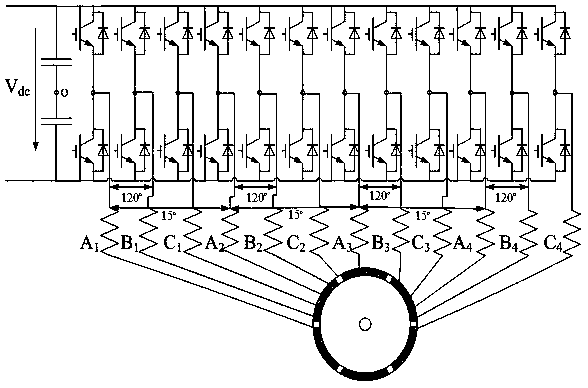
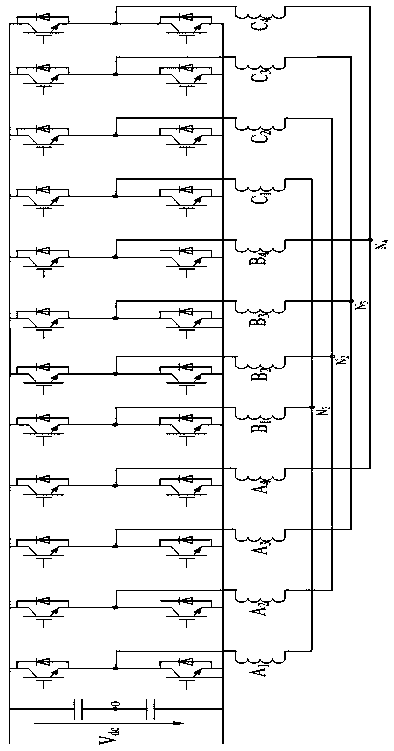
[0064] According to the fault-tolerant control method of the twelve-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor based on the maximum output torque described in embodiment 1 or 2, it is characterized in that: the specific process of establishing the model of the twelve-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor is: the stator is formed by Four sets of Y-connected three-phase symmetrical windings, A 1 B 1 C 1 For the first set of windings, A 2 B 2 C 2 For the second set of windings, A 3 B 3 C 3 For the third set of windings, A 4 B 4 C 4 It is the fourth set of windings, and the four sets of windings have a spatial difference of 15° in electrical angle. For the convenience of analysis, the following assumptions are made:
[0065] (1) The armature reaction magnetic field generated by the stator winding and the excitation magnetic field generated by the rotor permanent magnet are both sinusoidally distributed in the air gap;
[0066] (2) Neglect the magnetic saturation of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com