A MOS transistor driving circuit for suppressing a driving voltage spike
A MOS tube, driving voltage technology, applied in circuits, transistors, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in choosing TVS tubes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
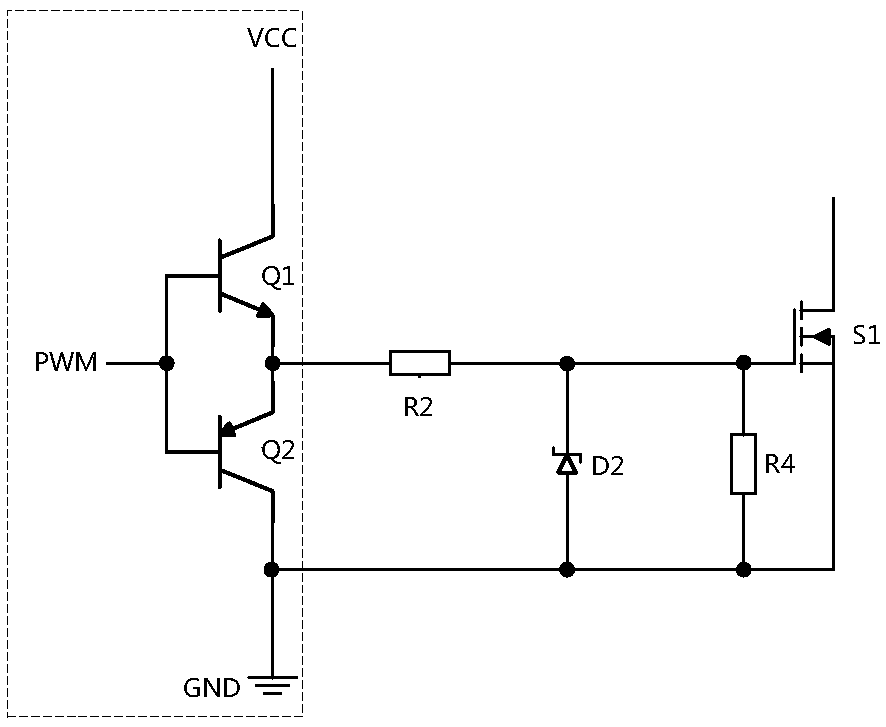
[0027] figure 2 A circuit diagram of the first embodiment of the power module burn-in system of the present invention is given. figure 2 In the above, the MOS tube drive circuit for suppressing the driving voltage spike and suppressing the driving voltage spike includes a push-pull circuit 1, a gate resistor R2 and an RCD absorbing circuit 2, and the push-pull circuit is composed of an NPN transistor Q1 and a PNP transistor Composed of Q2, the base of the NPN transistor Q1 and the base of the PNP transistor Q2 are connected to drive the PWM signal, the collector of the NPN transistor Q1 is connected to the power supply, and the collector of the PNP transistor Q2 The electrodes are connected to the ground level of the power supply, the emitter of the NPN transistor Q1 and the emitter of the PNP transistor Q2 are connected to the output end of the push-pull circuit, and the output end of the push-pull circuit is connected to the gate One end of the resistor, the other end of ...
Embodiment 2
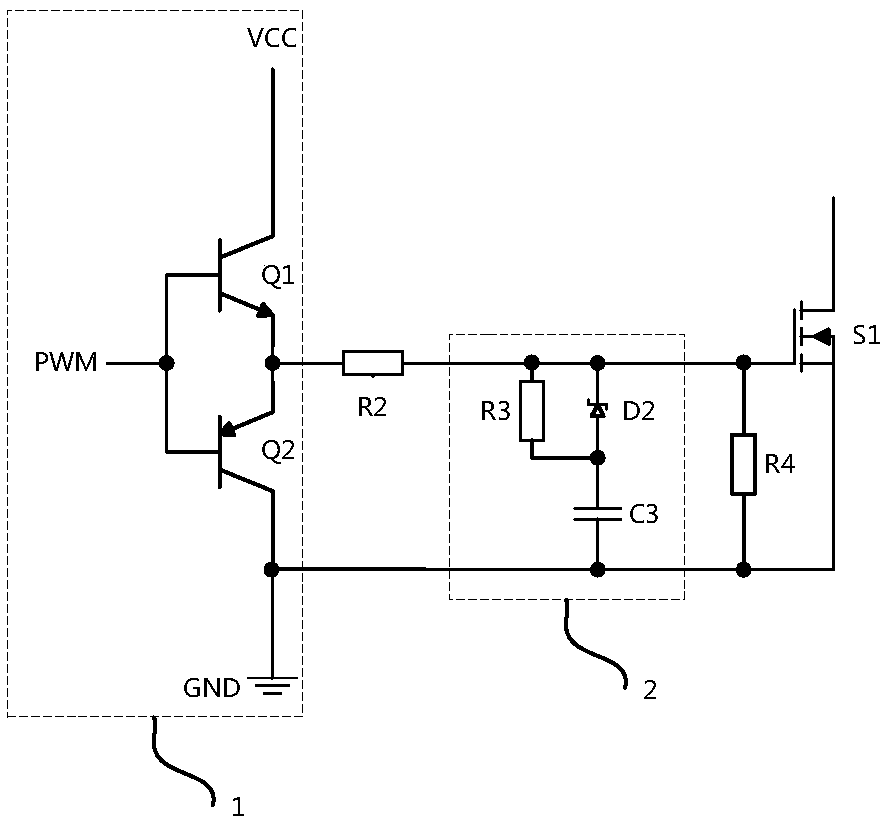
[0031] image 3 The circuit diagram of the second embodiment of the power module burn-in system of the present invention is given. image 3 In the above, the MOS tube drive circuit for suppressing the driving voltage spike and suppressing the driving voltage spike includes a push-pull circuit 1, a gate resistor R2 and an RCD absorbing circuit 2, and the push-pull circuit is composed of an NPN transistor Q1 and a PNP transistor Composed of Q2, the base of the NPN transistor Q1 and the base of the PNP transistor Q2 are connected to drive the PWM signal, the collector of the NPN transistor Q1 is connected to the power supply, and the collector of the PNP transistor Q2 The electrodes are connected to the ground level of the power supply, the emitter of the NPN transistor Q1 and the emitter of the PNP transistor Q2 are connected to the output end of the push-pull circuit, and the output end of the push-pull circuit is connected to the gate One end of the resistor, the other end of...
Embodiment 3
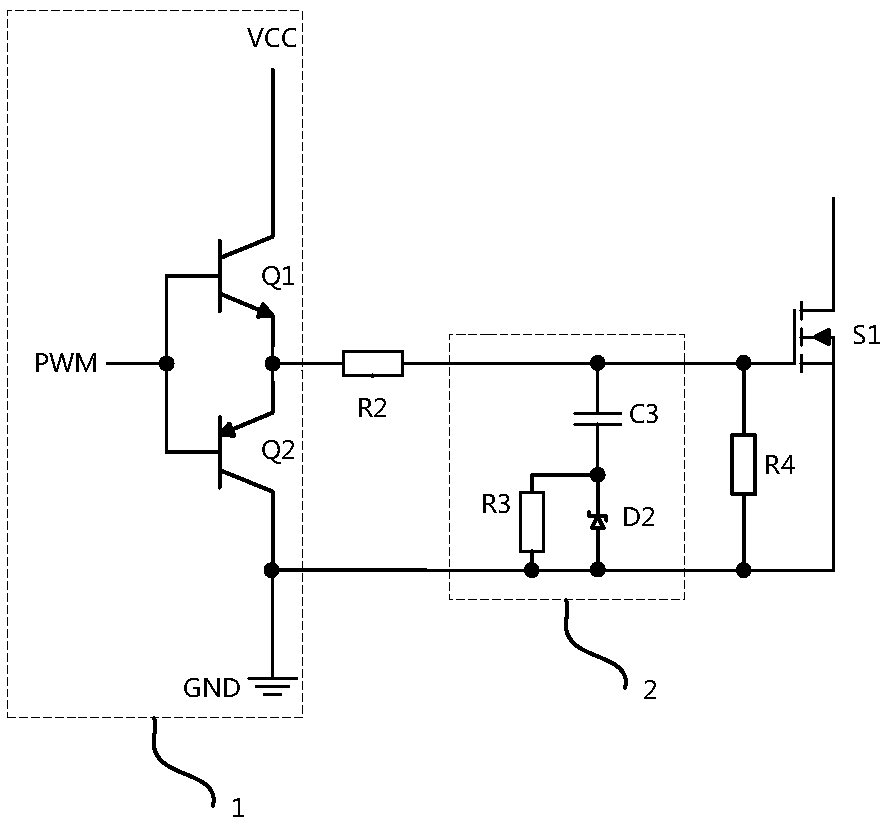
[0035] Figure 4 The circuit diagram of the third embodiment of the power module burn-in system of the present invention is given. Figure 4 In the above, the MOS tube drive circuit for suppressing the driving voltage spike and suppressing the driving voltage spike includes a push-pull circuit 1, a gate resistor R2 and an RCD absorbing circuit 2, and the push-pull circuit is composed of an NPN transistor Q1 and a PNP transistor Composed of Q2, the base of the NPN transistor Q1 and the base of the PNP transistor Q2 are connected to drive the PWM signal, the collector of the NPN transistor Q1 is connected to the power supply, and the collector of the PNP transistor Q2 The electrodes are connected to the ground level of the power supply, the emitter of the NPN transistor Q1 and the emitter of the PNP transistor Q2 are connected to the output end of the push-pull circuit, and the output end of the push-pull circuit is connected to the gate One end of the resistor, the other end o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com