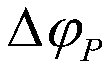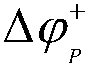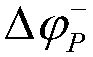A method for calculating and calibrating that zero angle of a rotor position sensor of a permanent magnet synchronous motor
A permanent magnet synchronous motor and rotor position technology, which is applied in the control of generators, motor generators, electromechanical brakes, etc., can solve problems such as large calibration errors, failure to meet product requirements, and errors in zero-angle calibration results of motor sensors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0071] The present invention provides a specific embodiment. A load, motor, and controller integrated product is known. The structure of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is 6 poles and 9 slots, and the effective value of the rated phase current is 30A. The forward load of the product is 0.71Nm, and the reverse load is 0.78Nm.
[0072] For a permanent magnet synchronous motor with 6 poles and 9 slots, there are 3 electrical angle periods in one rotation of the rotor, that is, there are 3 physical zero angle positions in one rotation of the rotor. Therefore, the current vector sequence output by the controller is shown in Table 2 below.
[0073]
[0074]
[0075] Table 2
[0076] The modulus length of the current vector (Is_x) pointing to the rotor locking angle x° is the rated phase current effective value, that is, 30A. The current vector is slowly output to the motor according to formula (5).
[0077]
[0078] In formula (5), the current change rate k is t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com