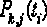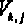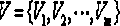Dynamic Fault-Tolerant Elastic Scheduling Method
A scheduling method and elastic technology, applied in the field of cloud computing, can solve problems such as increased failure probability, disk drive damage, 4%, etc., to achieve the effect of balance, high performance, reliability and resource optimization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Example 1: when the task in the VM When the above is weak fault tolerance.
[0080] In this case, by the definition of weak fault tolerance, the task It is quite possible to meet the deadline. To measure the likelihood of completion, the Defined as completing a task on a VM The probability:
[0081]
[0082] For clouds, there may be multiple virtual machines belonging to Weak fault tolerance, therefore, The global optimal scheduling strategy is to find each of The maximum value of , defined as , however, for lower , if it cannot be completed before the deadline, it will not only waste resources, but also affect the execution of subsequent tasks. Therefore, it is necessary to determine a threshold As a metric for determining scheduling policies.
[0083] Further, the decision tree method can be used to determine the threshold ,Such as Figure 5 As shown in , it can be seen that the decision tree has three outputs, "Completed", "Rejected" an...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: when the task in the VM When the above is strong fault tolerance.
[0090] In this case, the task It is always possible to meet the deadline. Considering overall resource optimization, the key issue is to determine when to use the replication mechanism and when to use the central commit mechanism.
[0091] when set up, initial task and the resubmitted task There will be a time overlap between them. However, if resubmission is used, the original task was in When it fails later, the resubmitted task does not have enough time slots to complete before the deadline. In this case, resubmitting cannot achieve effective fault tolerance. Therefore, to achieve effective fault tolerance, a replication mechanism must be employed.
[0092] if holds, there may be no time overlap, so the resubmission mechanism is available. but if just than Slightly larger, it may not have enough time for resubmission tasks to execute, such as Figure 6 shown. In t...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Embodiment 3: Using task scheduling analysis when resubmitting.
[0095] Due to the fluctuation of the running time of the task, the resubmission mode will have many forms, and these forms are abstracted into two categories.
[0096] Category 1:
[0097] Such as Figure 7 shown, where the arrow indicates the ready time . assumed can be satisfied.
[0098] Therefore, if , regardless of the initial task Whether or not it completes successfully, there is always enough time slot to ensure completion of the resubmitted task. According to the basic assumption of the fault model, if fail, can be completed successfully. Therefore, effective fault tolerance can be achieved.
[0099] Category 2:
[0100] Such as Figure 8 shown, if exist failure, where ,So should start from Begin execution. However, if the actual task runtime , the system cannot be fault-tolerant in this case. Therefore, the effective fault tolerance probability using the resu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com