Enhanced viscosity oat base and fermented oat base product
A technology of viscosity increase and oatmeal, which is applied in the direction of food ingredients as viscosity modifiers, dairy products, milk preparations, etc., to achieve the effect of improving gel properties and increasing viscosity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1. Process for producing the viscosity-improved oat base of the present invention from a state-of-the-art oat base
[0056] Materials: oat base produced according to EP 1124441 A1, containing about 1 wt% oat protein, to which rapeseed oil was added to increase the total fat content to about 3 wt%; transglutaminase ACTIVA TG-WM TM (100U / g), Ajinomoto (Japan); pea protein, Nutralys containing about 80 wt% protein TM S85F and F85F (Roquette, France); YoMix TM 511 Yogurt Culture, Danisco DuPont (Denmark); Rapeseed Oil (AAK, Sweden); Sugar. Aqueous solutions for addition during fermentation were prepared: a) 15U / g transglutaminase solution, b) 1.8wt% Yomix TM 511 solution.
[0057] Pea protein (3.8 g) was added to 94 g oat base in a glass flask, and the mixture was shaken to disperse the protein. The flask was immersed in a boiling water bath at 95 °C and kept at this temperature for 10 minutes, then cooled to room temperature by immersing it in cold water. T...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2. Cross-linking effect of different protein isolates
[0061] Some vegetable protein isolates were included to demonstrate their crosslinking properties at 4 wt% total protein content in a deamidated oat base. The results were confirmed by rheological measurements, as shown in Table 1 (sequential crosslinking and fermentation) and Table 2 (simultaneous crosslinking and fermentation). The oat base without added protein isolate had a zero shear viscosity of about 50 Pa·s, a modulus of elasticity (G') of about 5 Pa, and a yield point of about 1.
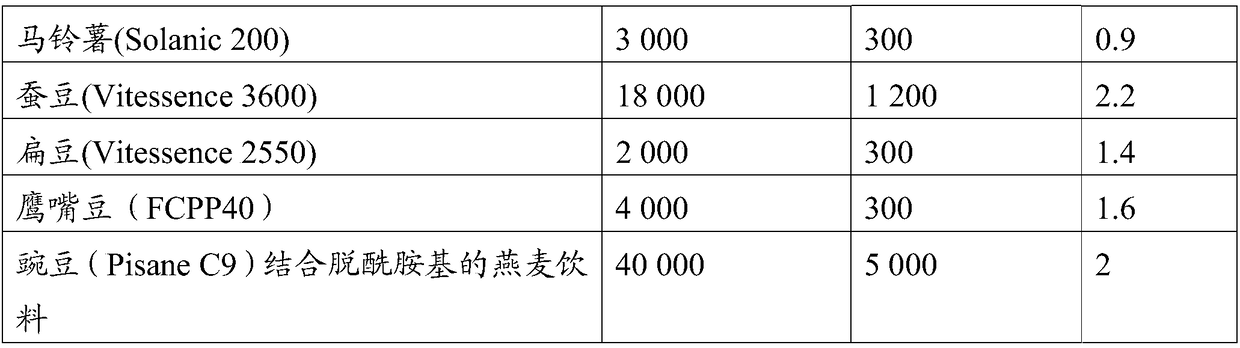
[0062] Table 1. Crosslinking effect of transglutaminase on fermentation product of protein isolate and deamidated oat base composition, sequential crosslinking and fermentation
[0063] Protein isolate added to 4% of total protein content
Viscosity Pa·s
Elastic modulus Pa'
Yield point
Peas (Nutralys S85F)
2 000
300
0.9
Chickpeas (FCPP40)
3 000
200
1.1
Pea (Pisa...
Embodiment 3
[0067] Example 3. Crosslinking effect of different starting materials
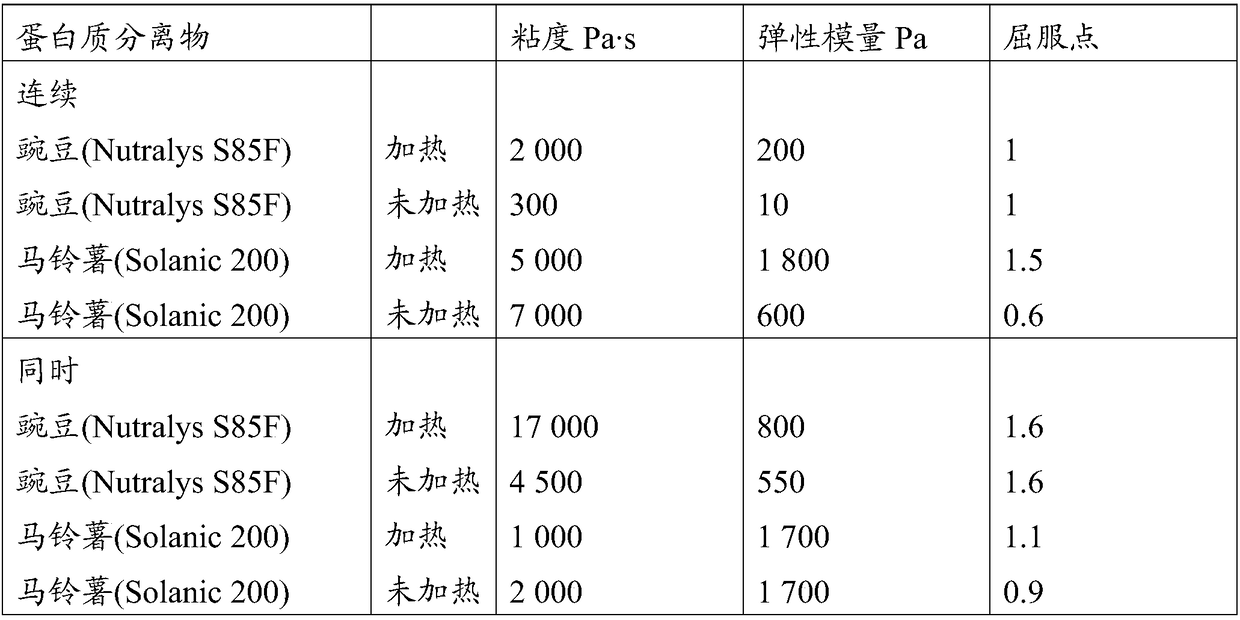
[0068] An important factor in the cross-linking properties is the nature of the protein isolate, as shown in Example 2. Another important factor is whether the protein isolate is heat-treated prior to cross-linking, as shown in Table 3. However, the effect of heat treatment does not appear to be of a general nature, but rather localized to certain protein isolates, such as pea protein isolate. According to the invention, the properties of the gel or curd obtained can be adjusted by varying the time and / or temperature of the heat treatment. Higher temperatures and / or longer treatment periods lead to increased viscosity and gel strength.
[0069] Oat-based or oat beverages containing deamidated groups and addition of viscosity promoters are additional factors affecting crosslinking performance and viscosity. Compositions of oat base and pea protein that had not been heat-treated prior to transglutaminase ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com