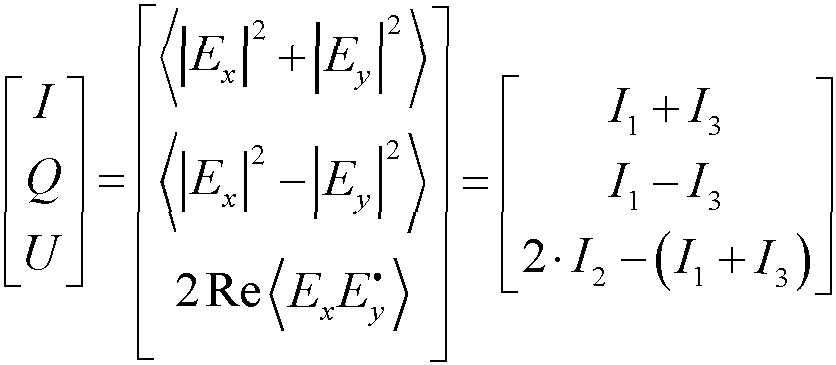Monocular Polarization 3D Reconstruction Method Based on Scattering Information Correction
A technology of 3D reconstruction and scattering information, which is applied in 3D modeling, 3D image processing, details involving processing steps, etc. It can solve problems such as low reconstruction accuracy, complex equipment, and inability to obtain object depth information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
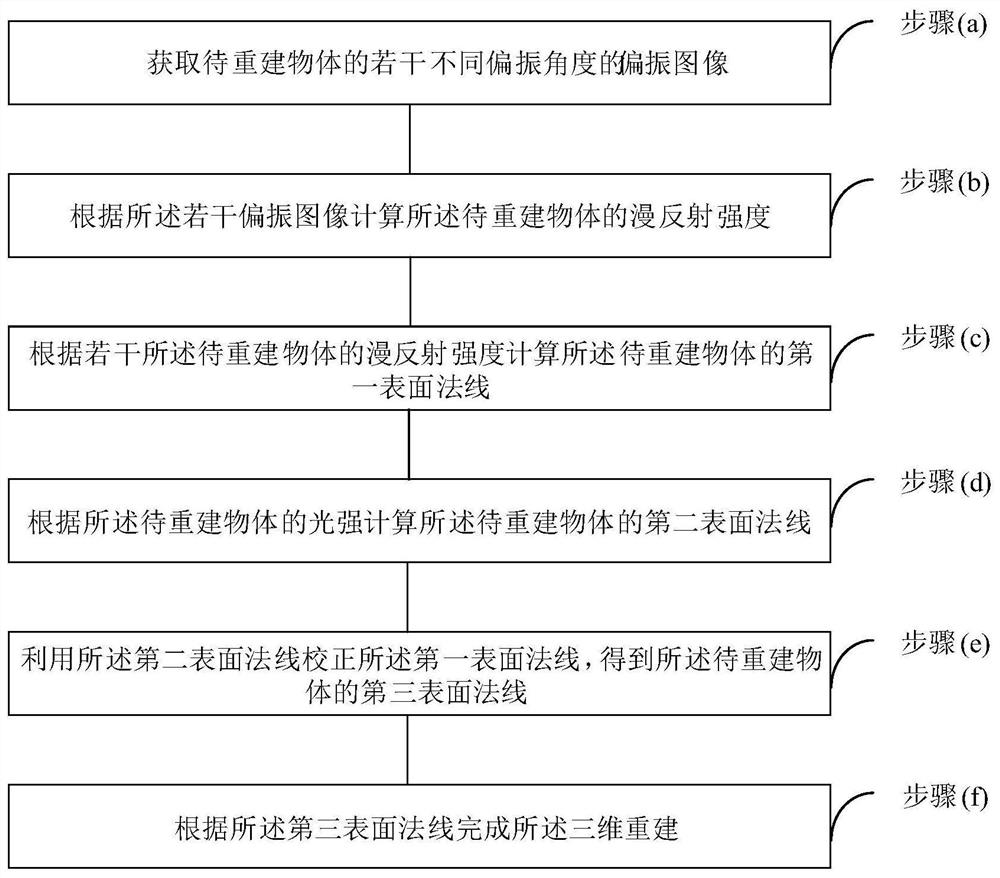
[0072] See figure 1 , figure 1 It is a schematic flowchart of a monocular polarization three-dimensional reconstruction method based on scattering information correction provided by an embodiment of the present invention.
[0073] A monocular polarization three-dimensional reconstruction method based on scattering information correction, comprising the following steps:
[0074] (a) acquiring polarization images of several different polarization angles of the object to be reconstructed;
[0075] (b) calculating the diffuse reflection intensity of the object to be reconstructed according to the plurality of polarization images;
[0076] (c) calculating the first surface normal of the object to be reconstructed according to the diffuse reflection intensities of the several objects to be reconstructed;
[0077] (d) calculating the second surface normal of the object to be reconstructed according to the light intensity of the object to be reconstructed;
[0078] (e) correcting ...
Embodiment 2
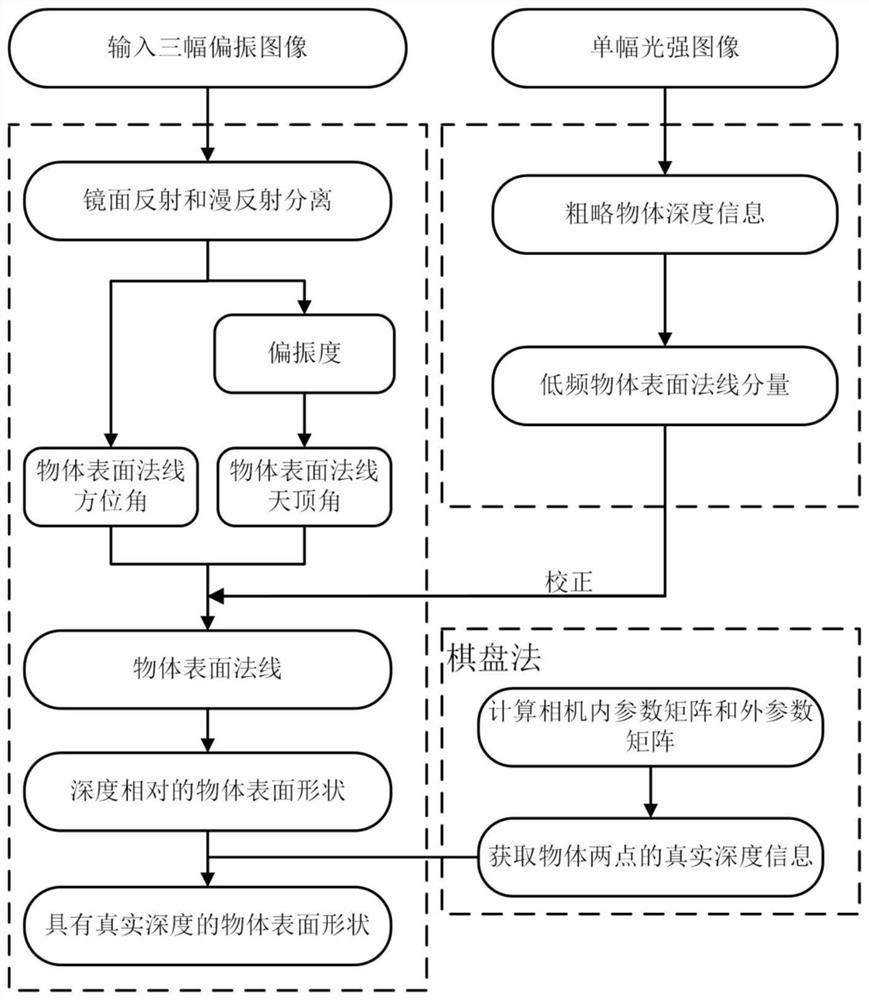
[0082] see again figure 1 In this embodiment, on the basis of the foregoing embodiments, a specific process of a monocular polarization three-dimensional reconstruction method based on scatter information correction will be described in detail.
[0083] (S10) Acquiring polarization images of several different polarization angles of the object to be reconstructed.
[0084] Scene polarization images at different angles of the object to be reconstructed are acquired.
[0085] Using the imaging detector and the polarizer, three different polarization images of the object to be reconstructed are obtained.
[0086] Rotate the polarizer at intervals of 45° and rotate three times to obtain the first polarized image I 1 , the second polarized image I 2 , the third polarization image I 3 .
[0087] It should be noted that, I 1 , I 2 , I 3 respectively refer to the light intensity of the first polarized image, the second polarized image, and the third polarized image.
[0088] (...
Embodiment 3
[0216] This embodiment includes all the content of the second embodiment, and on the basis of the second embodiment, the surface shape of the object in real depth is obtained.
[0217] (S70) Calculate the true depths of the two points of the object to be reconstructed by using the chessboard method according to the normalized Z-axis component.
[0218] Use the chessboard method to calculate two points Z of the object to be reconstructed real (x 1 ,y 1 ) and Z real (x 2 ,y 2 ) true depth information.
[0219] Step (S70) comprises the following steps:
[0220] (S701) The imaging detector collects checkerboard images under different angles.
[0221] (S702) Obtain an internal parameter matrix of the camera according to the checkerboard image.
[0222] Obtain the pixel coordinates m=[u, v, 1] of each corner point in the image according to the checkerboard image at different angles T And the corresponding actual coordinates M=[x, y, 1] T , and then calculate the internal p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com