Two-dimensional pattern modulation frequency hopping communication method
A technology of frequency hopping communication and two-dimensional patterns, which is applied to electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve the problems of information transmission rate limitation, limited anti-reconnaissance ability, and decreased ability of the system to resist different frequency interference, so as to reduce the number of tracked and The probability of interference, the effect of good resistance to partial frequency band interference, and good resistance to multi-tone interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
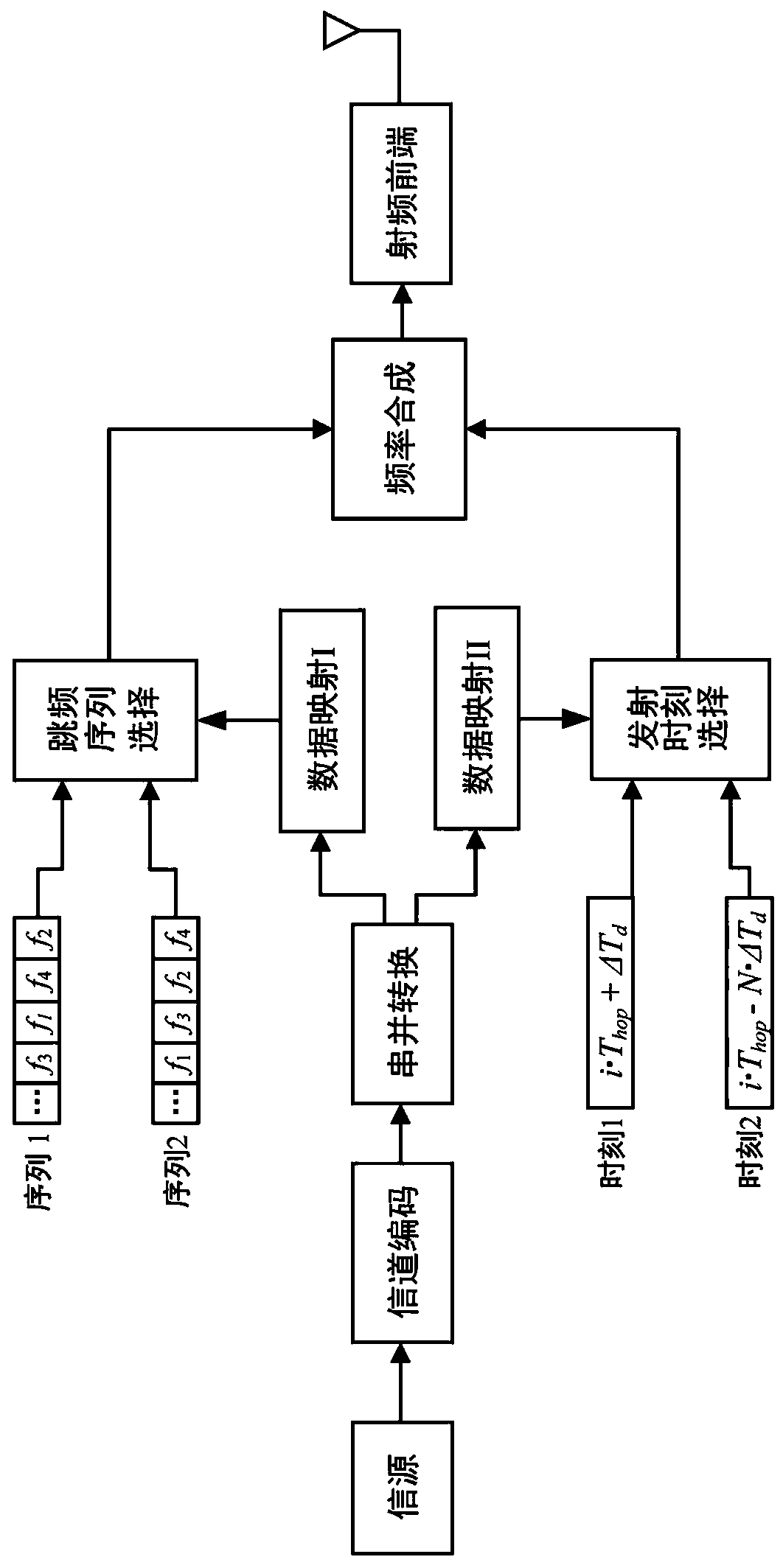
[0044] Embodiment 1 Signal transmission method
[0045] Such as figure 2 As shown, when sending a signal, the sender generates two frequency hopping sequences FS 0 and FS 1 . At time t, when the data sent to data map I after serial-to-parallel conversion is "0", the frequency hopping sequence FS is selected 0 The current frequency f (0,t) send a single frequency signal s 0 (t); when the data sent to the data mapping I after serial-to-parallel conversion is "1", select the frequency hopping sequence FS 1 The current frequency f (1,t) send a single frequency signal s 1 (t). And for each jump, there are two take-off times FT 0 and FT 1 . At time t, when the data sent to data map II after serial-to-parallel conversion is "0", select 0 =i·T hop Send the corresponding single-frequency signal; when the data sent to the data map II after serial-to-parallel conversion is "1", select FT at the take-off time 1 =i·T hop +T s Send the corresponding single frequency signal....
Embodiment 2
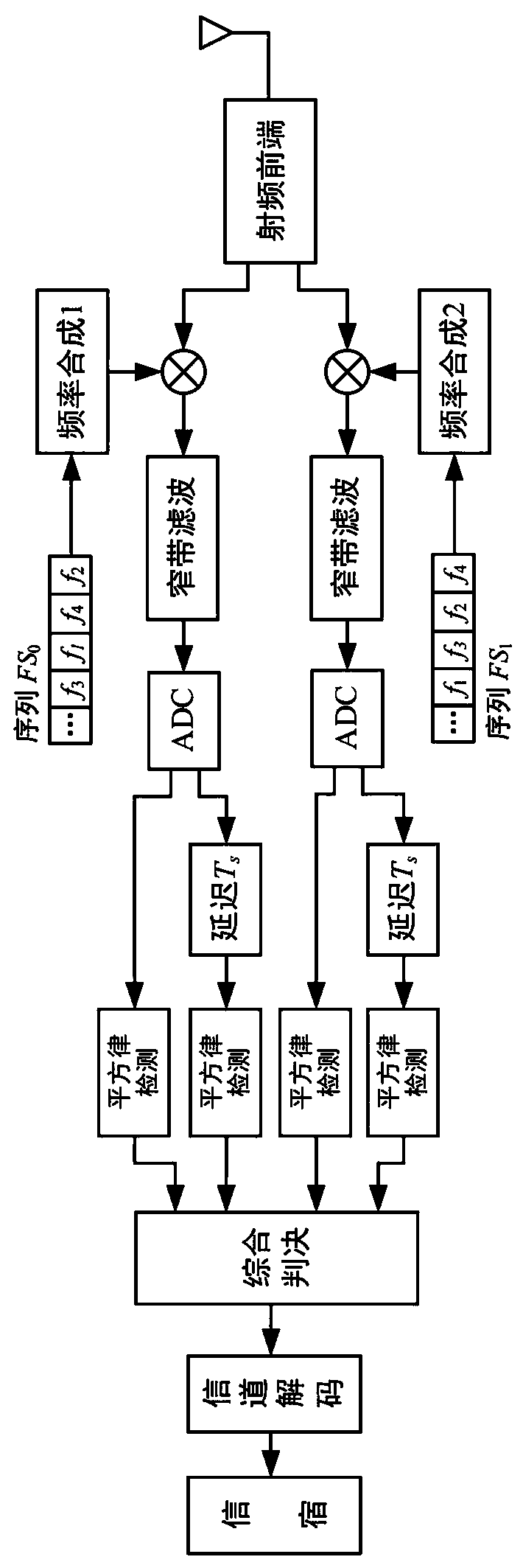
[0049] Embodiment 2 Receive signal method
[0050] When receiving a signal, a frequency hopping receiver receives in parallel on multiple channels, each of which is narrowband. Such as image 3 As shown, when M=2, there are 2 receiving channels in total. Each channel has an independent frequency synthesizer, controlled by its own frequency hopping sequence FS i . The reference local oscillator signal output by the frequency synthesizer of the i-th receiving channel is:
[0051]
[0052] In formula (1), Reference local oscillator signal frequency for the i-th receiving channel; is the estimated value of the received signal phase; is the delay T for the received signal d The estimated value of ; k is the time sequence number of the frequency hopping point.
[0053] Assuming that the processing of the frequency hopping receiver on the received signal is linear (generalized), the interference signal and the useful signal can be analyzed separately with the superposit...
Embodiment 3
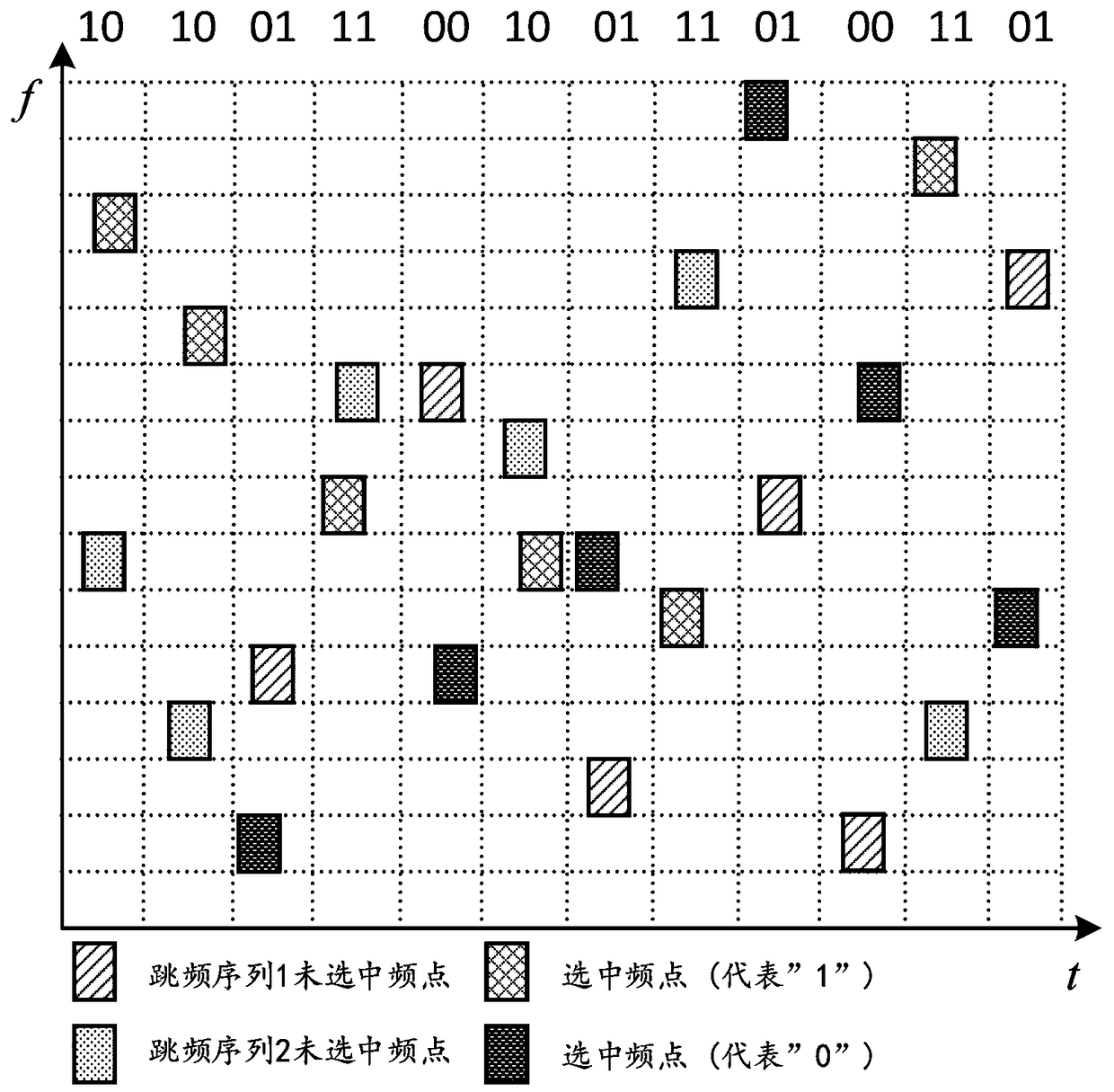
[0065] The reading of embodiment 3 result
[0066] The result is as Figure 4 shown by Figure 4 It can be seen that when using frequency hopping sequences for information modulation, multiple frequency hopping sequences work together to map the bit symbols to be transmitted into the serial numbers of frequency hopping sequences, and use the difference Random jumping achieves its hiding under tracking interference.
[0067] When using the hopping time for information modulation, divide the time available for frequency point jumping into multiple time slots within a frequency hopping cycle, and map the bit symbols to be transmitted to the sequence number of the current frequency point starting time slot, and the frequency point resides The time remains unchanged, and the difference in the take-off time is used to represent the information.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com