Frequency acquisition method and device of single chip microcomputer
A collection method and single-chip microcomputer technology, applied in the Internet field, can solve problems such as inaccurate calculations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
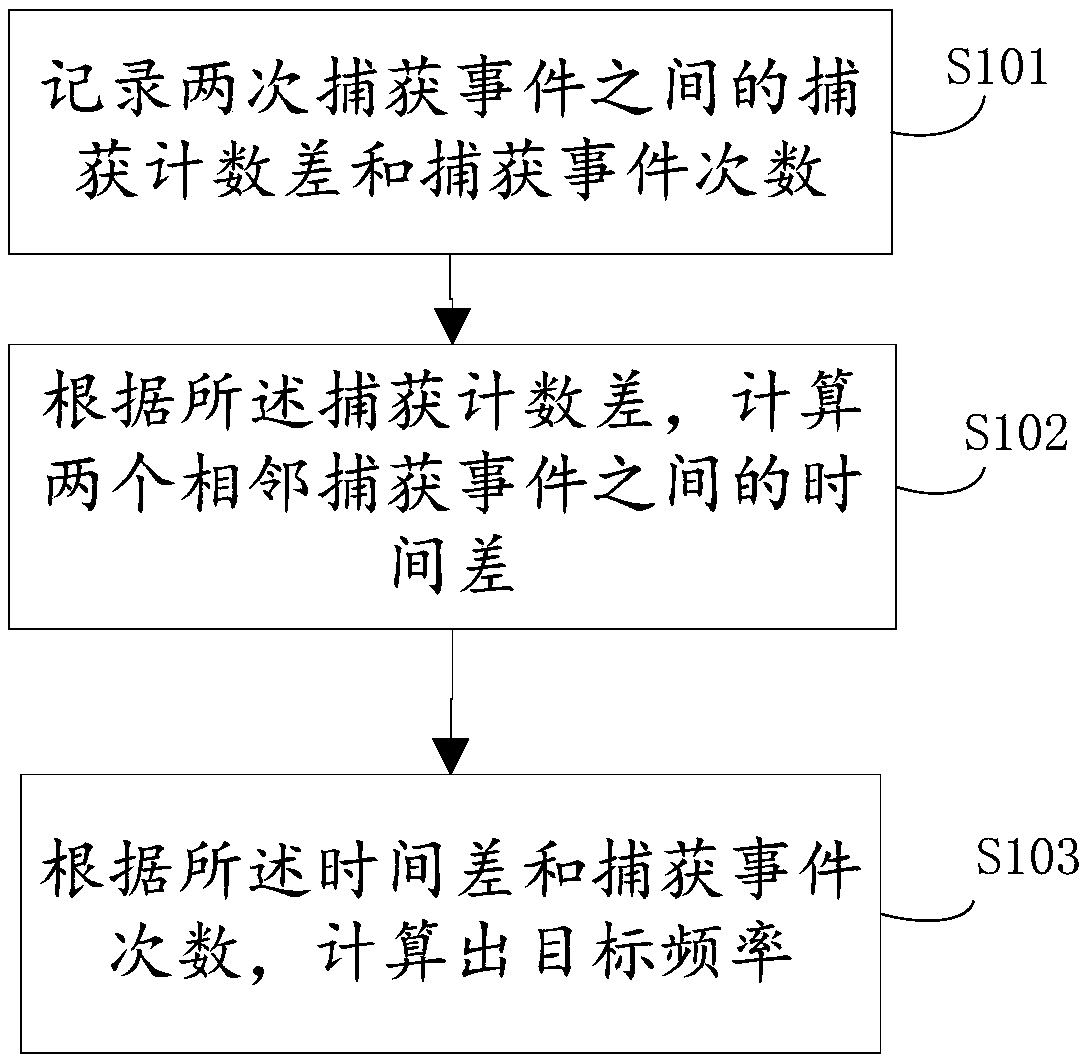
[0043] join figure 1 A flow chart of a single-chip microcomputer frequency acquisition method shown, the method specifically includes the following steps:
[0044] In the initial stage, first clear the timer flag and counting status.
[0045] S101. Record the capture count difference and the number of capture events between two capture events;
[0046] The number of capture events refers to how many times the microcontroller captures events between two recorded capture events.
[0047] S102. Calculate the time difference between two adjacent capture events according to the capture count difference;
[0048] S103. Calculate the target frequency according to the time difference and the number of capture events.
[0049] An embodiment of the present invention provides a single-chip frequency acquisition method, including: recording the capture count difference between two capture events and the number of capture events; according to the capture count difference, calculating th...
Embodiment 2
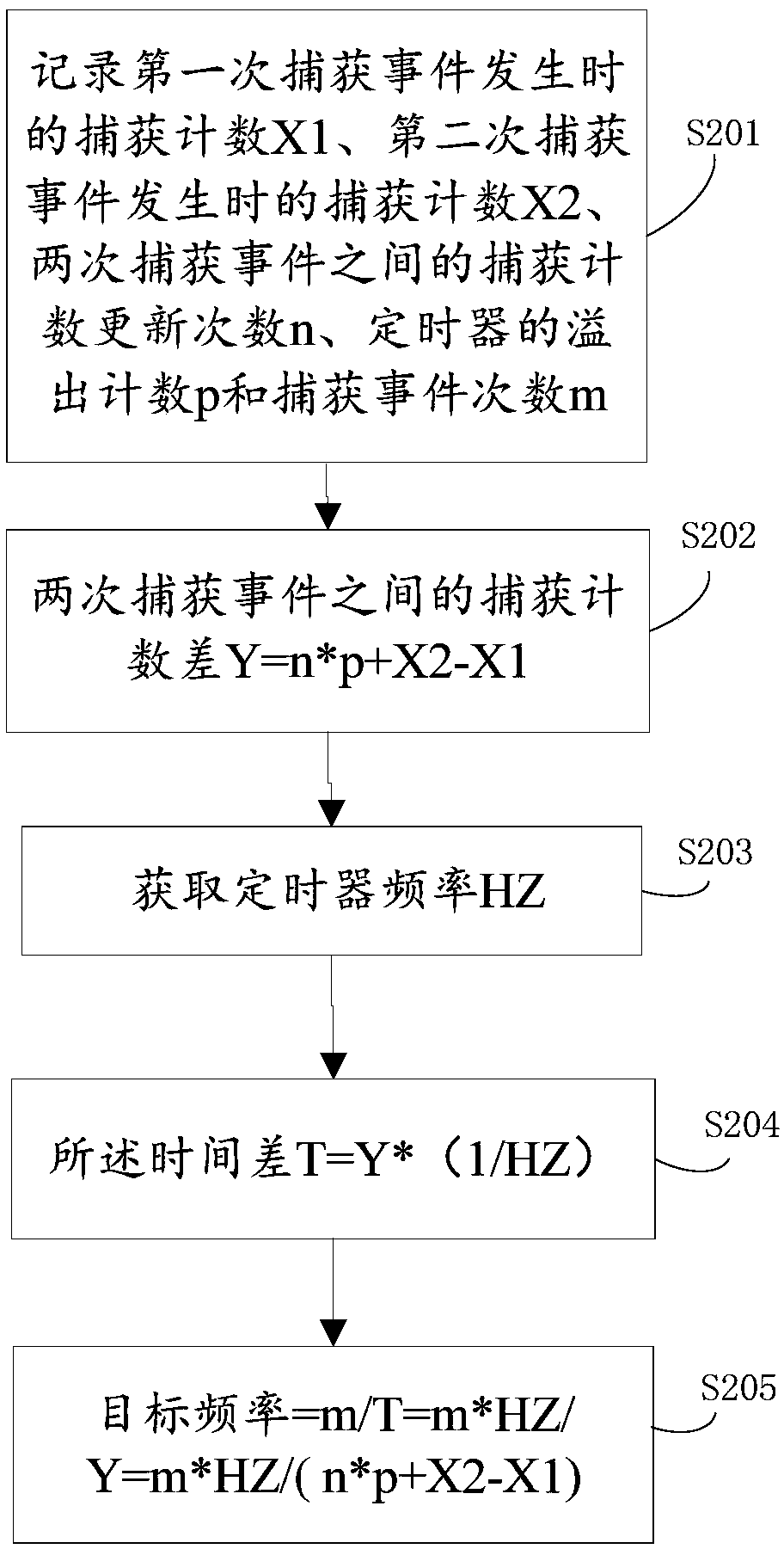
[0051] join figure 2 The flow chart of a kind of single-chip microcomputer frequency collection shown, this method is realized on the basis of the single-chip microcomputer frequency collection provided in embodiment one, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0052] S201. Record the capture count X1 when the first capture event occurs, the capture count X2 when the second capture event occurs, the capture count update times n between two capture events, the overflow count p of the timer, and the number of capture events m;
[0053] Wherein, the capture count is that the single chip microcomputer adds one to the original count every time q within the preset time length k, and the initial count is 0. When the preset duration k ends, the capture count is reset to 0, so that the capture count is updated once, and the capture count update times is 1. Every time the capture count is reset to 0, the number of capture count updates is incremented by 1 to the original value....
Embodiment 3
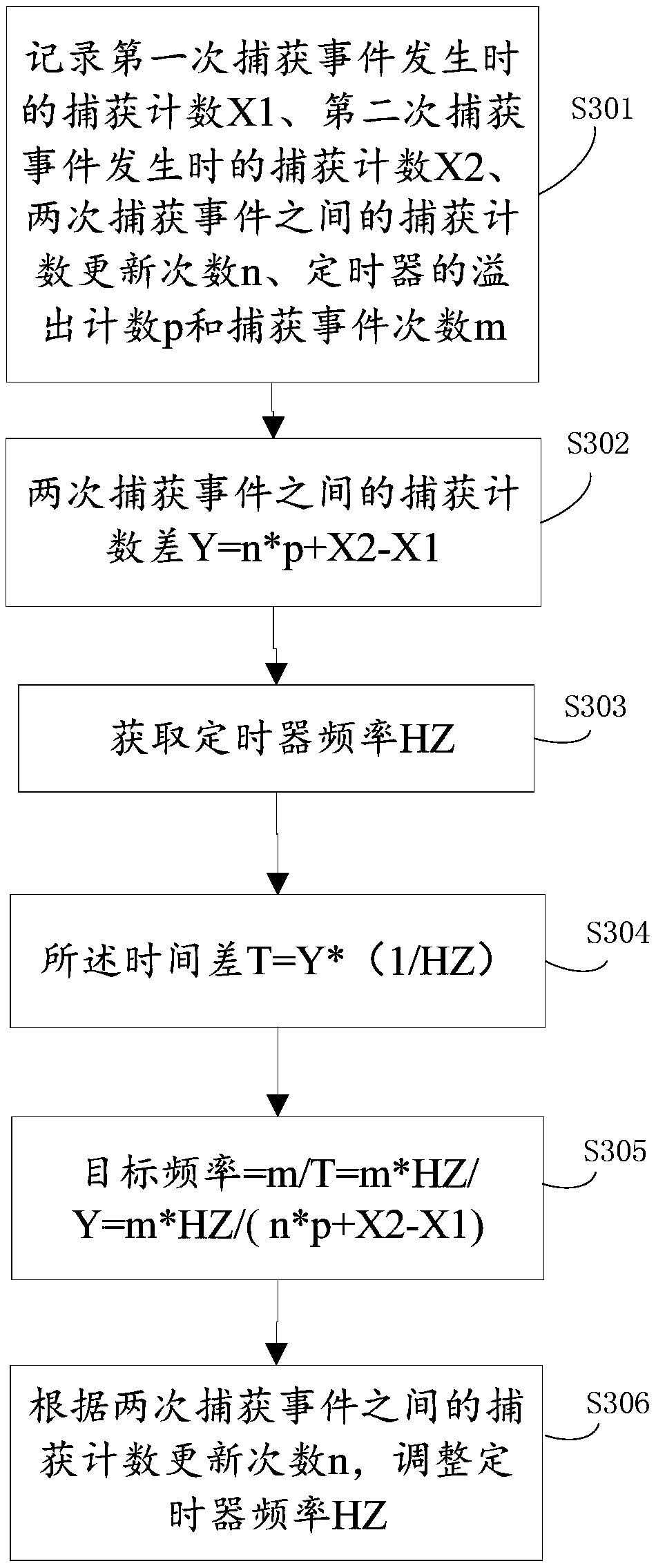
[0060] join image 3 A flow chart of the frequency acquisition of a single-chip microcomputer shown, the method is applied to specifically include the following steps:
[0061] S301. Record the capture count X1 when the first capture event occurs, the capture count X2 when the second capture event occurs, the capture count update times n between two capture events, the overflow count p of the timer, and the number of capture events m;
[0062] S302. Capture count difference Y=n*p+X2-X1 between two capture events.
[0063] S303. Obtain the timer frequency HZ;
[0064] S304. The time difference T=Y*(1 / HZ).
[0065] S305. Target frequency=m / T=m*HZ / Y=m*HZ / (n*p+X2-X1).
[0066] S306. Adjust the timer frequency HZ according to the capture count update times n between two capture events.
[0067] Among them, when n>2, it means that the frequency is high, and the timer frequency HZ should be reduced;
[0068] When n=0, it means that the frequency is low, and the timer frequency HZ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com