Non-local Haar transform image denoising method
A non-local, image technology, applied in the field of image denoising, to achieve the effect of improving image denoising ability, easy hardware implementation, and reducing computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
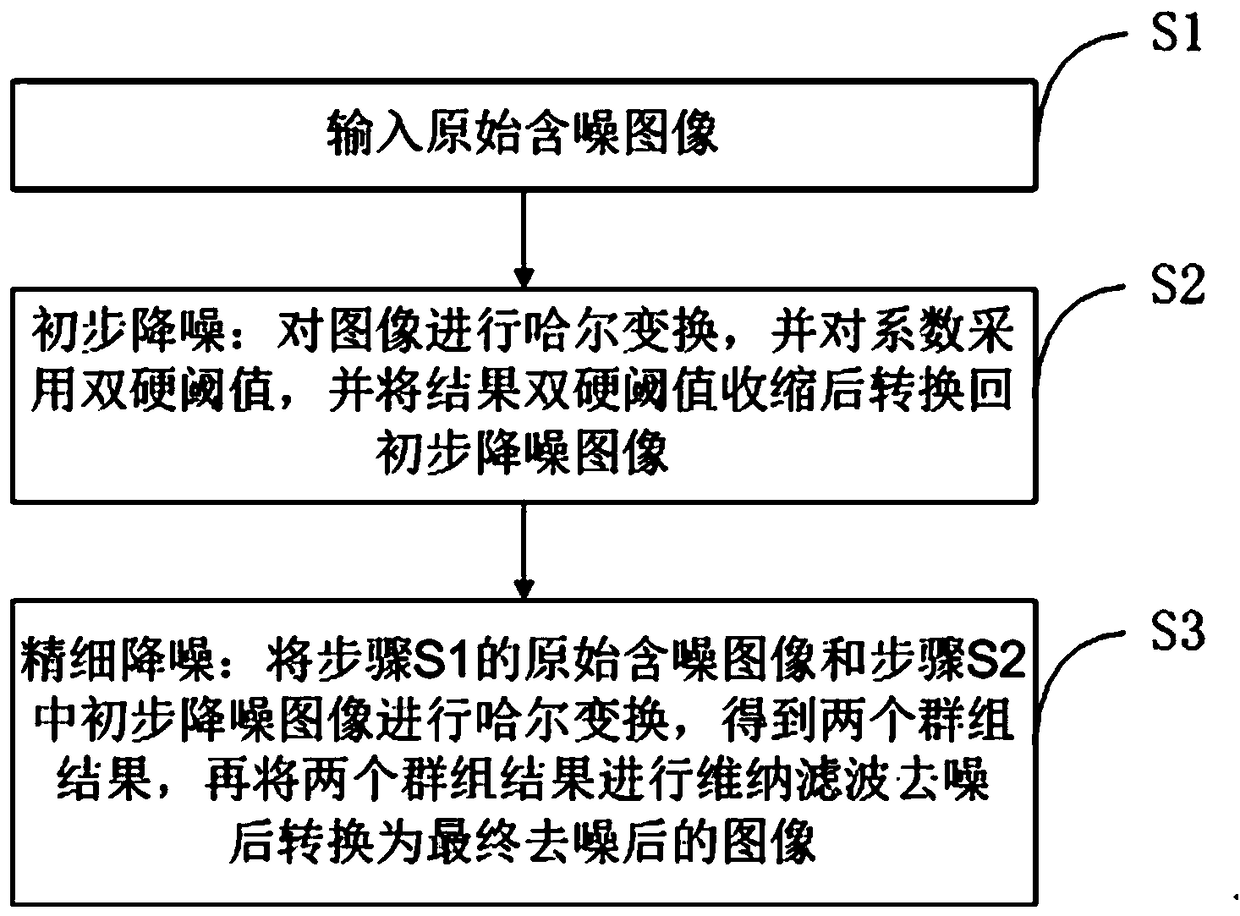
[0043] refer to figure 1 As shown, a non-local Haar transform image denoising method includes the following steps:
[0044] S1. Perform block matching on the input original noisy image and row matching after column scanning;
[0045] S2. Preliminary noise reduction: perform Haar transform on the image row matching result, and shrink the transformation coefficient by using the double hard threshold of the coefficient hard threshold and the structure hard threshold, perform the inverse Haar transform on the result, and then aggregate the image blocks to obtain a preliminary Noise-reduced image;
[0046] S3. Fine noise reduction: Synchronously perform block matching and line matching on the original noisy image in step S1 and the preliminary noise reduction image in step S2, perform Haar transform to obtain two sets of transformation coefficients, and then perform Wiener on the two sets of transformation coefficients Filtering and denoising, perform inverse Haar transform on th...
Embodiment 2
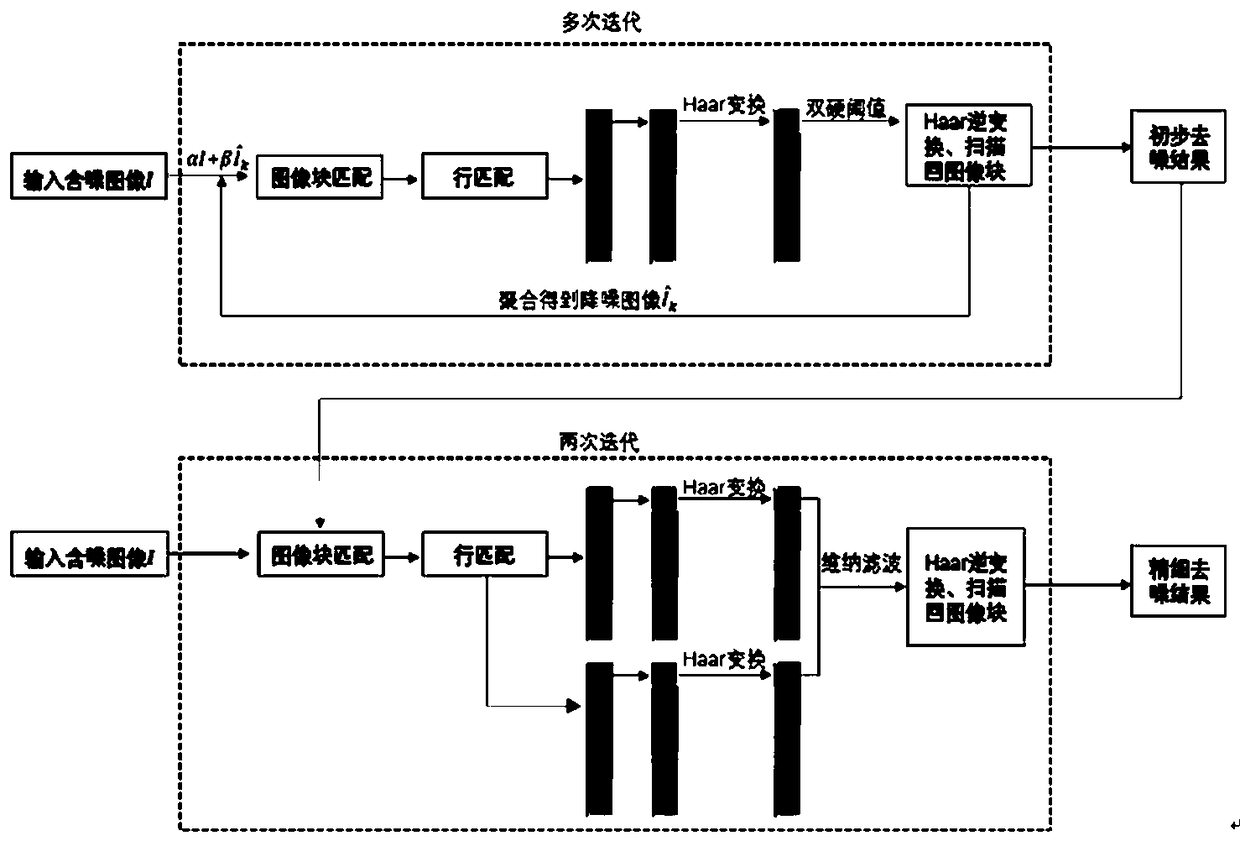
[0060] refer to figure 2 As shown, the image denoising method of this embodiment is generally divided into two stages, wherein the first stage is a preliminary denoising stage, and the second stage is a fine denoising stage.
[0061] Phase 1: Preliminary denoising
[0062] The first step: image block matching and line matching, corresponding to step S21 in the first embodiment,
[0063] First perform block matching of the original noisy image, extract an image block with a size of N1×N1 as a reference block according to a specified step size N_step, and then perform block matching in a neighborhood of size NS×NS centered on the reference block Match to obtain similar image blocks with a number of N2, and perform column scanning and splicing of all matched image blocks into a matrix M with a size of (N1×N1)×N2, and use each row as a reference row on M to calculate with all other rows Euclidean distance D, the minimum distance N3 row group to obtain the maximum degree of clus...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com