Devices for optical cooling of objects
A device, technology of objects, applied in the field of devices for optical cooling of objects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
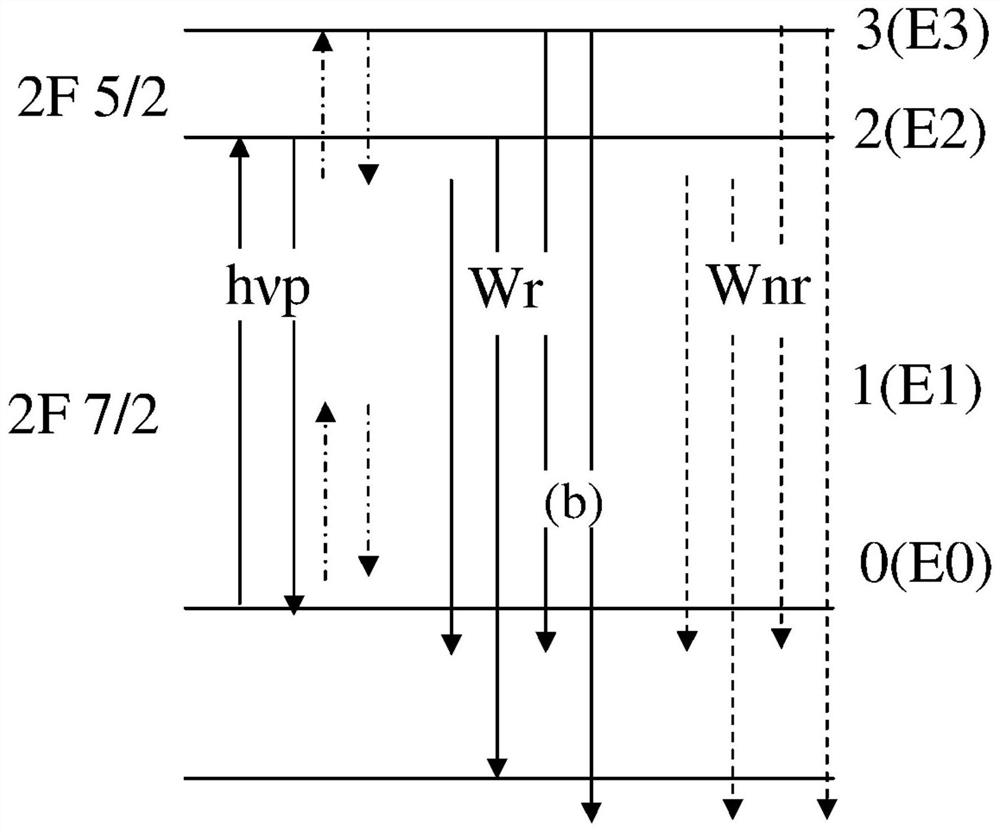
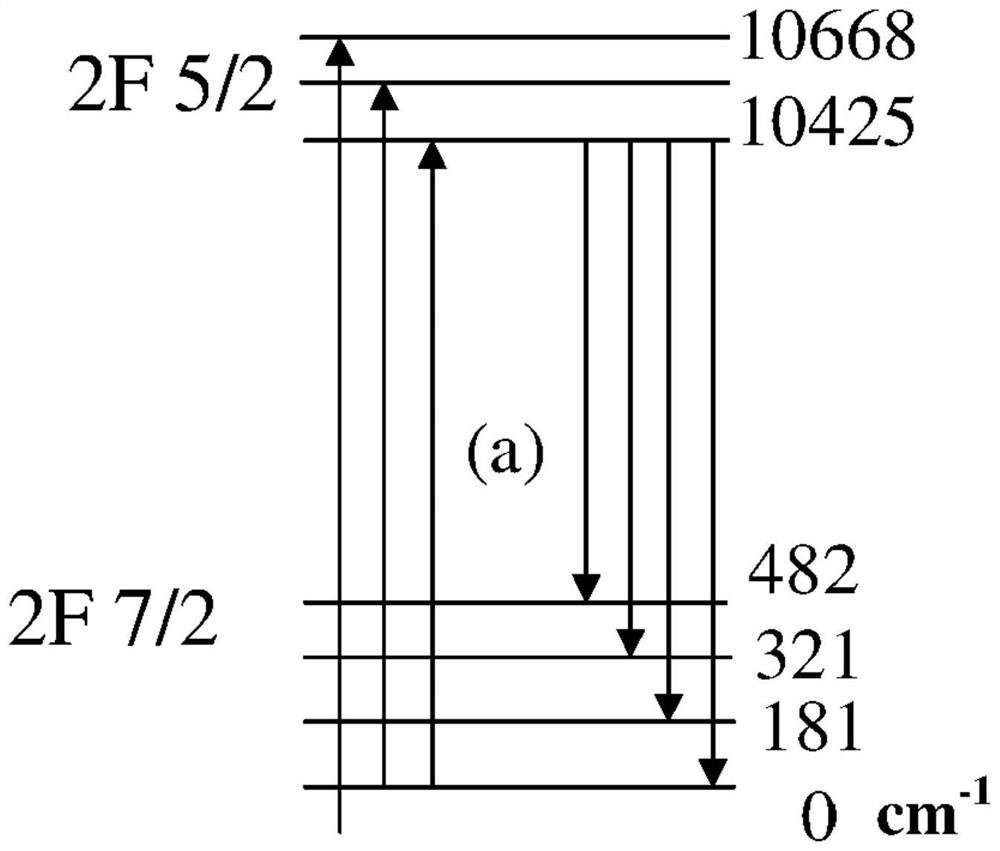
[0106] As mentioned above, Fig. 1(a) (reproduced from Nemova G., Laser Cooling of Solids, page 4, Figure 1(a) to Figure 1(b) ) shows a 4-level model for optical cooling of RE-doped glasses such as Yb 3+ : ZBLANP. Although the figure originally deals with laser cooling, it is equally relevant for broadband radiation. Specific calculations for the Level 4 model are shown in Fig. 1(b) (units are cm -1 ).
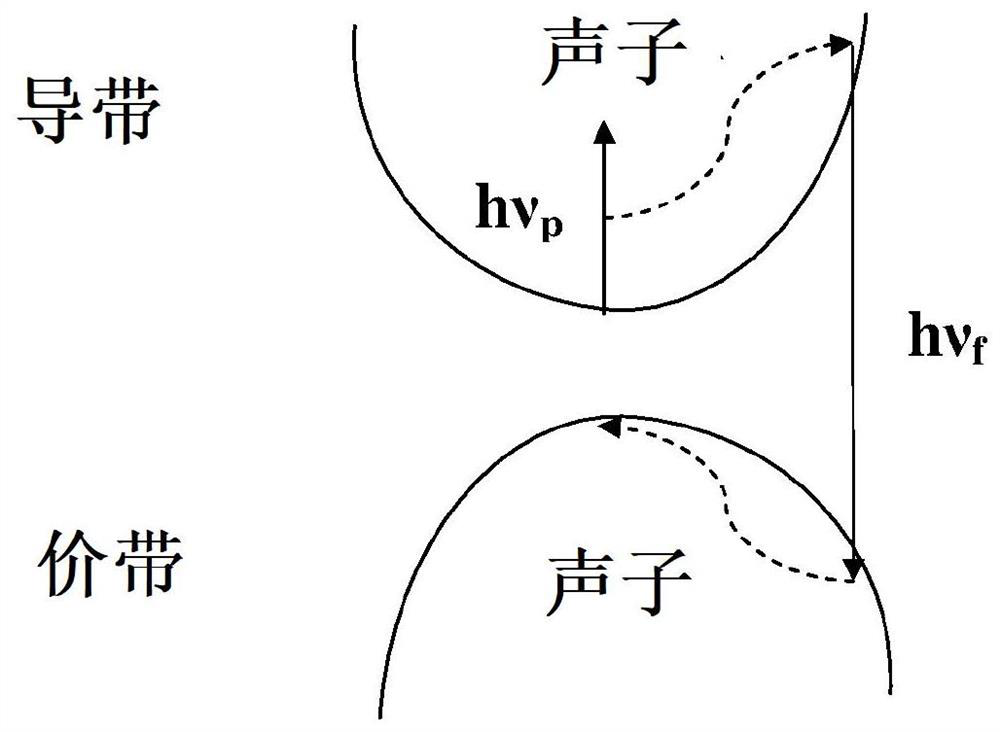
[0107] Optical cooling in semiconductors in figure 2 is schematically illustrated in , and has been discussed earlier in this application. Upconverting excitation photons resulting from thermal equilibrium between adjacent excitation levels results in the emission of photons with higher energies than the absorbed photons. Thus, the optical cooling effect in semiconductor materials is achieved through phonon absorption and conversion of thermal energy to electromagnetic energy.
[0108] image 3 (Reproduced from Jun Zhang, Dehui Li, Renjie Chen, Qihua Xiong, Laser Cooli...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com