Application of glycocholic acid in preparation of antitumor drugs
An anti-tumor drug, glycocholic acid technology, applied in the direction of anti-tumor drugs, drug combinations, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as short history
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] The in vitro antitumor experiment of embodiment 1 glycocholic acid
[0029] 1. Cell lines: 4T1 (mouse breast cancer cells), MCF-7 (human breast cancer cells), NIH: OVCAR-3 (human ovarian cancer cells), RL95-2 (human endometrial cancer cells), HCC827 ( Human non-small cell lung cancer cells) (all of the above were purchased from the Shanghai Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences)
[0030] 2. Culture medium: RPMI-1640 (Gibco product number 31800022); high glucose DMEM medium (Gibco product number 11965092)
[0031] 3. Method
[0032] 3.1 Collect the cells in the logarithmic growth phase, adjust the cell concentration to 5×10 with 1640 medium and DMEM medium respectively 4 cells / ml, add 100 μl of cell suspension into a 96-well plate.
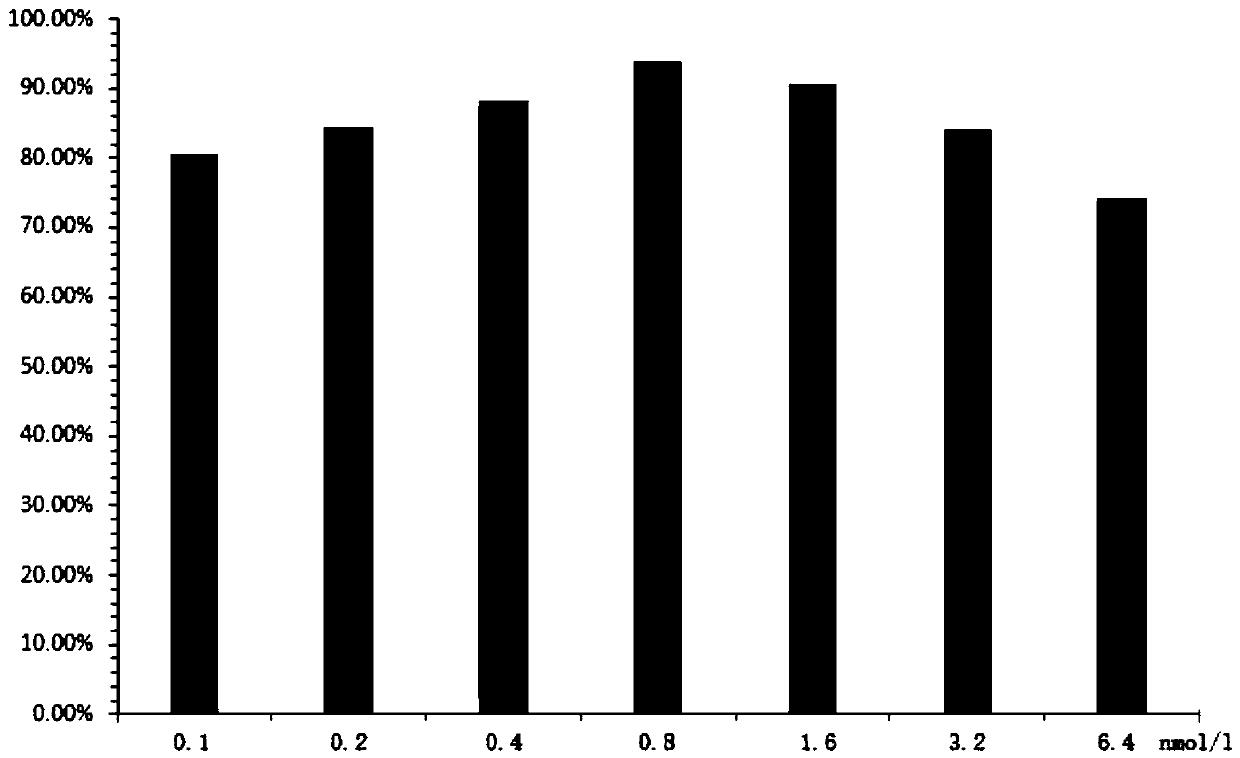
[0033] 3.2 5% CO 2 After culturing at 37°C for 24 hours, the 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells were added with a concentration gradient of (0.1nmol / L, 0.2nmol / L, 0.4nmol / L, 0.8nmol / L, 1.6nmol / L, 3.2nmol / L, 6.4nmol / L), MCF-7, NIH:OVCA...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2 animal model measures glycocholic acid tumor inhibition rate
[0038] 1. Materials: 10-week-old female BABL / c mice were purchased from the SPF Experimental Animal Center of Dalian Medical University. 4T1 tumor cells were purchased from the Shanghai Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[0039] 2. Method:
[0040] 2.1 Modeling: Collect 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells in the logarithmic growth phase, adjust the cell concentration to 2×10 with PBS 6 / ml. Inject 0.1 ml of the cell suspension into the right underarm of the mouse with a sterile syringe.
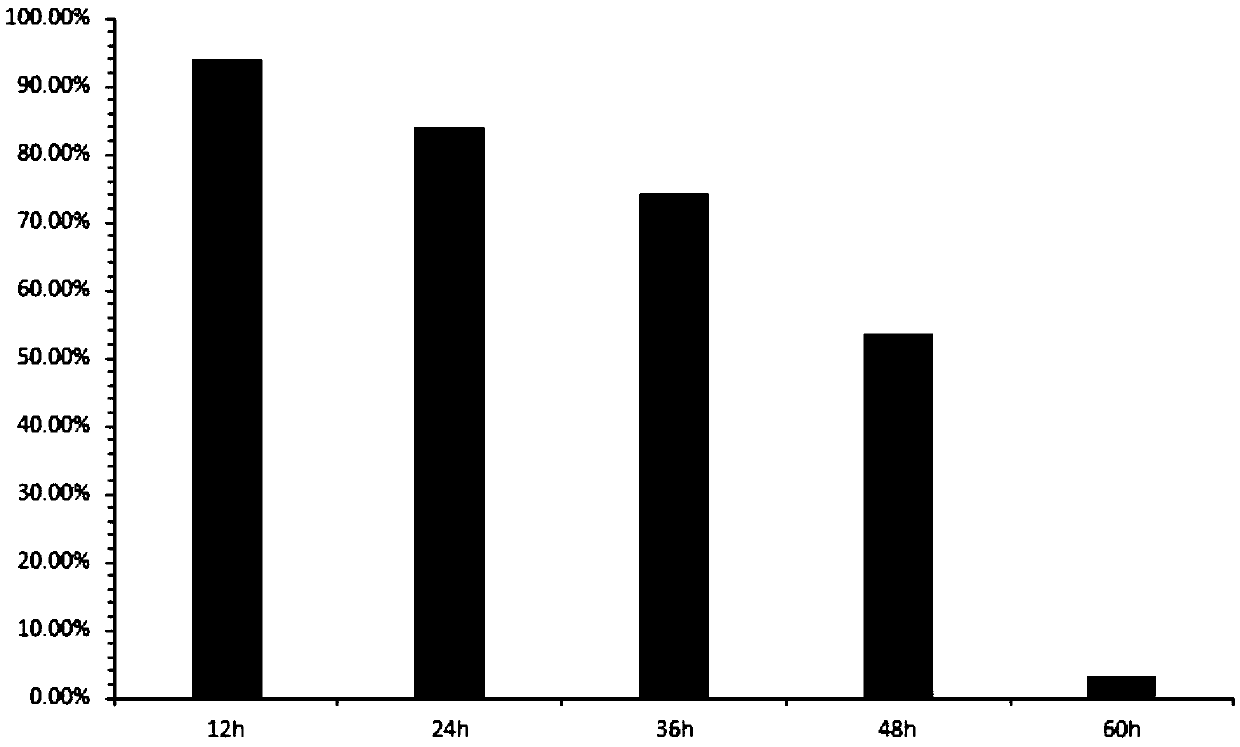
[0041] 2.2 Administration: Glycocholic acid 15 mg / kg (twice / day) was administered on the second day after modeling, 0.2 mL each time, for two consecutive weeks. On the evening of the last administration, the mice were fasted, and the mice were killed by neck dislocation on the 15th day. The axillary tumor tissues of the mice were aseptically removed, weighed and pressed Calculate the tumor inhibitio...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Real-time PCR Determination of Glycocholic Acid-specific Target RNA Expression in Tumor Cells
[0044] 1. Materials: 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells were purchased from the Shanghai Cell Bank of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
[0045] 2. Methods: RNA was extracted from 4T1 cells after glycocholic acid intervention, and Real-time PCR was performed after reverse transcription to determine the changes in the expression of glycocholic acid-specific target RNA.
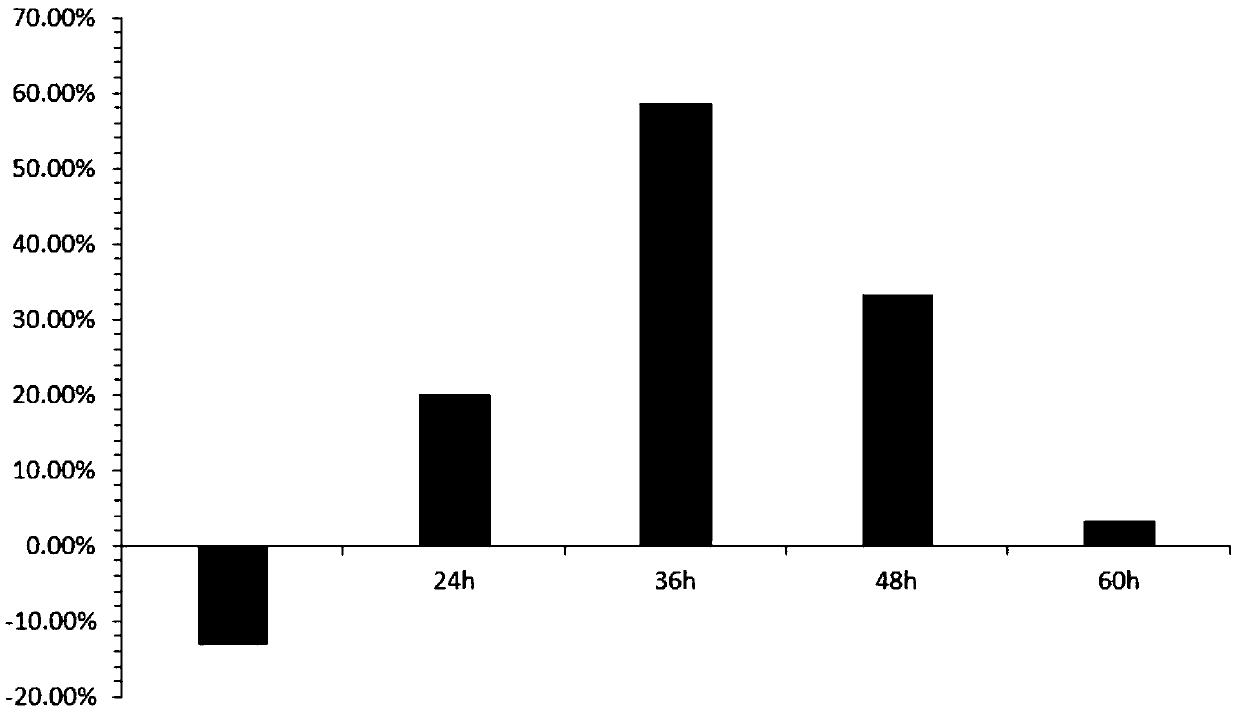
[0046] 3. Results: After the intervention of glycocholic acid, the expression of related RNA increased by 1.5 times, see Figure 5 , Image 6 . The results of the intervention of glycocholic acid on tumor cells were confirmed from the RNA level, and the mechanism of glycocholic acid inhibiting the growth of tumor cells was revealed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com