Preparation method of zinc antimony bismuthate self-assembled nanorods with self-supporting structure and its products and applications
A self-supporting structure, zinc bismuth acid technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc. for materials and surface science, can solve the problem of antimony nanoparticles being difficult to combine together to form a Schottky heterojunction, preparation Problems such as complex process and large-scale preparation limitations, to achieve good photocatalytic decomposition performance of dyes, simple synthesis method, and easy control of the preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
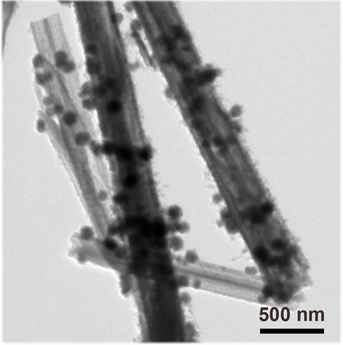
[0021] A antimony / zinc bismuthate self-assembled nanorod with a self-supporting structure, using sodium bismuthate, zinc acetate and antimony trichloride as raw materials, is synthesized by high-temperature calcination, and is prepared according to the following steps:
[0022] Accurately weigh 12.01g sodium bismuthate and 0.22 g zinc acetate (the molar ratio of sodium bismuthate to zinc acetate is 38:1), mix well, then place the mixed powder of sodium bismuthate and zinc acetate in the corundum tube reaction vessel High temperature zone; at the same time, 3.67 g of antimony trichloride was accurately weighed and placed in the low temperature zone of the corundum tube reaction vessel. The mass of antimony trichloride accounted for 30% of the mass of sodium bismuthate and zinc acetate.
[0023] Then seal the corundum tube and heat the high temperature zone to a temperature of 1400 o C. Heating the low temperature zone to 200 o C, keep warm for 20 h, the flow rate of argon is 2...
Embodiment 2
[0026] A self-assembled antimony / zinc bismuthate nanorod of self-supporting structure, the same as the steps in the examples, is prepared as follows:
[0027] Accurately weigh 6.32g sodium bismuthate and 0.22 g zinc acetate (the molar ratio of sodium bismuthate to zinc acetate is 20:1), mix well, then place the mixed powder of sodium bismuthate and zinc acetate in the corundum tube reaction vessel High temperature zone; at the same time, accurately weigh 1.96 g of antimony trichloride and place it in the low temperature zone of the corundum tube reaction vessel. The mass of antimony trichloride accounts for 30% of the mass of sodium bismuthate and zinc acetate. Then seal the corundum tube and heat the high temperature zone to a temperature of 1200 o C. Heating the low temperature zone to 200 o C, keep warm for 24h, the flow rate of argon is 200 cm 3 / min, finally obtained on the low-temperature surface at the end of the corundum tube is a nanorod with a diameter of 100-500nm...
Embodiment 3
[0029]A self-assembled antimony / zinc bismuthate nanorod of self-supporting structure, the same as the steps in the examples, is prepared as follows:
[0030] Accurately weigh 6.32g sodium bismuthate and 0.22 g zinc acetate (the molar ratio of sodium bismuthate to zinc acetate is 20:1), mix well, then place the mixed powder of sodium bismuthate and zinc acetate in the corundum tube reaction vessel High-temperature zone; at the same time, accurately weigh 0.98 g of antimony trichloride and place it in the low-temperature zone of the corundum tube reaction vessel. The mass of antimony trichloride accounts for 30% of the mass of sodium bismuthate and zinc acetate.
[0031] Then seal the corundum tube and heat the high temperature zone to a temperature of 1300 o C. Heating the low temperature zone to 200 o C, keep warm for 22 h, the flow rate of argon is 200 cm 3 / min, the nanorods with a diameter of 100-500 nm and a length of 3-8 μm were finally obtained on the low-temperature s...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com