Radioactive source positioning and intensity estimation method in mobile robot's nuclear environment
A mobile robot and radioactive source technology, applied in radiation intensity measurement and other directions, can solve the problems of locating radioactive sources and mobile robot source seeking, achieving high-precision and high-efficiency positioning, accelerating prediction convergence speed, and strong robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
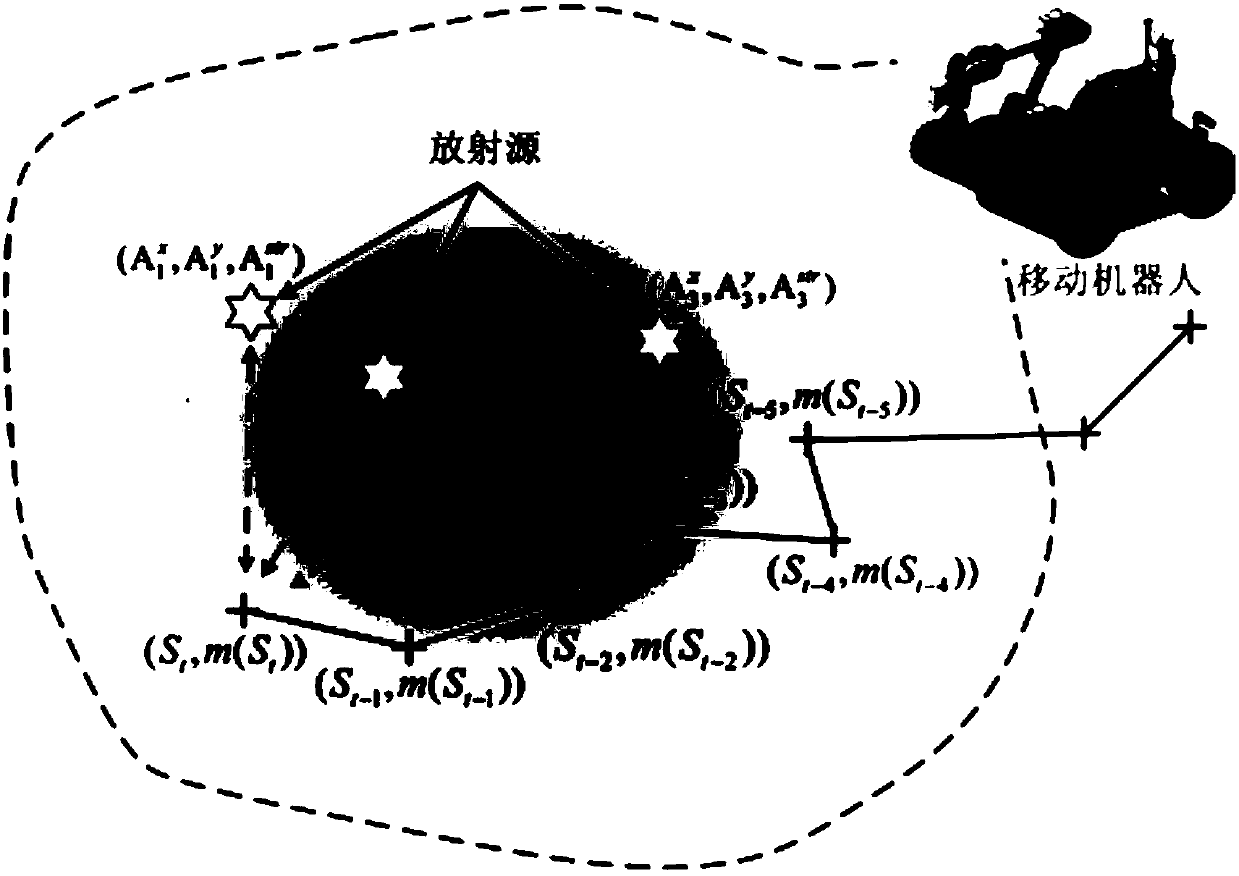
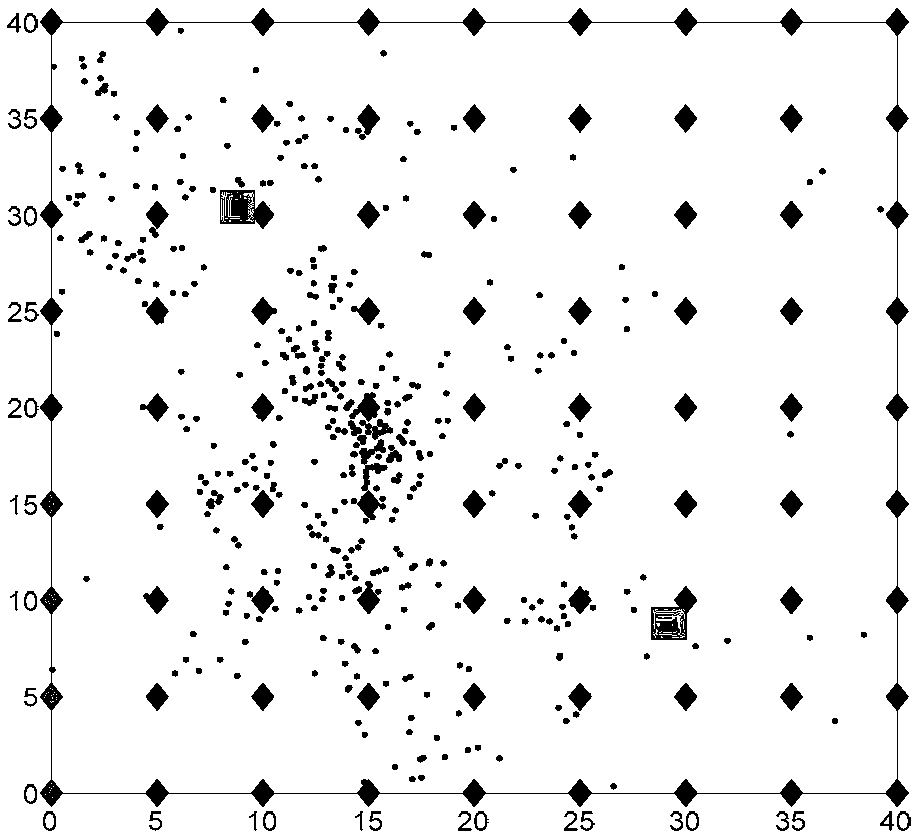
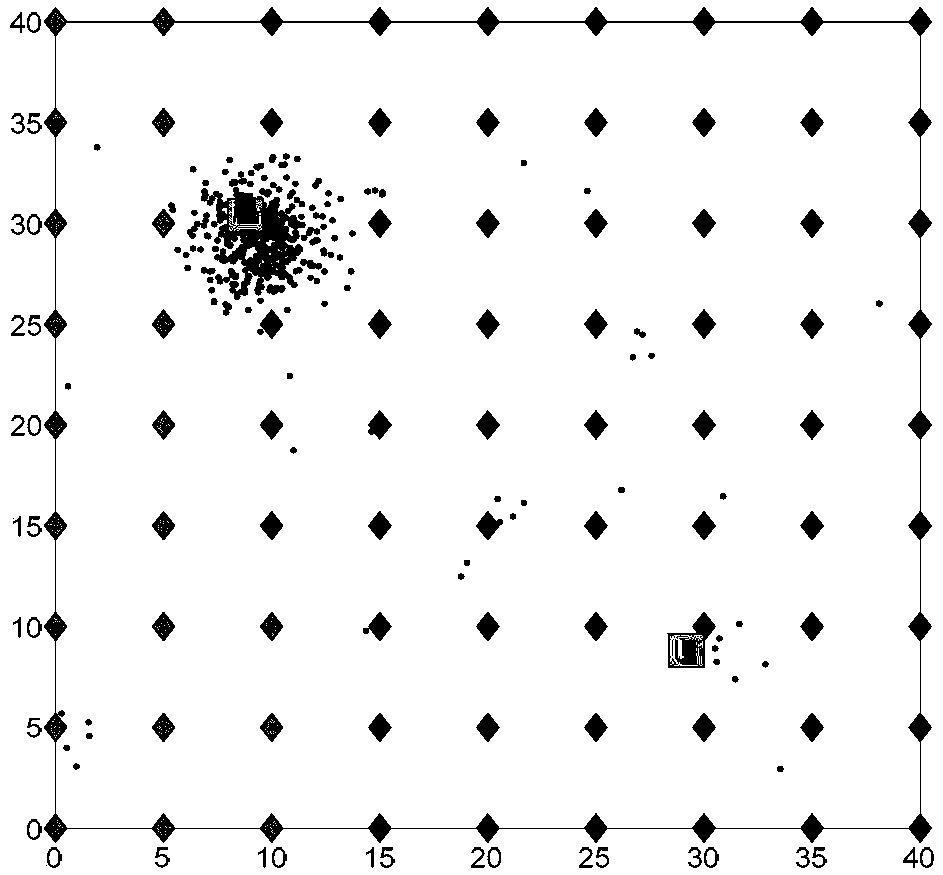
[0032] Specific implementation mode one: the following combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the radioactive source positioning and intensity estimation method under a kind of mobile robot nuclear environment described in this embodiment, the specific steps of this method are:
[0033] Step 1. Under the particle filter estimation framework, the active particles collected by the sensor at the current measurement point are marked by setting the active range of the observation value, and the effective particle set of the sensor at the current measurement point is obtained;
[0034] Step 2, calculating the observation weight of each effective particle in the effective particle set;
[0035] Step 3, correcting the observation weight of the effective particle; obtaining the corrected weight of each effective particle;
[0036] Step 4, resampling the effective particles after correcting the weight;
[0037] Step 5. Randomly sow the resampled particles of the effective part...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0042] Specific embodiment two: The present embodiment will be described below in conjunction with FIG. 2. This embodiment will further explain the radioactive source positioning and intensity estimation method in the nuclear environment of a mobile robot described in the first embodiment. In this embodiment, step 1 The specific method to obtain the effective particle set in is:
[0043] The effective particle set P' is calculated by formula (1):
[0044]
[0045] In the formula, the distance between the effective particle set P' and the sensor measurement point is d i The set of all active state particles within the range, and there is no obstacle between the active state particles and the measurement point, S i is the position information of the i-th measurement point of the sensor, i is a positive integer, Represents the position information of the jth predicted particle, p j represents the three-dimensional information of the jth predicted particle, Represents obs...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0046] Specific embodiment three: This embodiment further explains the radioactive source positioning and intensity estimation method in the nuclear environment of a mobile robot described in embodiment two. In this embodiment, in step two, calculate the The specific method of observing the weight is:
[0047] Calculate and obtain each particle p through the weight calculation formula (2) j The weight w(p j t );
[0048]
[0049] In the formula, Represents the use of particles for sensors Jointly predict state points with other clustered radioactive sources The radiation intensity information of the radiation source at the measurement point; the radiation sources of the other clusters are the radiation field and the removal state point A radioactive source other than the radioactive source in which it is located; The subscript k of is the particle The label of the cluster state point to which it belongs, m(S i ) indicates that the sensor is at the measuring p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com