A network characterization method based on cross-double-layer network random walk
A random walk, two-layer network technology, applied in data exchange networks, digital transmission systems, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to characterize adjacency and structural similarity at the same time, and not being able to handle non-connected networks well. achieve effective representation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
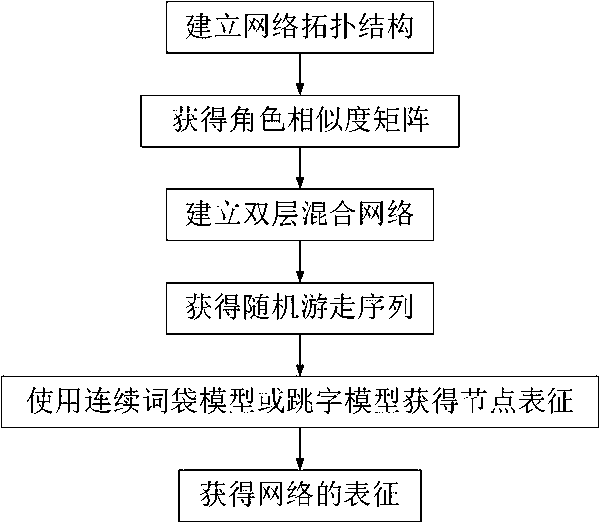
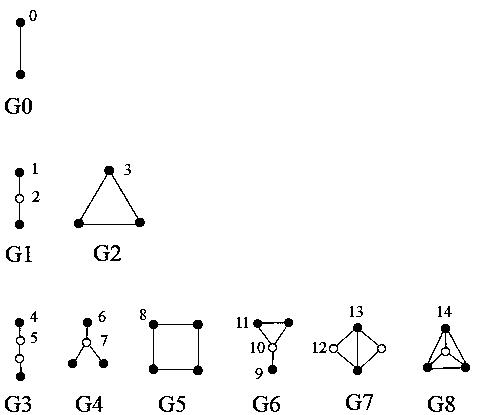
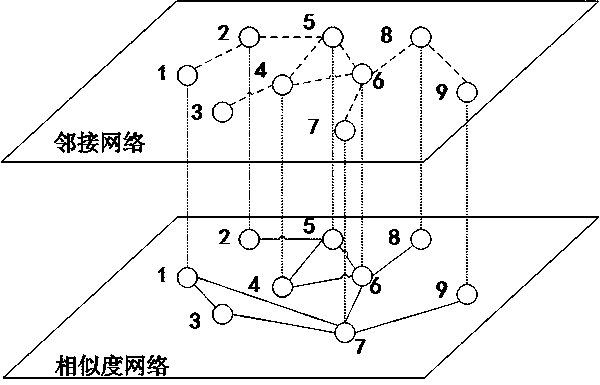
[0026] A network representation method based on random walks across two-layer networks, such as figure 1 As shown, it is a block diagram of a network characterization method in Embodiment 1. This embodiment includes the following steps: A) Establish a network topology structure according to the relationship between entities in the real system, and obtain the network adjacency matrix W={w ij}, i, j∈[1, n], n is the number of nodes in the network topology; B) Obtain the role sequence of the nodes in the induced subgraph whose size does not exceed a given value k, record it as a representation vector, and establish the relationship between nodes The role similarity matrix S={s ij}, i, j∈[1,n]; C) According to the one-to-one correspondence between the nodes in the network neighbor matrix W and the role similarity matrix, establish a two-layer hybrid network; D) start from each node in turn, and perform h times Random walk across the double-layer mixed network, a total of h groups...
Embodiment 2
[0049] In this embodiment, the word skipping model is used for the two-layer hybrid network obtained in step C of the embodiment, and node features are extracted to form a node representation, and then form a network representation. The skip-gram model realizes node representation. The process is to predict words that may co-occur with it by giving a central word and training it through a simple neural network with only one hidden layer. In this embodiment, a central node, which is the starting point of the random walk, is used to predict the probability of another node that may appear in its random walk sampling sequence. If the probability of two nodes appearing in the same random walk sampling sequence at the same time is higher, the role similarity of the two nodes is higher.
[0050] For any sampling sequence L i , given a central node i to generate a background node i k The conditional probability of can be obtained by performing a softmax operation on the vector inner...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com