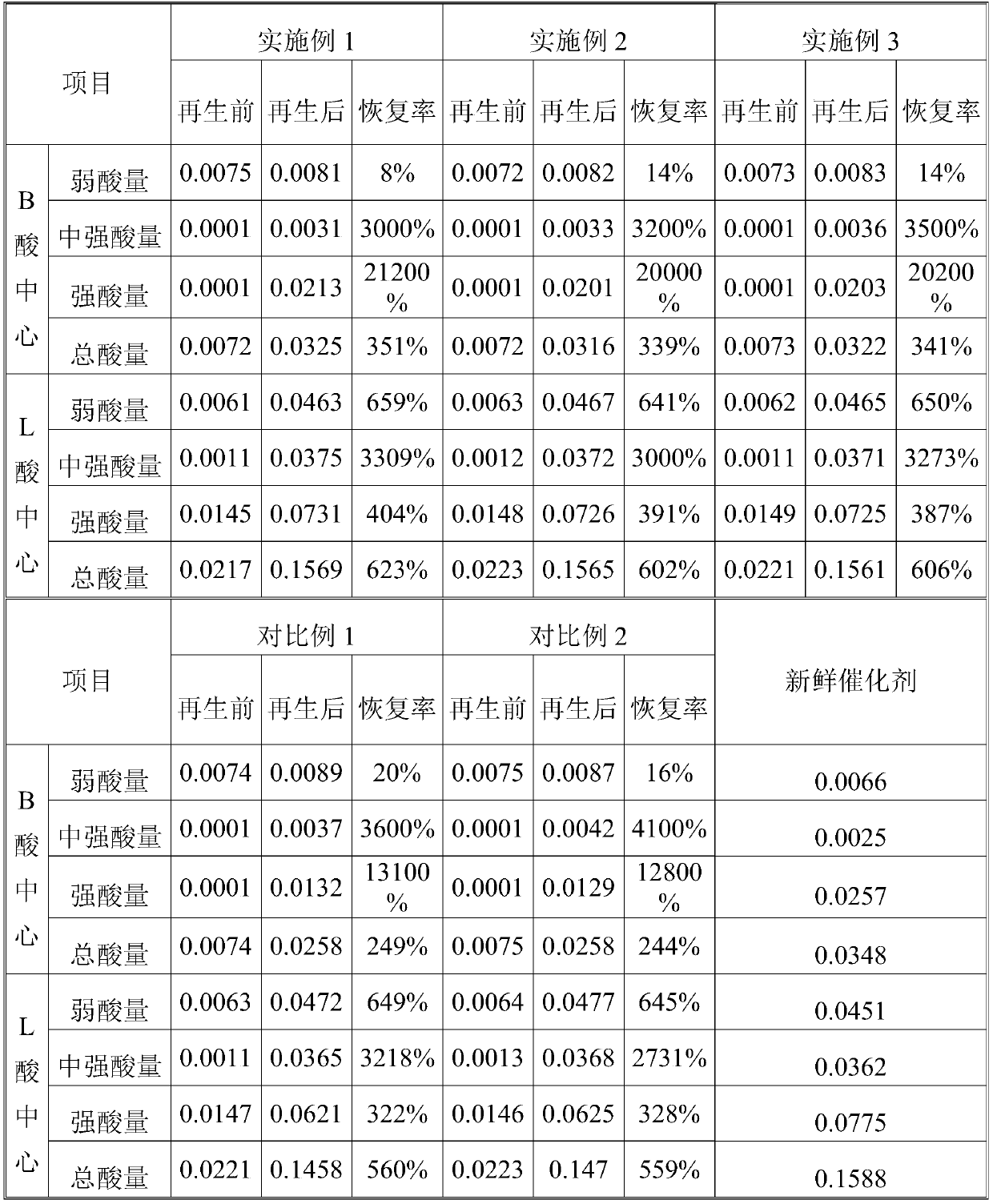
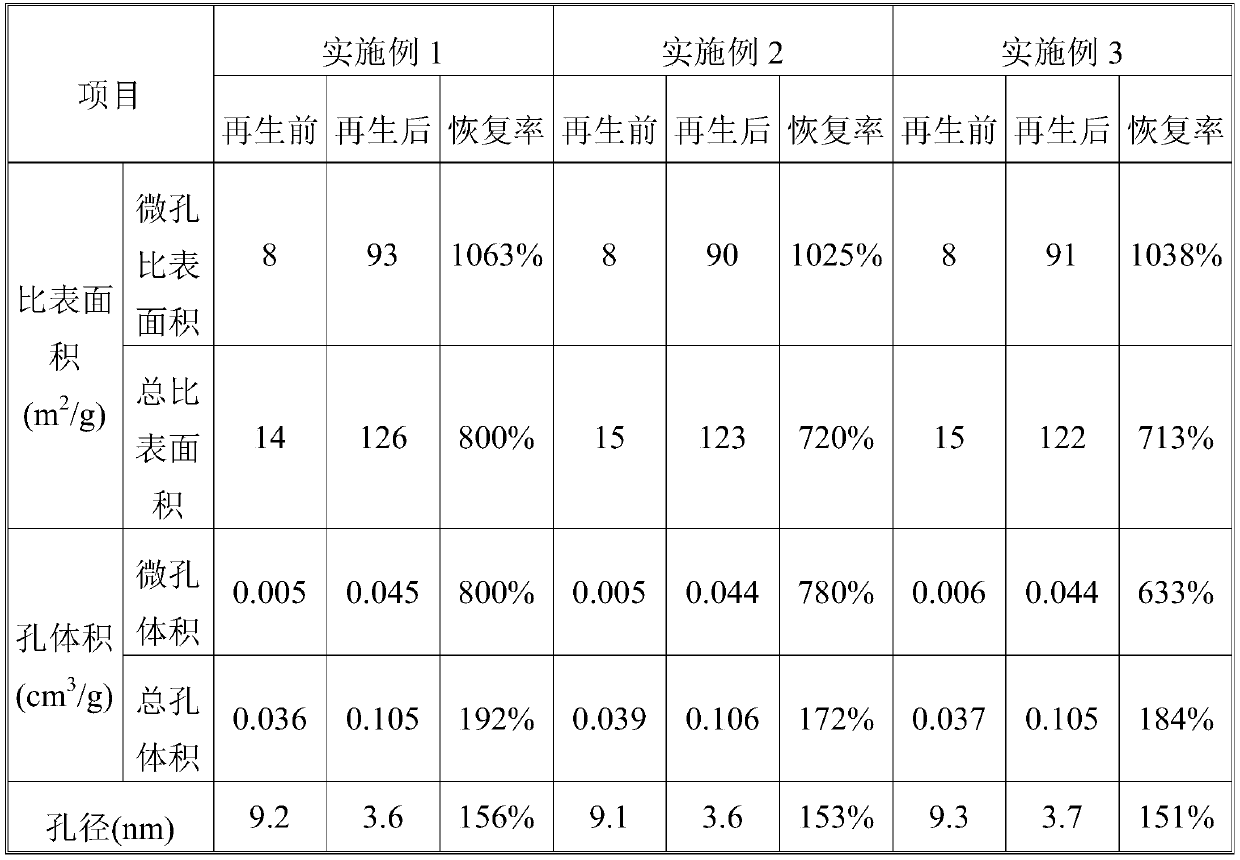
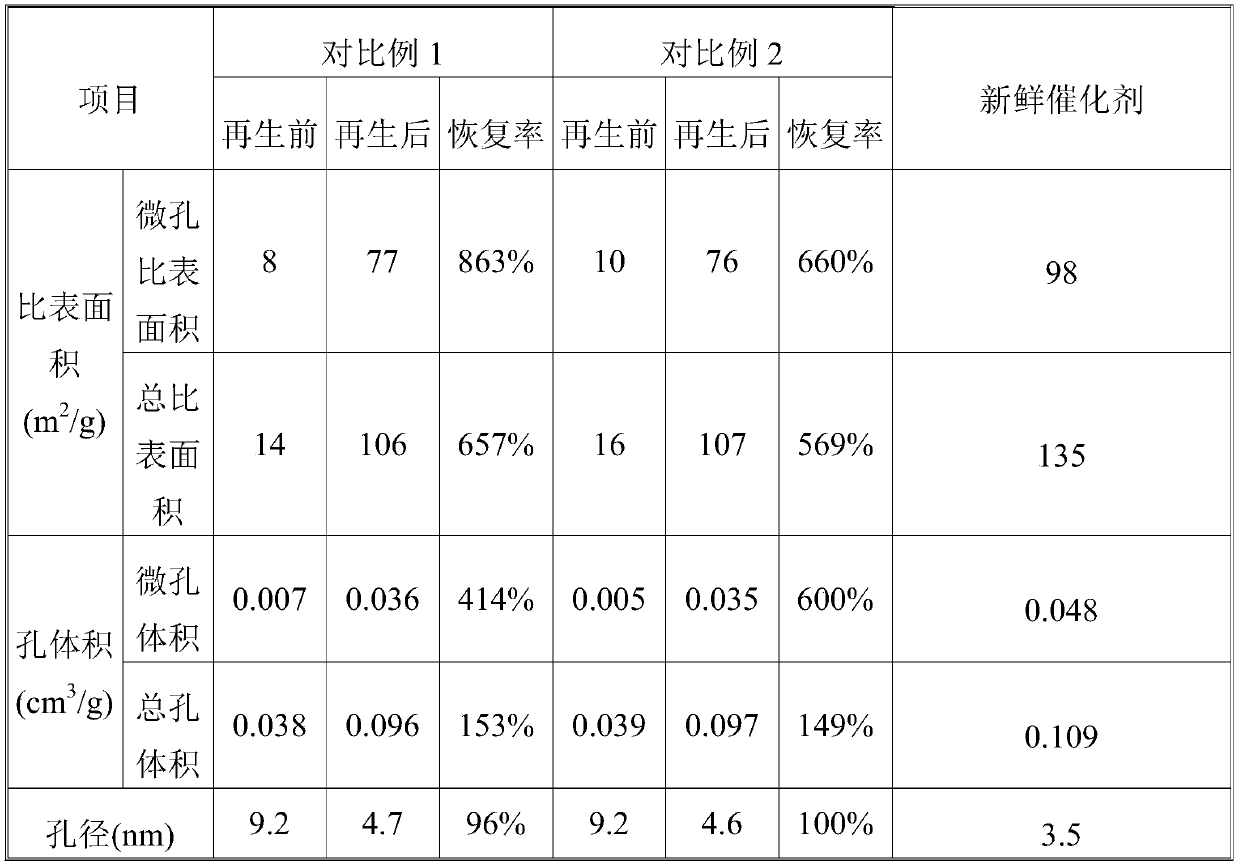
A kind of regeneration method of aromatization catalyst
A catalyst and aromatization technology, applied in catalyst regeneration/reactivation, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of easy carbon deposition, low recovery ability, catalyst deactivation, etc. The effect of carbon deposition in micropores and improving regeneration level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] A regeneration method for an aromatization catalyst, comprising the following steps:
[0018] (1) Switch the reactor: gradually reduce the feed load of the reactor to be regenerated to 30%, and at the same time slowly reduce the temperature in the reactor, and the cooling rate does not exceed 30°C / h; when the temperature in the reactor drops to 300°C, reduce Reactor feed load to 20%; when the temperature in the reactor drops below 250°C and the furnace temperature of the heating furnace is below 300°C, stop the feed to the reactor and stop heating the reactor; the reactor to be regenerated Switch to another reactor that has been warmed up to operating temperature and isolate the reactor to be regenerated.
[0019] (2) Nitrogen circulation heating with oil: Turn on the nitrogen circulation, and when the pressure and flow of nitrogen are stable, slowly raise the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated to 327°C at a heating rate of 14-16°C / h.
[0020] (3) Burning in ...
Embodiment 2
[0026] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the operations from step (2) to step (5) are:
[0027] (2) Nitrogen circulation heating with oil: Turn on the nitrogen circulation, and when the pressure and flow of nitrogen are stable, slowly raise the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated to 300°C at a rate of 10-12°C / h.
[0028] (3) Burning in the first stage: When it is observed that the combustible gas in the reactor to be regenerated is exhausted, a small amount of air is added to the circulating gas. When the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated is stabilized, the amount of air added continues to be The temperature of the layer is below 450°C; when the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated, CO 2 When the content does not change and there is no generated water, increase the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated to 480°C.
[0029] (4) Burning in the second stage: when the CO in the reactor to be regenerated 2 When the co...
Embodiment 3
[0032] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that the operations from step (2) to step (5) are:
[0033] (2) Nitrogen circulation heating with oil: Turn on the nitrogen circulation, and when the pressure and flow of nitrogen are stable, slowly raise the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated to 350°C at a rate of 18-20°C / h.
[0034] (3) Burning in the first stage: When it is observed that the combustible gas in the reactor to be regenerated is exhausted, a small amount of air is added to the circulating gas. When the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated is stabilized, the amount of air added continues to be The temperature of the layer is below 450°C; when the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated, CO 2 When the content does not change and there is no generated water, raise the temperature in the reactor to be regenerated to 525°C.
[0035] (4) Burning in the second stage: when the CO in the reactor to be regenerated 2 When the conte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com