Soaping method for fibers dyed by reactive dye
A reactive dye and soaping technology, applied in the field of fiber dyeing, can solve the problems of reducing fiber color fastness, increasing process cost, high energy consumption, etc., and achieving the effect of improving color fastness and improving stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Select the CF40 / 1 pure cotton yarn of the same yarn batch, arrange the following dye formula (Table 1) for conventional pre-treatment and dyeing. After dyeing, it is discharged from the vat and divided into two vats evenly. The post-treatment process and The post-treatment process of Example 1 of the present invention was tested and compared.
[0034] Table 1
[0035] Dye combination
Dye dosage OWF
Reactive Red 1
2.10%
Reactive Yellow 1
1.51%
Reactive Blue 1
3.25%
[0036] The post-processing process is as follows:
[0037] (1) The post-treatment process of comparative example 1: water washing (50℃×5min)→acid washing (50℃×5min)→soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent)→soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent )→soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (60℃×5min);
[0038] (2) The post-treatment process of Example 1 of the present invention: water washing (50°C×5min) → pickling (50°C×5min) → soaping (120...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Select the CF40 / 1 pure cotton yarn of the same yarn batch, arrange the following dye formula (Table 3) for conventional pretreatment and dyeing. After dyeing, it is discharged from the vat and divided into two vats evenly, using the post-treatment process of Comparative Example 2 and The post-treatment process of Example 2 of the present invention was tested and compared.
[0049] table 3
[0050] Dye combination
Dye dosage OWF
Reactive Red 2
1.10%
Reactive Yellow 2
1.51%
Reactive Blue 2
4.25%
[0051] The post-processing process is as follows:
[0052] (1) The post-treatment process of Comparative Example 2: water washing (50℃×5min)→acid washing (50℃×5min)→soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent)→soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent) )→soaping (98℃×10min+soaping agent)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (80℃×5min)→water washing (60℃×5min);
[0053] (2) The post-treatment process of Example 2 of the present invention: water washing (50℃×5min) → pickl...
Embodiment 3
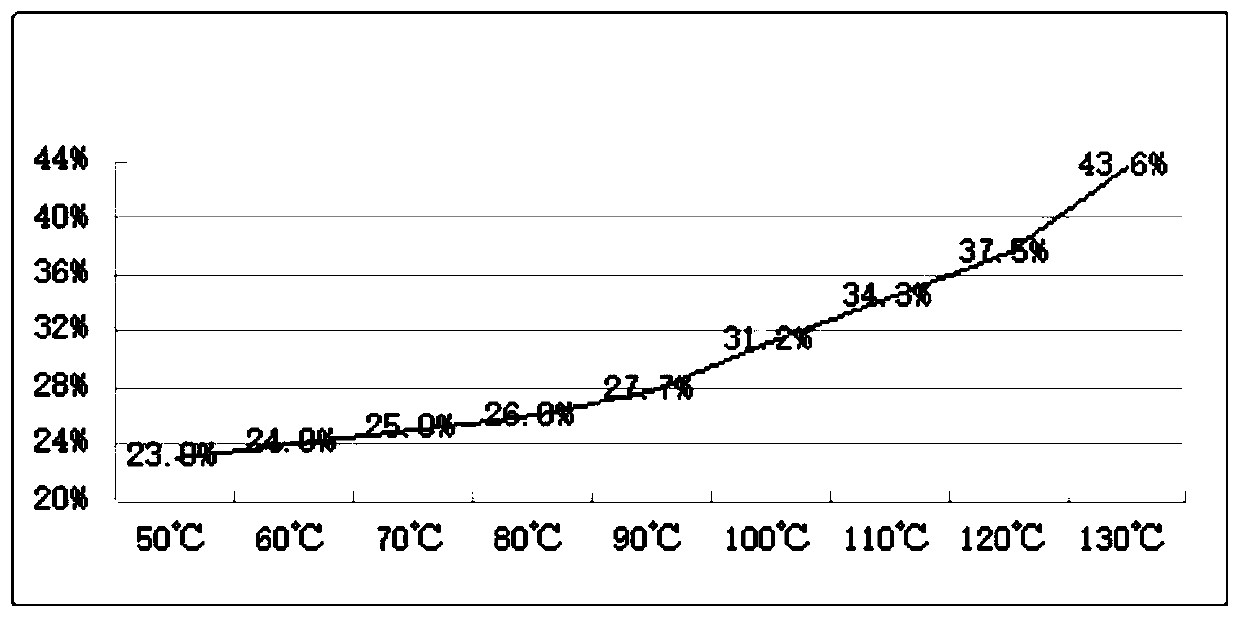
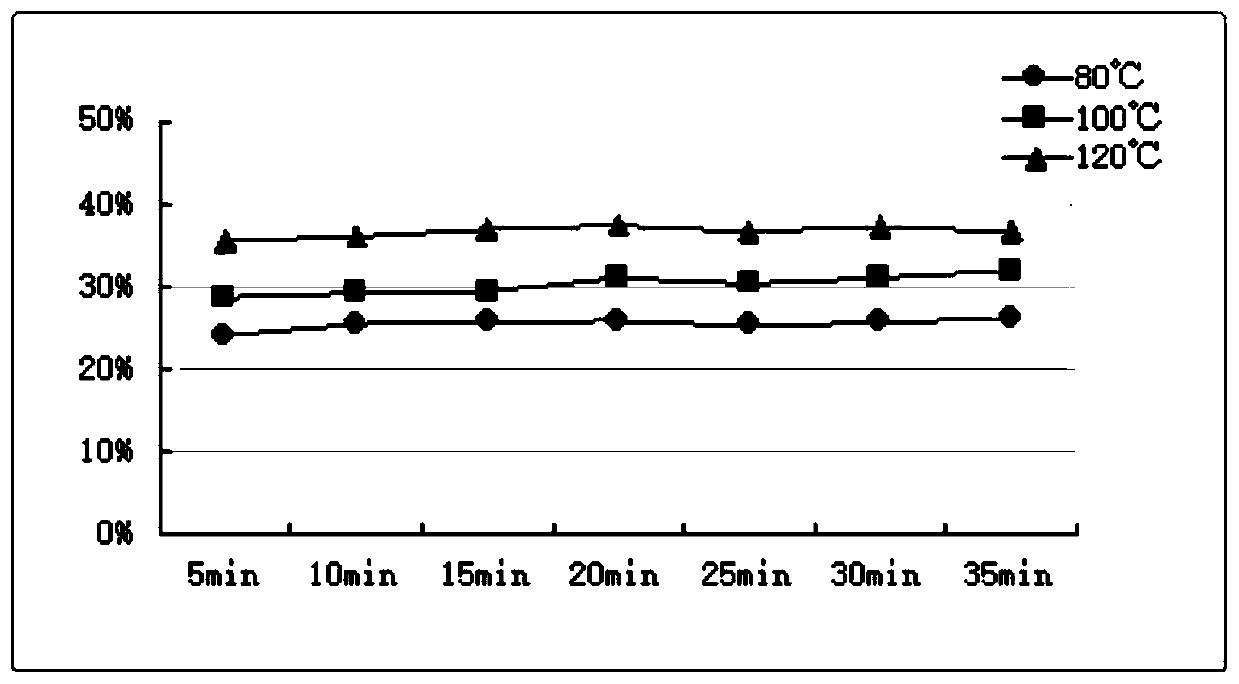
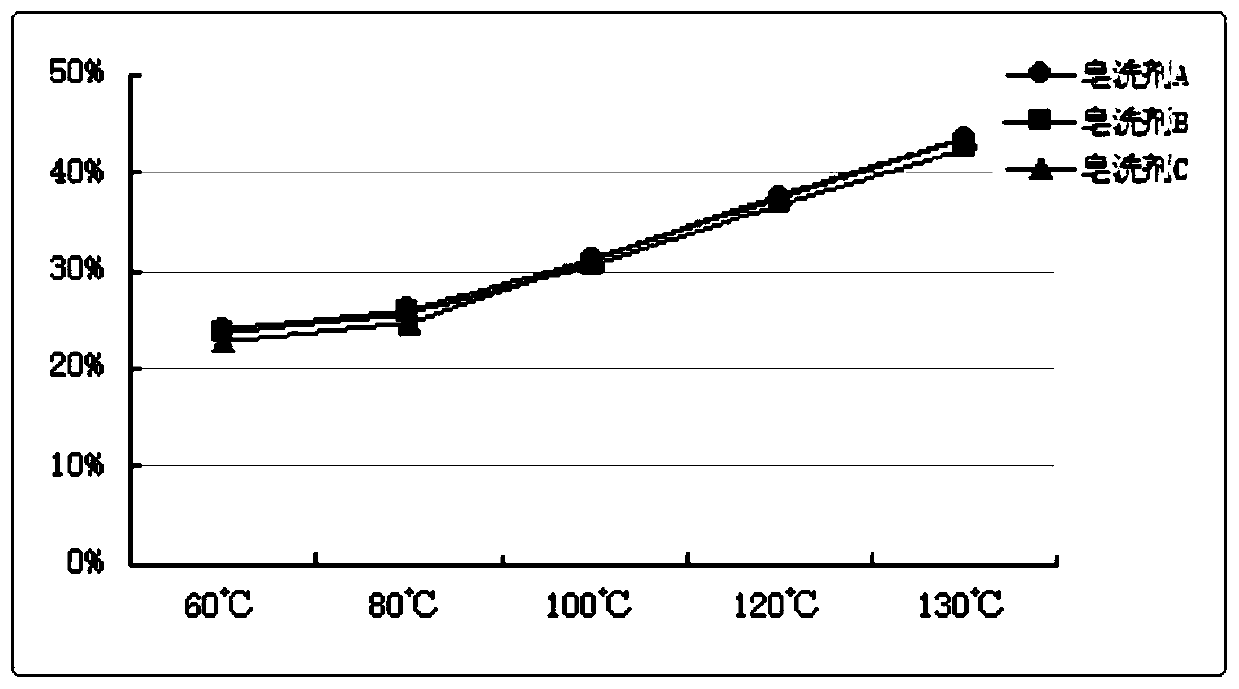
[0061] According to the same post-treatment process of Example 1, the effect of reactive dye hydrolysis dye removal under different soaping temperature, different soaping time or different soaping agent conditions and the effect of high soaping temperature on color fastness were studied. The results are as follows Figure 1-3 And shown in Table 5.
[0062] table 5
[0063]
[0064] by figure 1 It can be seen that with the increase of the soaping temperature, the washing removal rate gradually increases, and when the temperature rises above 110°C, the rising range greatly increases, and the washing removal rate between 110°C and 130°C is 34.3% to 43.6%. Compared with 100°C soaping, the floating color removal rate is increased by 10-40%, and the floating color removal rate is significantly improved.
[0065] by figure 2 It can be seen that with the increase of the soaping time, there is little difference in the washing removal rate, and the present invention can be reasonably controll...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com