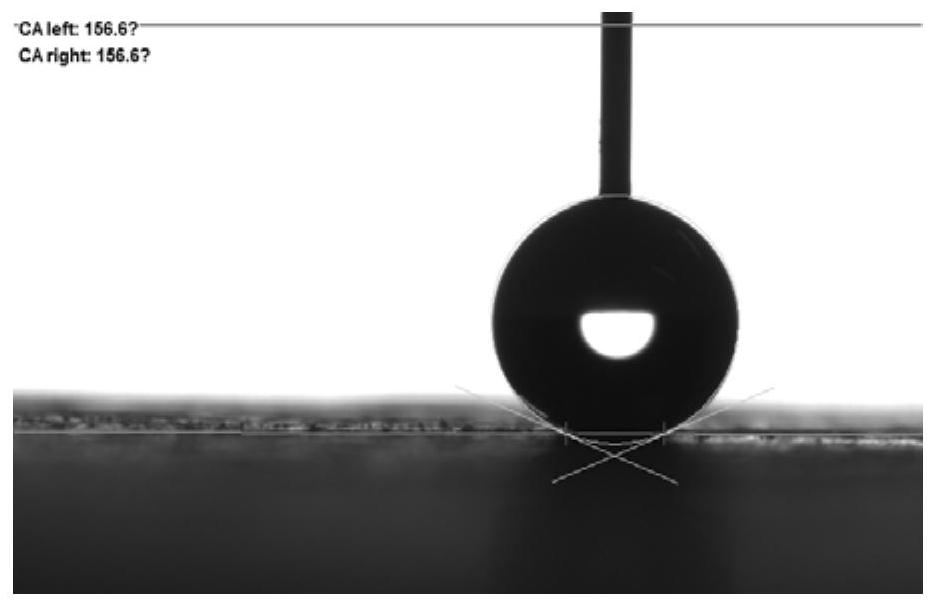
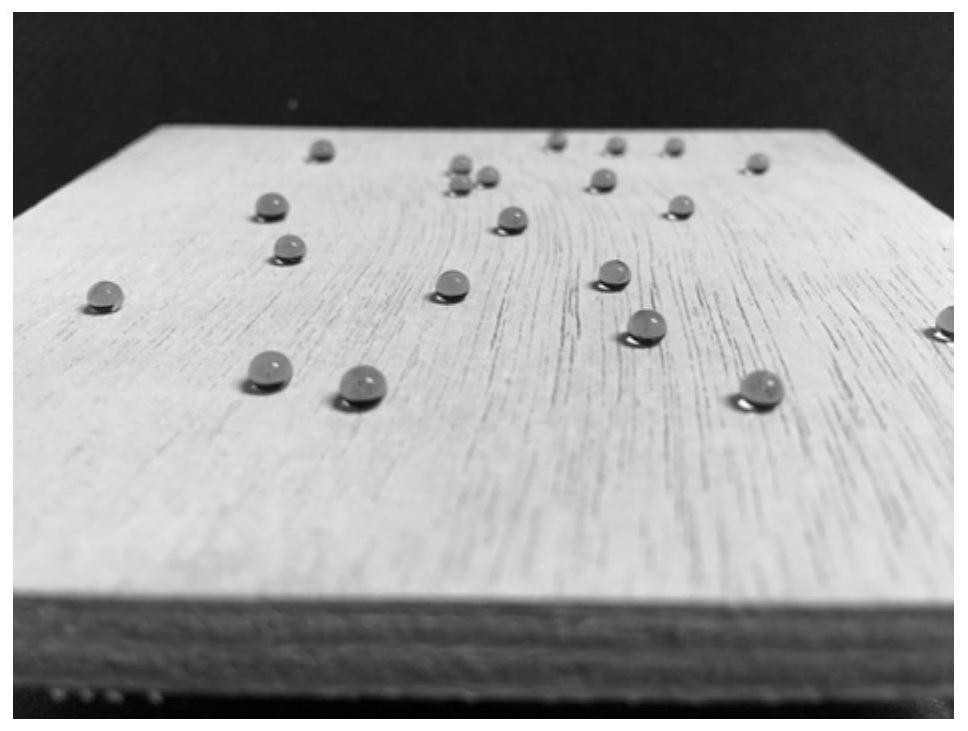
Preparation method of room temperature curing wood multifunctional modifier and wood modification method
A multifunctional modifier, room temperature curing technology, applied in wood treatment, wood impregnation, wood impregnation and other directions, can solve the problems of poor anti-shedding ability, high construction temperature, single function, etc., to achieve improved resistance to bleed and low cost , the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0043] Specific embodiment one: the preparation method of the room temperature curing wood multifunctional modifier of this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0044] 1. Weigh 1%-50% hydrophobic polymer resin, 0.1%-1% additives, 0.1%-10% curing agent and the rest of the solvent according to mass percentage, and stir at room temperature for at least 2 hours, the functional reagent A was obtained;
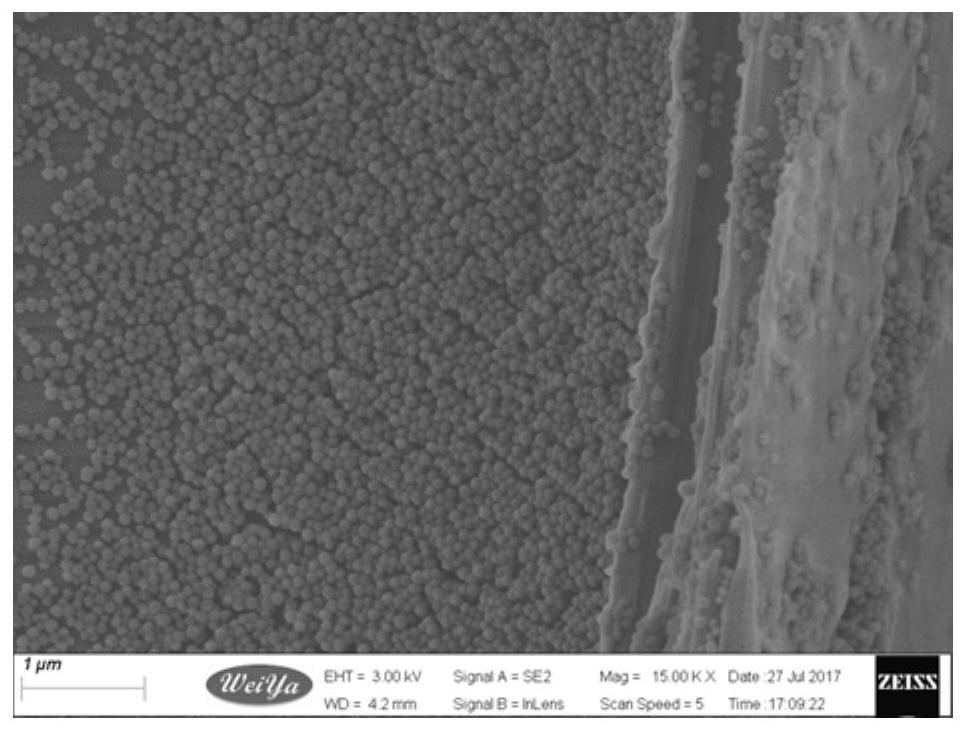
[0045] 2. Weigh 0.1%-5% of nanoparticles, 0.1%-2% of surface modifier and the rest of toluene according to mass percentage, mix and stir for 72-76 hours, then wash with acetone, and then set the temperature at 8000-9000rpm Centrifuge for 3-5 times, then dry at 78-82°C for 12-14 hours to obtain functional reagent B;
[0046] 3. Add functional reagent C to functional reagent A, stir evenly, then add functional reagent B, and ultrasonicate for at least 30 minutes to obtain a wood multifunctional modifier; the quality of functional reagent B is 0.1%-1 of the mass of functional r...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0047] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: in step 1, the hydrophobic polymer resin is a fluorocarbon resin with less than 8 F atoms. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0048] The fluorocarbon resin in this embodiment is purchased from Shangmeng Technology Wuxi Co., Ltd., which meets the environmental protection standards of Europe, Japan and the United States.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0049] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: in step one, the auxiliary agent is dibutyltin dilaurate. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
[0050] The role of the auxiliary agent in this embodiment is to play a drying effect.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com