Plant drought inducible synthetic promoter SP16 and application thereof
An SP16, inducible technology, applied in the field of biotechnology and genetic engineering, can solve the problem that natural promoters cannot finely regulate genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] Example 1 Design of plant drought-inducible promoter SP16
[0017] By combining the soybean stress transcriptome sequencing data with the existing soybean stress expression profile data in Genbank, 63 target genes regulated by drought were screened out, and then they were listed for cluster module classification; after obtaining 4 clusters, they were identified using motifs The software identified motifs for each cluster separately, and finally obtained 46 common expression elements of promoters related to stress regulation; among them, ERF1, ABFs, ABRE, ABRE like, and Root specific motifs were selected as basic cis-elements, and 2 One copy of ERF1 element, 2 copies of ABFs element, 1 copy of ABRE element, 2 copies of Root specific motif, 2 copies of ABRE like element, 2 copies of Root specific motif constitute a series unit, each two elements With a specific sequence interval of 10 bases in the middle, the above design fragment was connected with a 131bp Root base mini...
Embodiment 2
[0018] Example 2 Construction of promoter SP16 expression vector
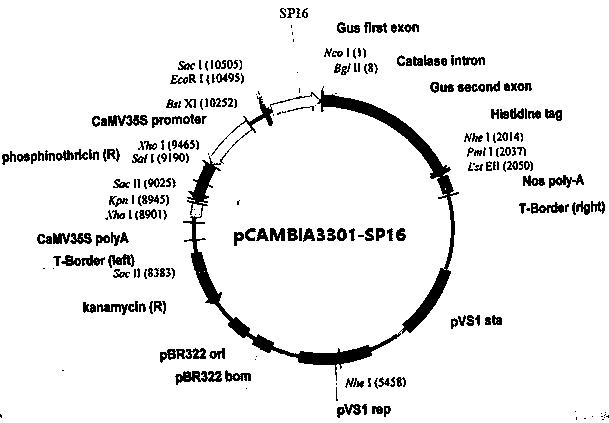
[0019] The sequence of SP16 (SEQ ID No.1) was synthesized into the vector pUC57 by artificial synthesis method, and enzyme cutting sites were added at both ends of the sequence Sac l and Nco I; the pUC57-SP16 vector and the pCAMBIA3301 plasmid were used respectively Sac l and Nco I carried out double enzyme digestion, and after recovering the enzyme digestion products respectively, through connection, transformation and identification, the expression vector pCAMBIA3301-SP16 was obtained ( figure 1 ); the vector pCAMBIA3301-SP16 was transformed into Agrobacterium rhizogenes K599 for infecting soybean cotyledonary nodes.
Embodiment 3
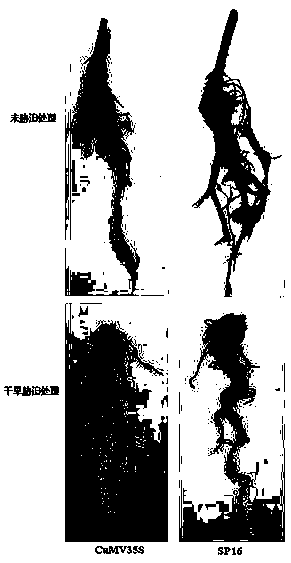
[0020] Example 3 Obtaining of Hairy Roots of Transgenic SP16 Soybean
[0021] Using the established soybean hairy root induction system, Agrobacterium rhizogenes K599 containing the pCAMBIA3301-SP16 carrier was used to infect soybean cotyledon nodes. After induction and identification, transgenic positive hairy roots were obtained; drought stress treatment was carried out; the specific method was as follows :
[0022] (1) After mixing sodium hypochlorite and concentrated hydrochloric acid 1:1, sterilize soybean seeds with chlorine gas overnight;
[0023] (2) Wash the soybeans with sterile water and plant them in high-temperature and high-pressure sterilized vermiculite, and moisturize with 1 / 4 Hoagland's solution;
[0024] (3) Cultivate for about 6 days in an artificial climate chamber at 25°C, under light for 16 hours;
[0025] (4) Agrobacterium rhizogenes K599 containing the recombinant plasmid pCAMBIA3301-SP16 was cultured overnight in an incubator at 28°C;
[0026] (5) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com