Display panel and display device
A display panel and substrate layer technology, applied to electrical components, electrical solid devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of low light transmittance and large opening diameter of panel stacking, and achieve improved light transmittance and high screen-to-body ratio , the effect of reducing the diameter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
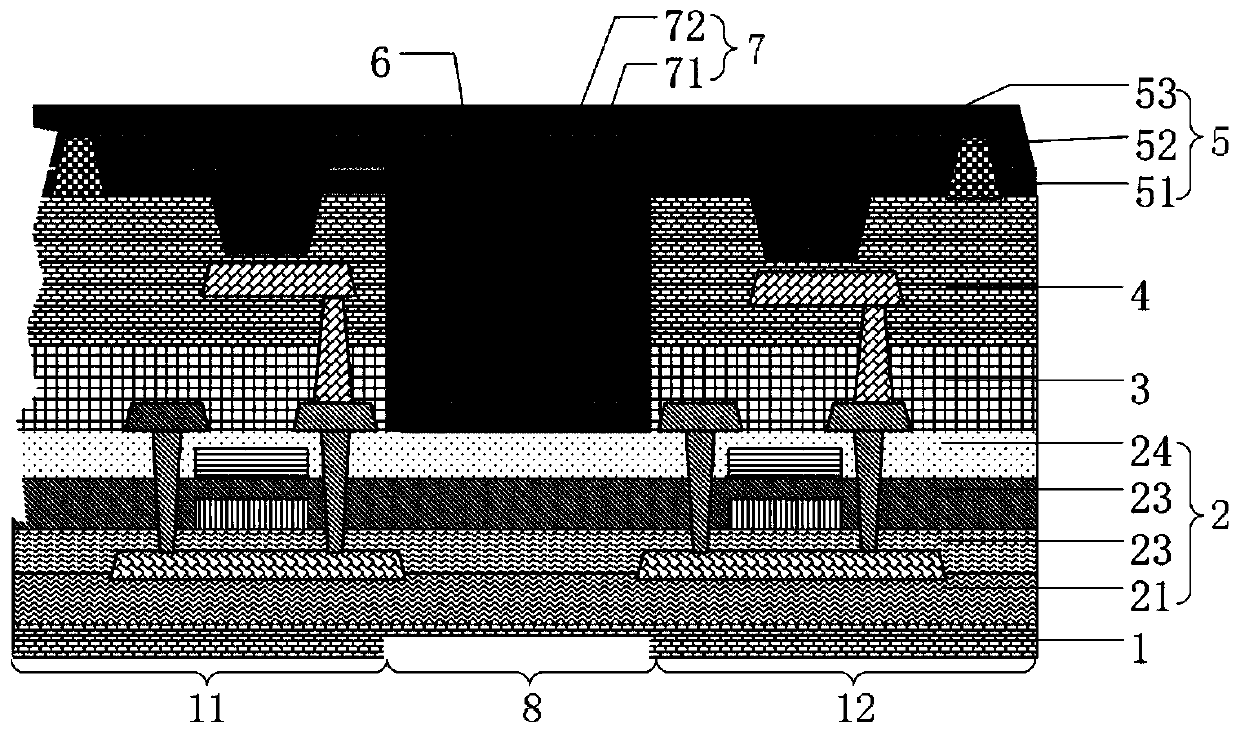
[0026] see figure 1 , figure 1 The schematic cross-sectional view of the display panel provided in this embodiment, in order to achieve the above purpose, the present invention provides a display panel, including a substrate layer 1, a thin film transistor layer 2, a flat layer 3, a pixel definition layer 4 and a thin film encapsulation layer arranged in sequence Layer 5.
[0027] The substrate layer 1 is a PI film layer, that is, a polyimide film, which is used as the base of the display panel; the polyimide film is a thin film insulating material with better performance in the world, and has a strong tensile strength. It is formed by polycondensation of pyromellitic dianhydride and diaminodiphenyl ether in a strong polar solvent, casting into a film and then imidization.
[0028] The thin film transistor layer 2 includes a buffer layer 21, a first gate insulating layer 22, a second gate insulating layer 23 and a barrier layer 24; wherein the buffer layer 21 is arranged on ...
Embodiment 2
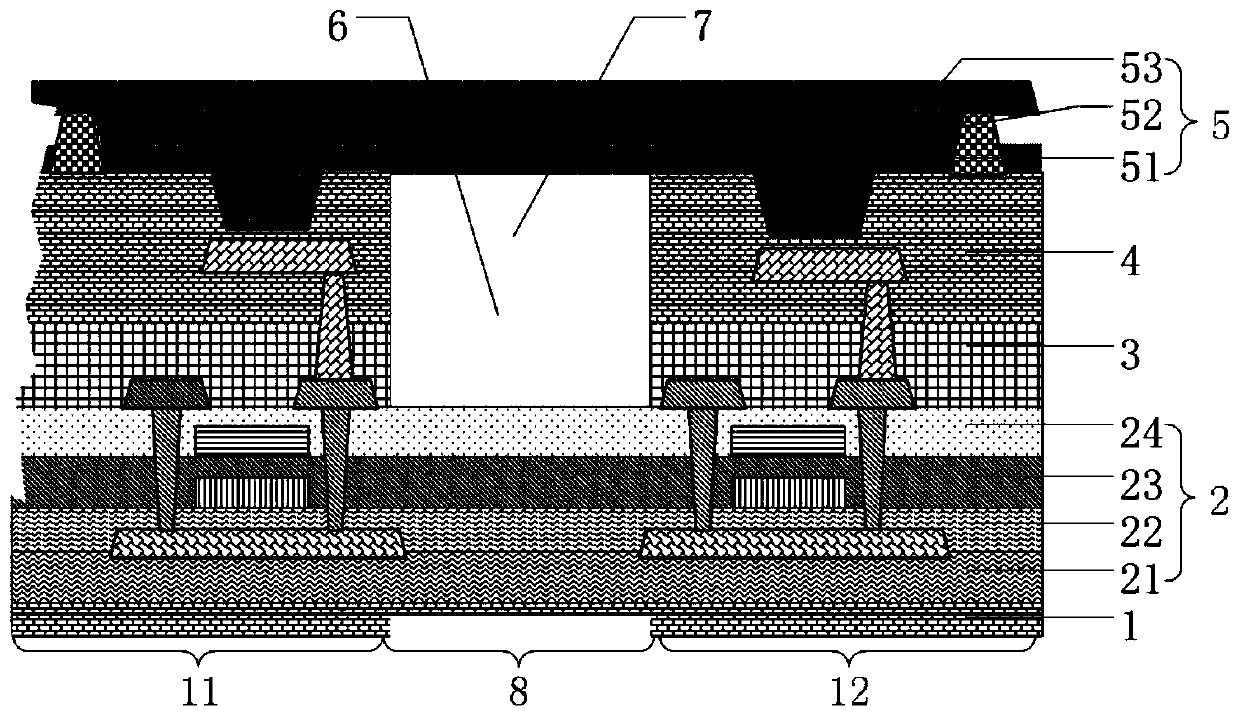
[0036] see image 3 , image 3 Shown is a schematic cross-sectional view of the display panel provided by this embodiment. The structure of the transparent display panel in this embodiment is roughly the same as that of Embodiment 1. For the same structure, refer to the above method, which will not be repeated here. The main differences are The reason is that the material of the filling layer 7 is a transparent organic material, and its light transmittance is greater than that of the pixel definition layer 4 and the flat layer 3. Therefore, such an arrangement improves the light transmittance to a certain extent, and can further reduce the light transmittance. The small opening diameter achieves a high screen-to-body ratio.
Embodiment 3
[0038] see Figure 4 , Figure 4Shown is a schematic cross-sectional view of the display panel provided by this embodiment. The structure of the transparent display panel in this embodiment is roughly the same as that of Embodiment 1. For the same structure, refer to the above method, which will not be repeated here. The main differences are The reason is that the cross-sectional shape of the via hole 6 is an inverted trapezoid, and the side wall of the via hole 6 forms an obtuse angle with its bottom surface. As the angle increases, the film thickness evaporated on the side increases. When the formed angle is greater than 120 degrees, the sidewall of the via hole 6 cannot reflect. Therefore, when the angle between the side wall of the via hole 6 and its bottom surface is controlled to be greater than 90 degrees and less than 120 degrees, the side wall of the via hole 6 can serve as a reflector to reflect light, so that more electronic components placed under the groove 8 can...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com