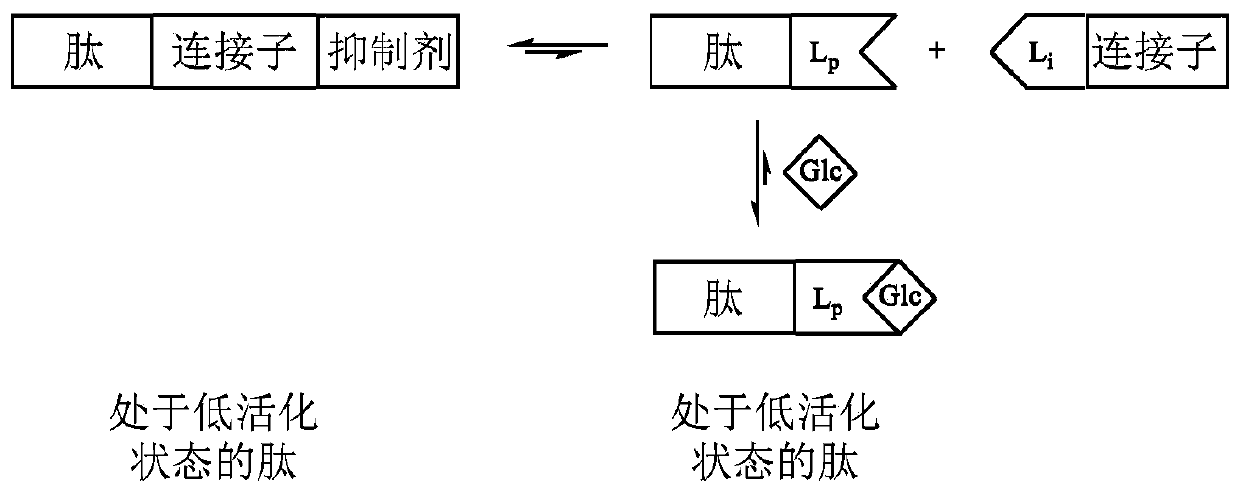
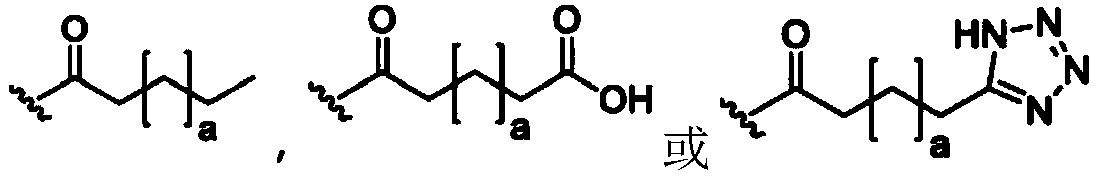
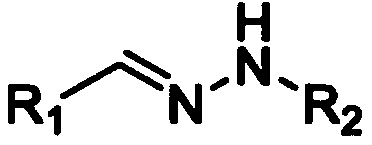
Glucose-sensitive peptide hormones
A technology for glucose and peptide hormones, applied in the field of pharmaceutical or veterinary compositions, drugs for treating diabetes, and reagents for inactivating or inhibiting the activity of peptide hormones, and can solve problems such as changing the activity of peptide hormones
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0166] Example 1 illustrates the synthesis of exemplary hydrolyzable linker (L) molecules.
Embodiment 2
[0167] Example 2 illustrates a method for forming a linker (L) with a handle ready for grafting peptide (P) and inhibitor (I).
Embodiment 3
[0168] Example 3 illustrates the synthesis of a linker attached to an inhibitor (I). In this example, the inhibitor or inactivator complex (I) is a C18 fatty acid, which does not itself inhibit the activity of the peptide (see Example 4), but which is known to bind albumin in vivo. Thus, inactivation in vivo is ultimately achieved by inhibitor binding and aggregation of the conjugate to albumin.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com