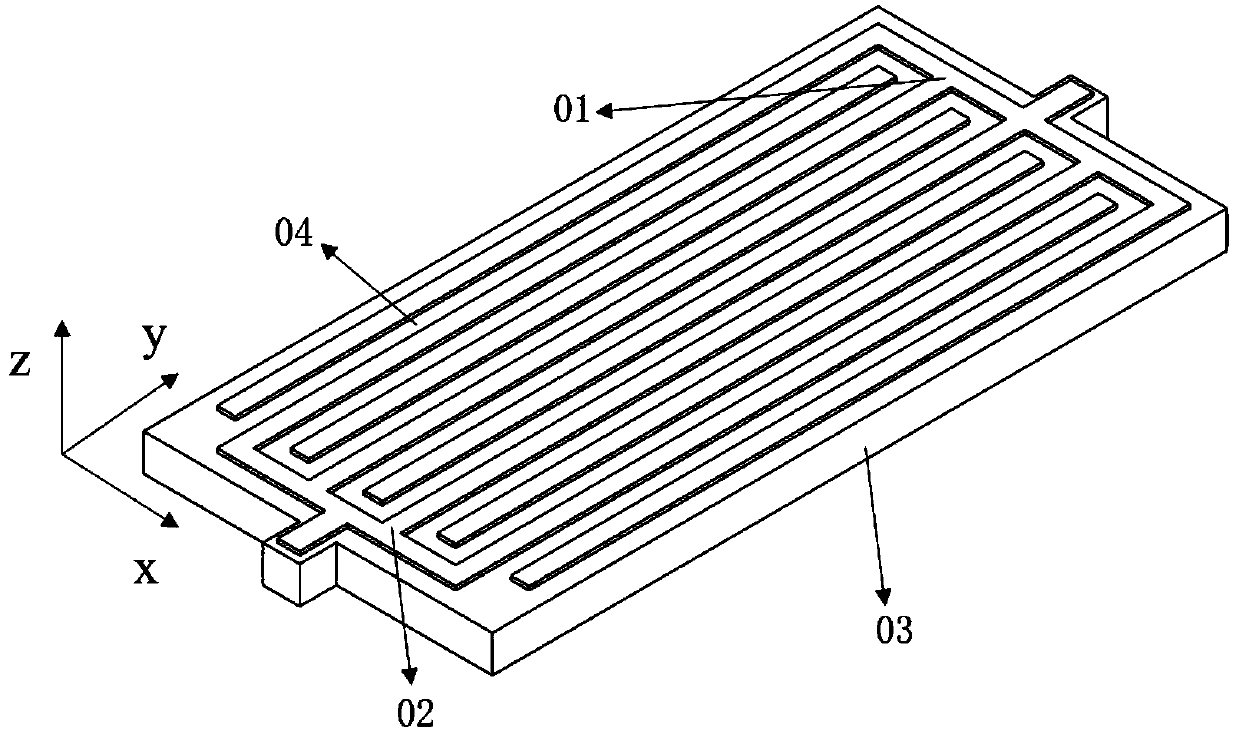
Two-dimensional Lamb wave resonator
A Lamb wave resonator and positive electrode technology, applied in the field of resonators, can solve the problems of no solution to Lamb wave coupling effect, affecting signal transmission quality, affecting device performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
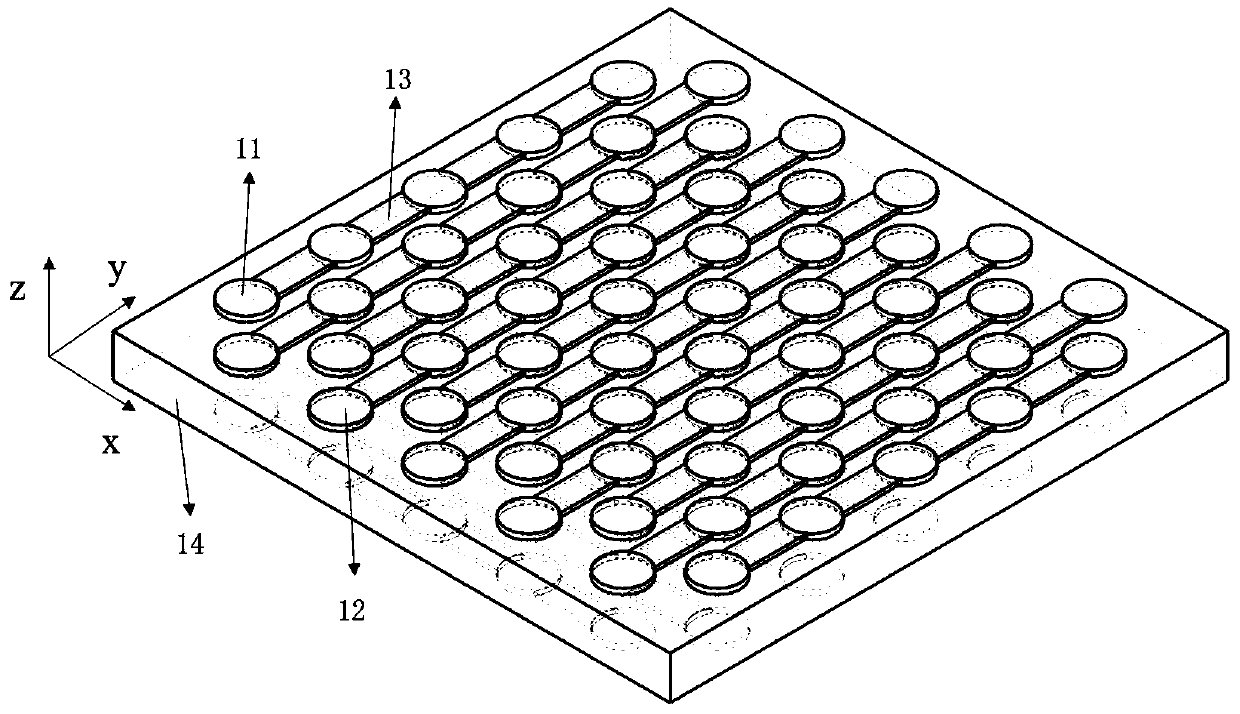
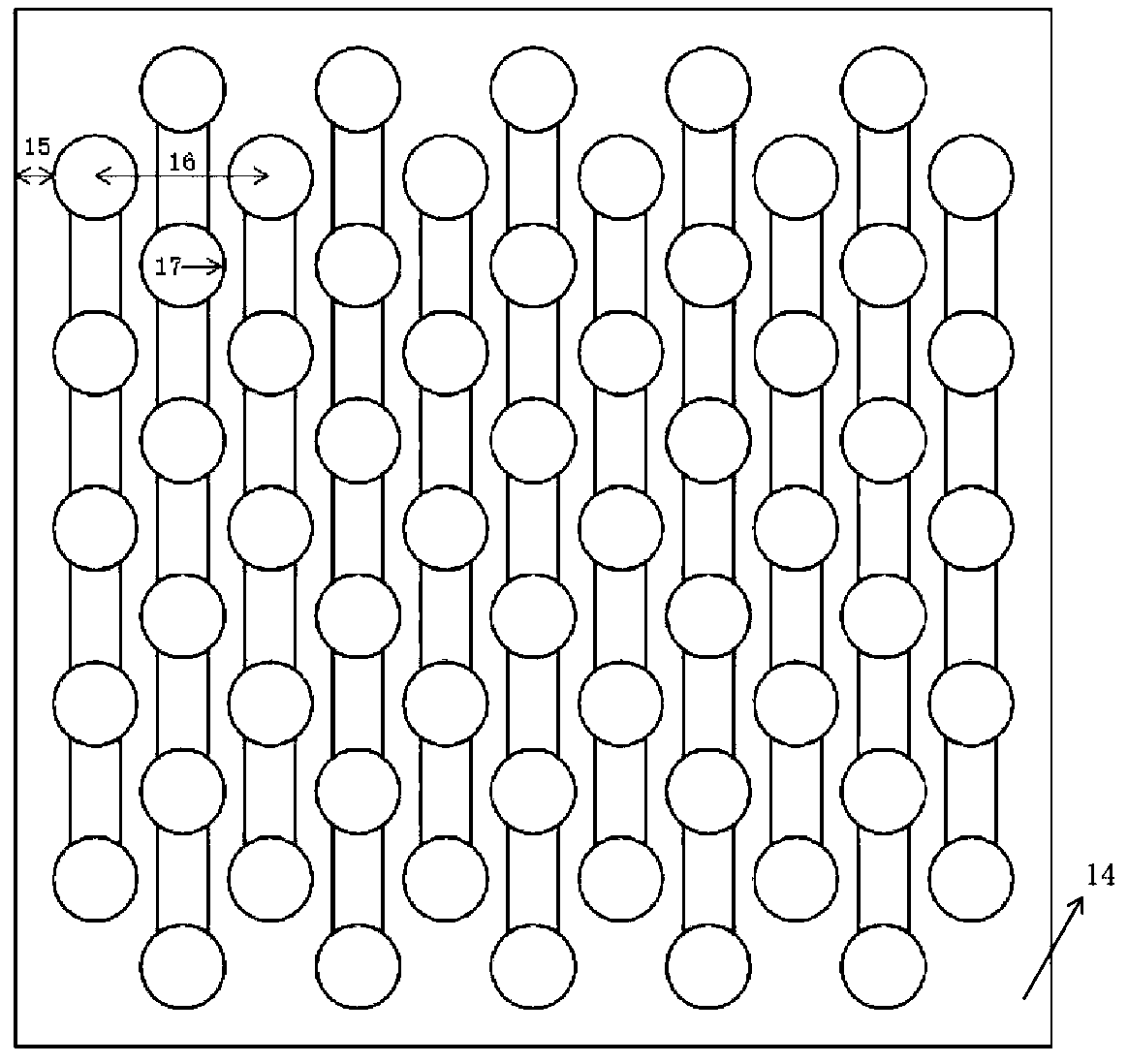
[0038] Embodiment 1 provides a two-dimensional Lamb wave resonator, such as figure 2 As shown, it includes: a first electrode array and a second electrode array; the first electrode array and the second electrode array are respectively arranged on the upper and lower surfaces of the piezoelectric layer 14 .
[0039]The first electrode array includes a plurality of first positive electrode columns and a plurality of first negative electrode columns arranged along a first direction, and the first positive electrode columns and the first negative electrode columns are arranged alternately; the The first positive electrode column includes a plurality of first positive electrodes, and two adjacent first positive electrodes are connected by a bridge 13; the first negative electrode column includes a plurality of first negative electrodes, and two adjacent The first negative electrodes are connected through a bridge 13 .
[0040] The second electrode array includes a plurality of s...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2 provides a two-dimensional Lamb wave resonator, such as Figure 6 Shown is a two-dimensional Lamb wave resonator of an inclined bridge. On the upper and lower surfaces of the piezoelectric layer 24, positive electrodes 21 (circular electrodes with positive voltage) and negative electrodes 22 (circular electrodes with negative voltage) are arranged uniformly, thereby applying alternating current to the upper and lower surfaces of the piezoelectric layer 24. Voltage. A plurality of positive electrodes 21 are connected through a bridge 23, and a plurality of negative electrodes 22 are connected through a bridge 23. The bridge 23 may or may not be in contact with the surface of the piezoelectric material. The orientation of the bridge 23 is non-parallel to the x and y axes. The electrode directions of the upper surface and the lower surface of the piezoelectric layer 24 are vertically intersecting.
Embodiment 3
[0052] Embodiment 3 provides a two-dimensional Lamb wave resonator, such as Figure 7 Shown is a two-dimensional Lamb wave resonator with square electrodes. Positively charged square electrodes 31 and negatively charged square electrodes 32 are evenly arranged on the upper and lower surfaces of the piezoelectric layer 34 , so that AC voltage is applied on the upper and lower surfaces of the piezoelectric layer 34 . A plurality of square electrodes 31 with positive voltages are connected through a bridge 33 , and a plurality of square electrodes 32 with negative voltages are connected through a bridge 33 . The bridge 33 may or may not be in contact with the surface of the piezoelectric layer 34 . If the direction of the bridges 33 on the upper surface of the piezoelectric layer 34 is arranged in parallel along the y-axis, the direction of the bridges 33 on the lower surface of the piezoelectric layer 34 is arranged along the x-axis.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com