Semi-Unauthorized Random Access Method Based on Grouping of Machine Type Communication Devices
A machine-type communication and random access technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as increased energy consumption, access collision, and low data transmission efficiency, and achieve the effect of improving effectiveness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Massive machine type communication (mMTC) is one of the three application scenarios of the fifth generation mobile communication system (5G) defined by 3GPP, aiming to support the development of the future Internet of Things. In the future, mMTC scenarios will mainly develop in the direction of high connection density, low terminal power consumption, and high coverage. Among them, high connection density is the most important design enhancement goal of mMTC. If the current random access scheme is adopted in the mMTC scenario, it will face the problems of excessive signaling overhead, low data transmission efficiency, increased access collisions, and increased access delay and power consumption. The current research on MTC random access schemes mainly includes two categories: Grant-based random access schemes that optimize the handshake process and Grant-free random access schemes that omit the handshake process between the base station and the device. Since multiple han...
Embodiment 2
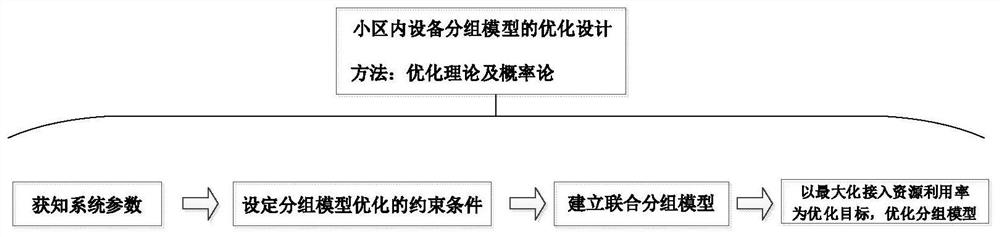
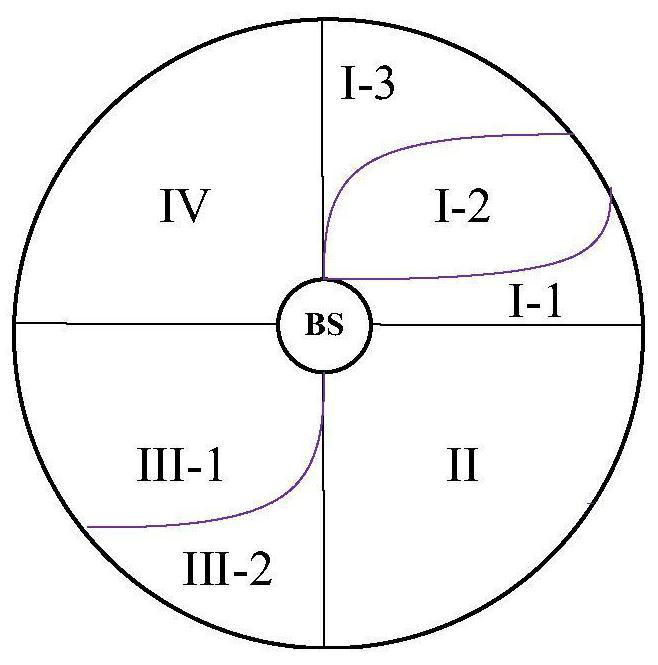
[0044] The semi-Grant-Free random access method based on the grouping of MTC devices is the same as that in Embodiment 1, and the active MTC devices described in step 1 of the present invention send access request information according to the grouping scheme, see figure 2 , including the following steps:
[0045] (1a) Obtaining system parameters: According to the mMTC application scenario, first obtain the system parameters of a single cell, including counting the total number of MTC devices in the cell, obtaining the service radius of the base station, counting the activation probability of the MTC device, and obtaining the number of antennas configured by the base station.
[0046] (1b) Set the constraints of the grouping model optimization problem: when grouping the MTC devices in the cell, in order to make full use of the transmission resources, it should be ensured that the number of active devices in each device group is less than the maximum number of devices that can b...
Embodiment 3
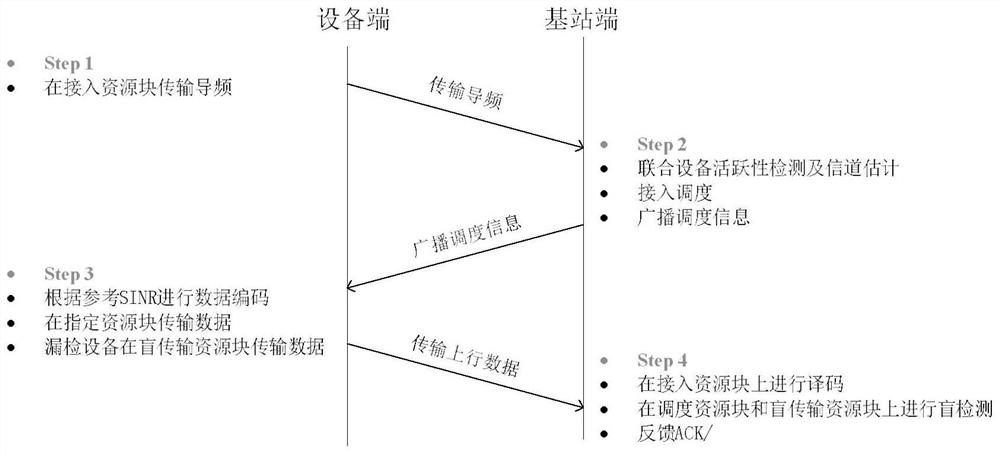
[0051] The semi-Grant-Free random access method based on MTC device grouping is the same as that in Embodiment 1-2, and the base station described in step 2 of the present invention performs joint device detection and channel estimation, see Figure 4 , including the following steps:
[0052] Considering that the activation state of the MTC equipment is sparsely distributed, and considering that the channel parameters between the MTC equipment and the base station obey the independent Gaussian distribution, the joint equipment detection and channel estimation problem can be mapped to a row sparse matrix recovery problem; in the present invention, the MTC equipment grouping In some cases, the number of MTC devices in each group is limited, and the length of the pilot sequence used by the MTC devices on each access resource block is limited. In this case, the approximate message passing algorithm based on asymptotic assumption cannot guarantee good algorithm convergence. Therefor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com