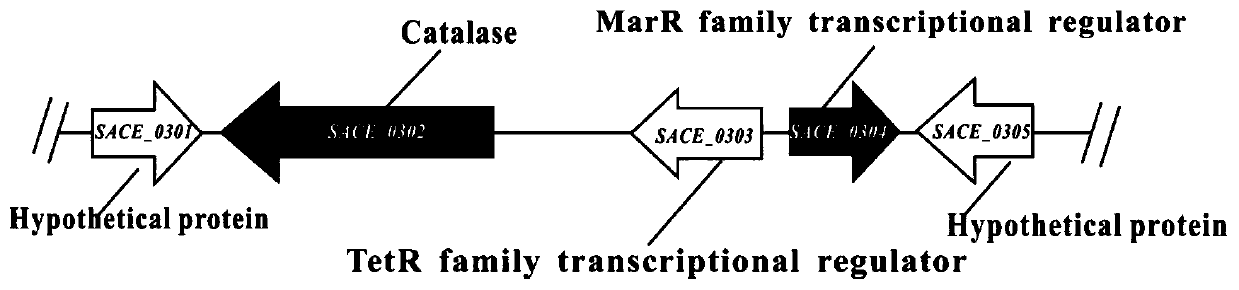
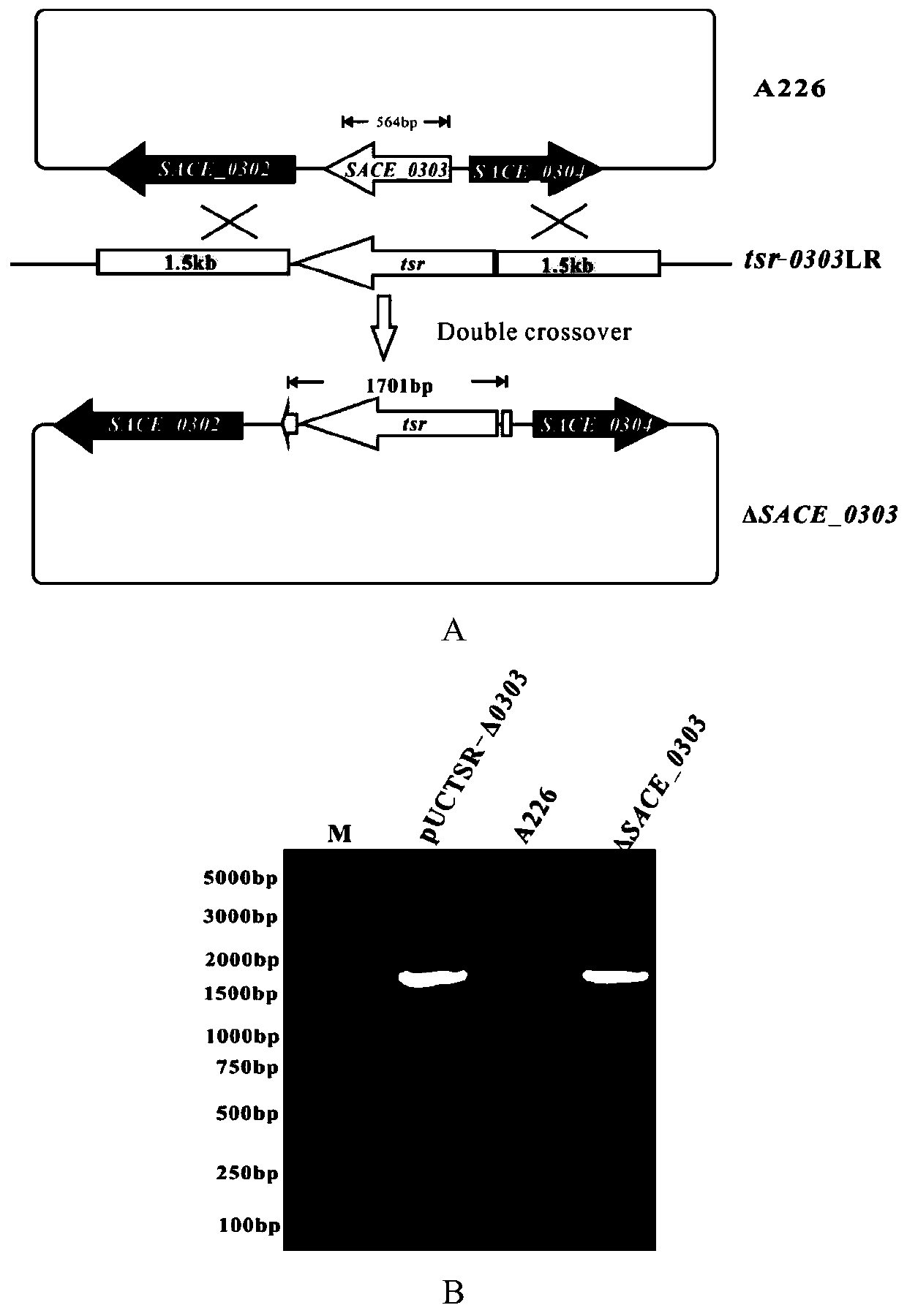
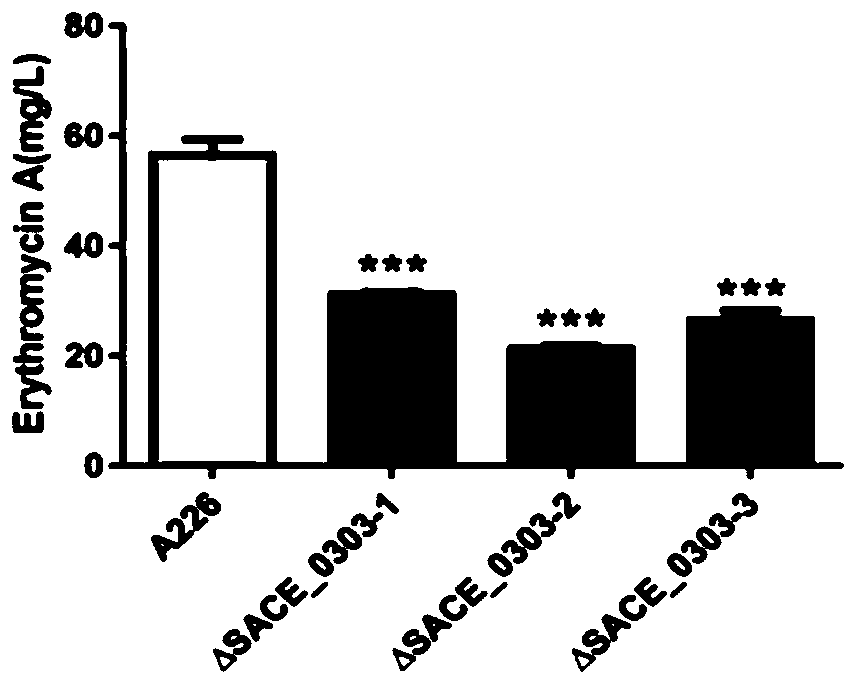
Method for increasing yield of erythromycin by transforming streptomyces erythraea SACE_0303 gene
A technology of Saccharopolyspora erythromycetes and erythromycin, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of large randomness, time-consuming, inability to provide theoretical guidance for breeding, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below. This embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following implementation example.
[0022] The bacterial strains and plasmids used in the examples are shown in Table 1. Escherichia coli were cultured in liquid LB medium at 37°C or on solid LB plates supplemented with 1.25% agar. The erythromycin-producing erythromycin-producing erythromyces Saccharopolyspora wild strain A226 and its engineered strain WB were cultured in tryptone soy broth (TSBY) medium at 30°C or on MGM plates containing 2.2% agar.
[0023] Bacterial strains and plasmids used in the present embodiment of table 1
[0024]
[0025]
[0026]
[0027] In the examples, PEG3350, lysozyme, TES, casamino acids, thiostrepton, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com