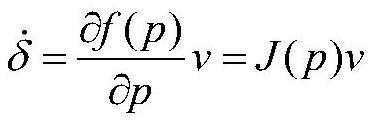An Improved Adaptive Zero-Space Behavior Fusion Method for Multi-robot Formation
A multi-robot, fusion method technology, applied in the field of mobile robot formation motion planning, can solve problems such as unfavorable engineering applications, misexecution of tasks, lack of adaptability, etc., to achieve both efficiency and performance, improve formation task efficiency, and facilitate formation The effect of formation hold
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
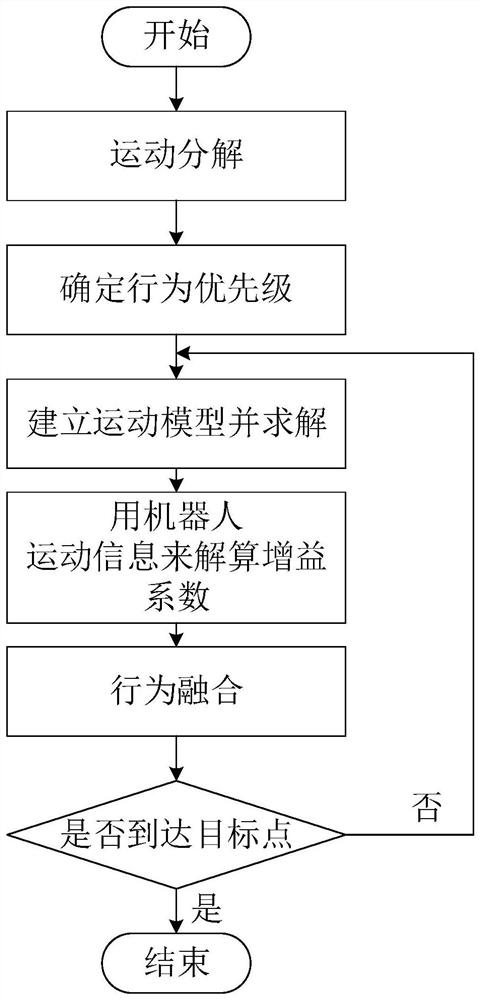
[0054] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0055] The present invention discloses an improved adaptive null-space behavior fusion method for multi-robot formation. zero space behavioral fusion
[0065] (7) Judging whether the robot reaches the end point, if it reaches the process ends, if it does not arrive, it returns to step (3).
[0082]
[0084]
[0086]
[0089]
[0090]
[0091]
[0092] Wherein, the variable r>0. The gain coefficient λ for the behavior towards the target point
[0094]
[0095]
[0098]
[0099]
[0100]
[0102] The logic priority obstacle avoidance strategy selects obstacles: the robot is numbered, and the execution robot is judging the obstacle to avoid collision.
[0104] Considering the priority order of the three behaviors, the final speed output can be obtained as shown in the following formula.
[0105] v=v
[0106] Determine whether the robot has reached the end point.
[0110] FIG...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com