Radio receivers
A radio receiver and circuit technology, applied in the field of zero-IF radio receiver equipment, can solve problems such as the reduction of receiver linearity, and achieve the effects of reducing DC offset, reducing noise, and reducing linearity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
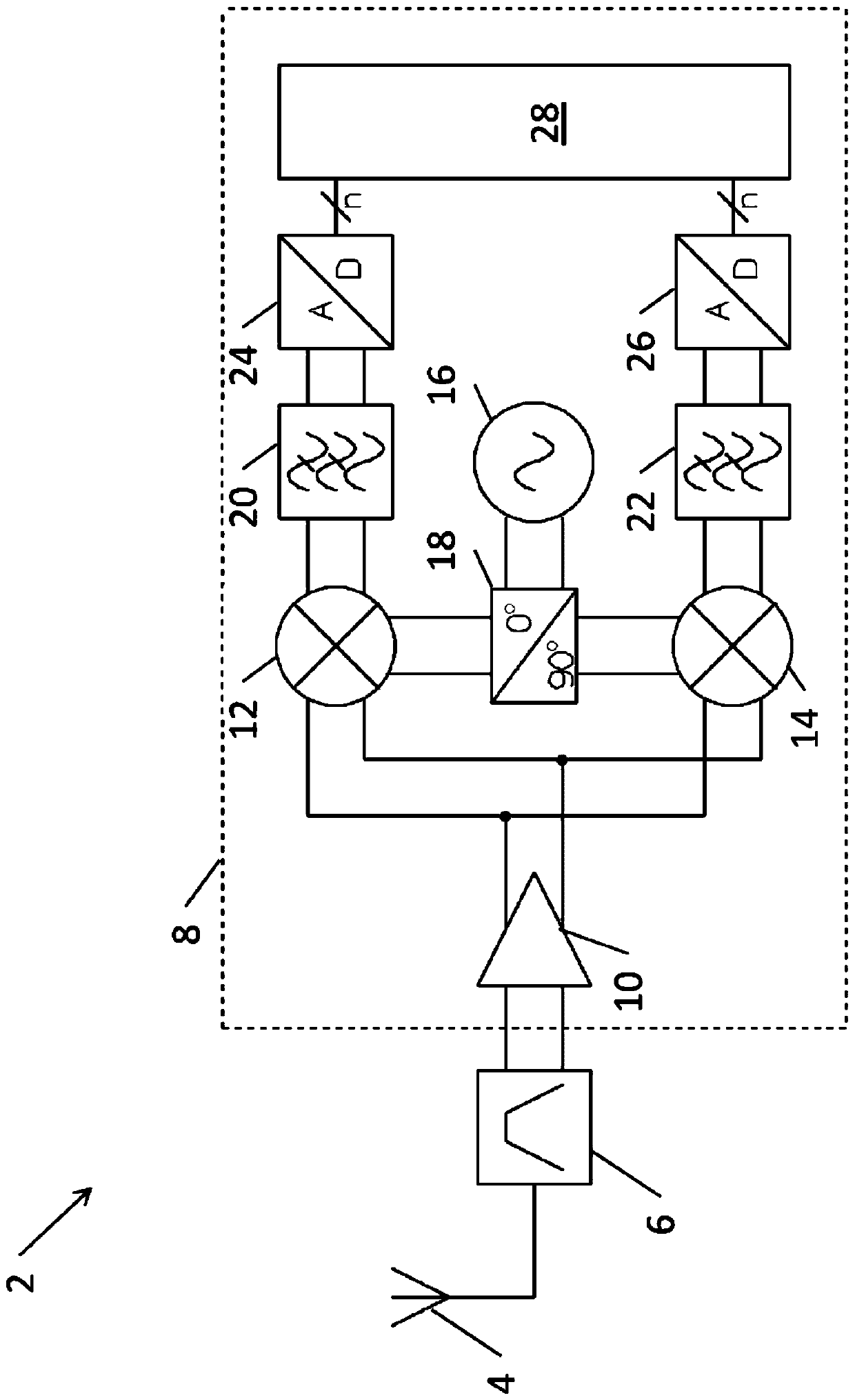
[0028] FIG. 1 is a block diagram of a conventional fully balanced zero-IF radio receiver architecture 2 . The radio receiver 2 includes an antenna 4 , an RF bandpass filter 6 and a radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) 8 . The RFIC 8 includes: a low noise amplifier (LNA) 10; two mixers 12, 14; a local oscillator 16; a quadrature phase shifter 18; two low pass filters 20, 22; , 26; and digital circuit 28. It is of course understood that the RFIC 8 may include other components (eg, RF transmitters), but these are not shown here for ease of illustration.
[0029] Antenna 4 picks up the RF signal, which passes through bandpass filter 6 , which provides an incoming balanced signal to LNA 10 . The LNA 10 amplifies the input signal and provides the amplified signal to two mixers 12 , 14 . Local oscillator 16 generates a local oscillator signal, which is used by phase shifter 18 to generate an in-phase (I) local oscillator signal and a quadrature (Q) local oscillator signal. A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com