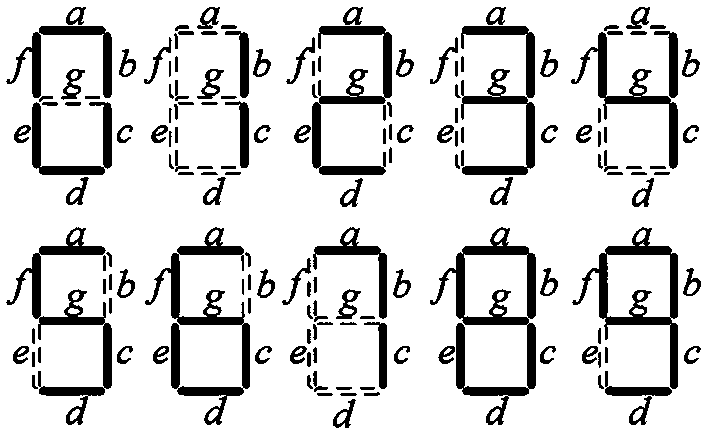
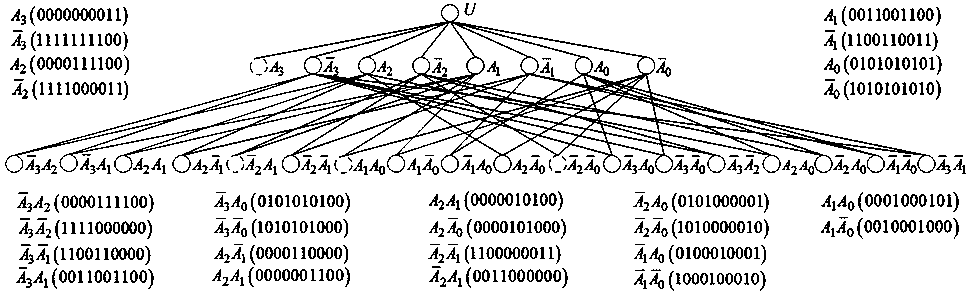
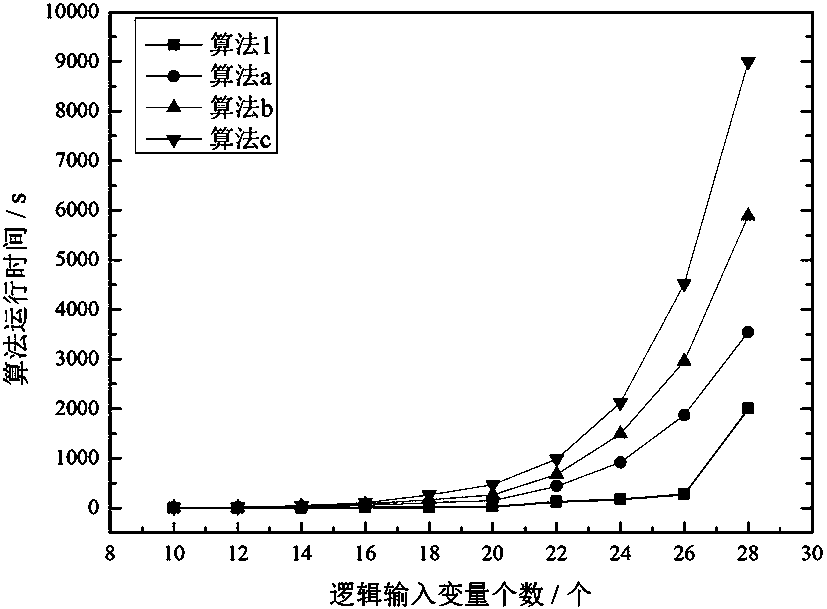
Form vector-based reduction method for multi-input multi-output truth table
A truth table and multi-input technology, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as complex calculation of prime implicants, non-unique reduction results, and difficult programming
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0078] Example 1: Truth table T 1 =(U,R,V,f) as shown in Table 1, where U={1,2,3,4,5,6} logic input variable X={a,b,c}, logic output variable Y= {y}.
[0079] Before using the formal vector to solve the reduction problem of the truth table, it is necessary to transform the truth table into a decision-making formal background. According to definition 5, the truth table can be transformed into the decision form background DT = (U, C', I, D', J), as shown in Table 2.
[0080] where U={1,2,3,4,5,6}, condition attribute Decision attribute D'={y}.
[0081]
[0082] Table 1 Truth table T 1
[0083] Since only the rules whose output is "1" need to be identified in the process of truth table reduction, there is no need to convert the "0" logic output variable in the truth table. Additionally, for use a 1 represents the original variable, a 0 Indicates the inverse variable.
[0084] From the decision-making formal background in Table 2, seven single-attribute formal vecto...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com