Epigenetically regulated site-specific nucleases
A nuclease, target site technology, applied in the field of site-specific nucleases regulated by epigenetics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0120] The invention is further described by the following examples, which do not limit the scope of the invention described in the claims.
[0121] Example #1: Sequence-specific nucleases regulated by epigenetics
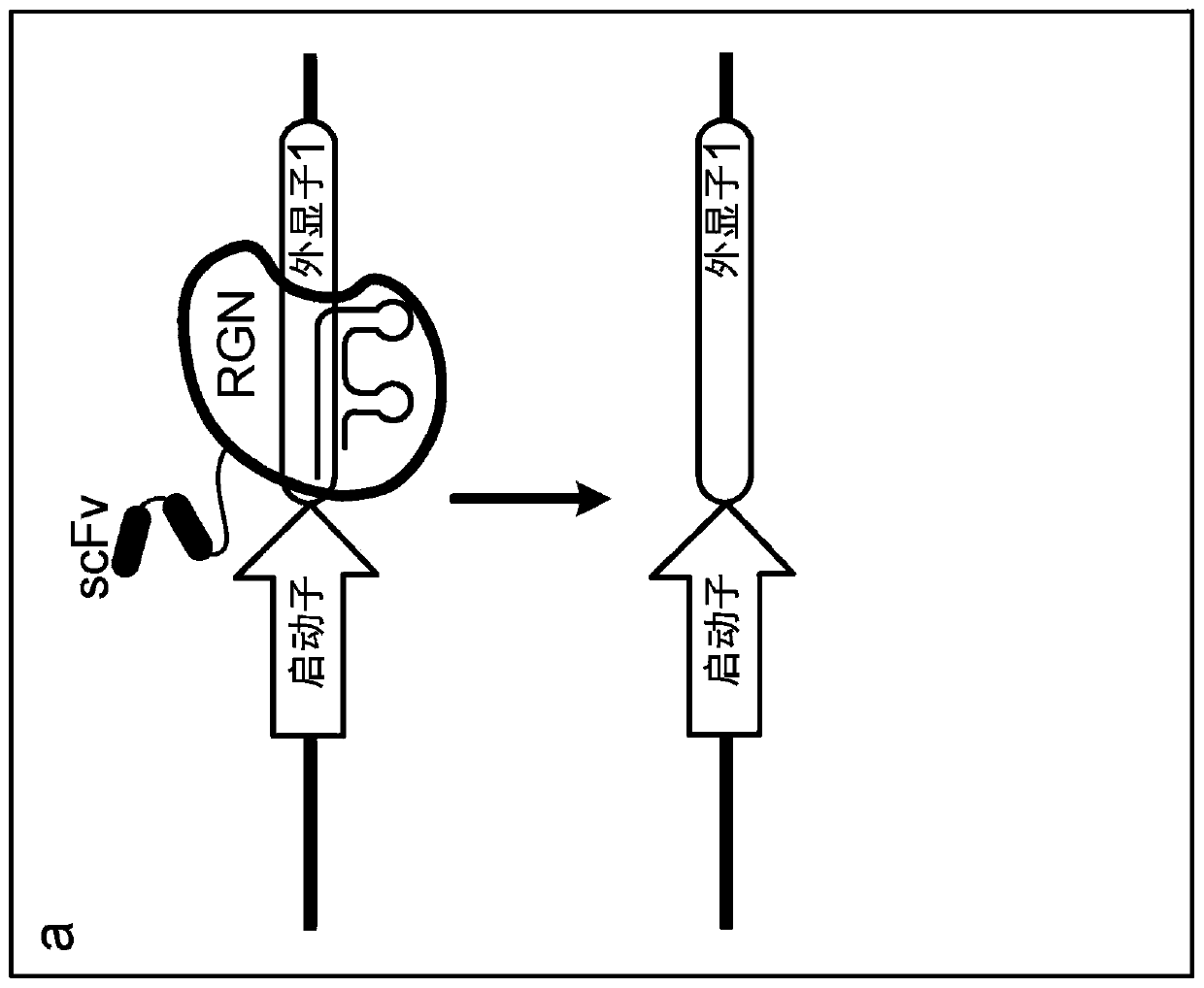
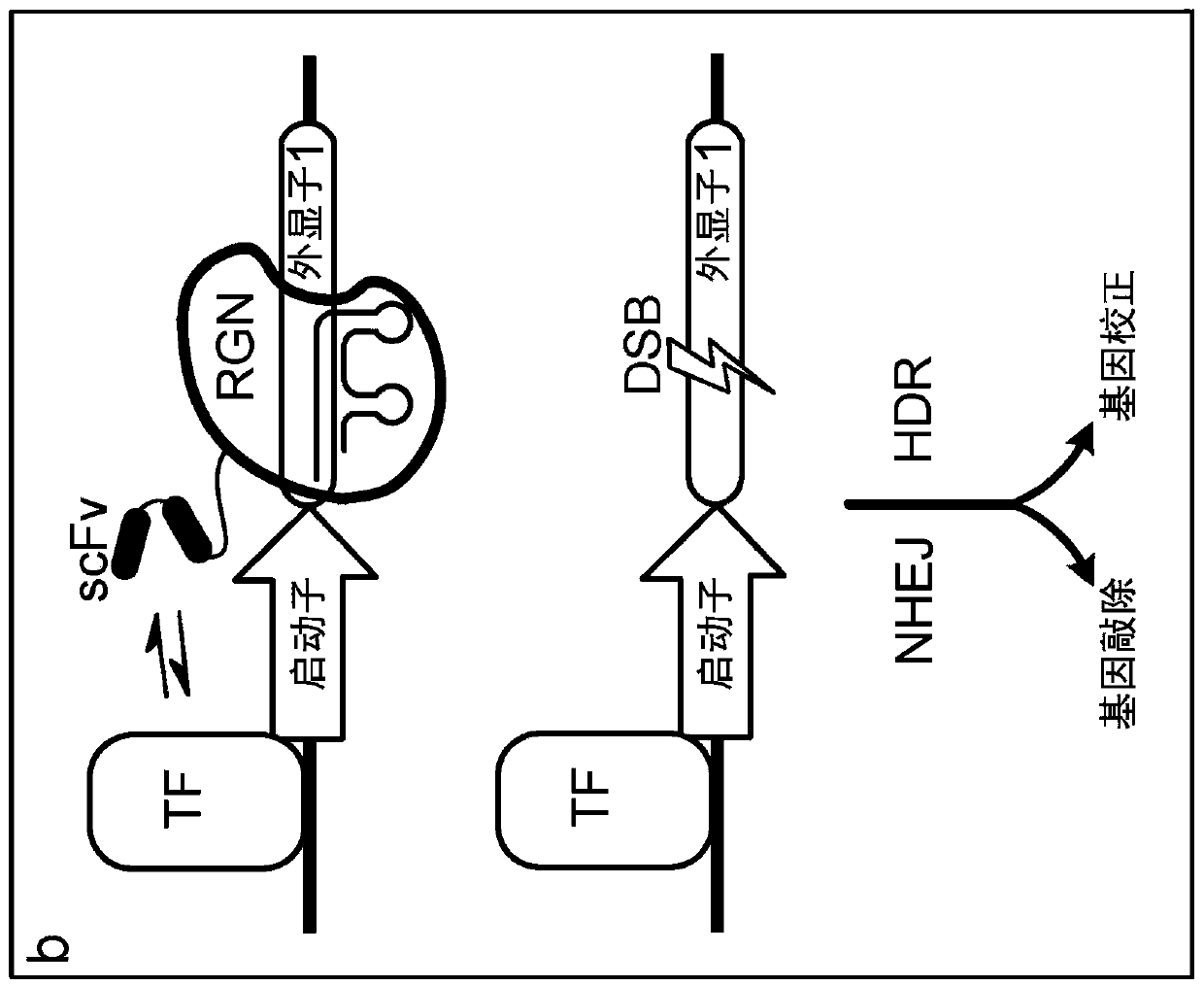
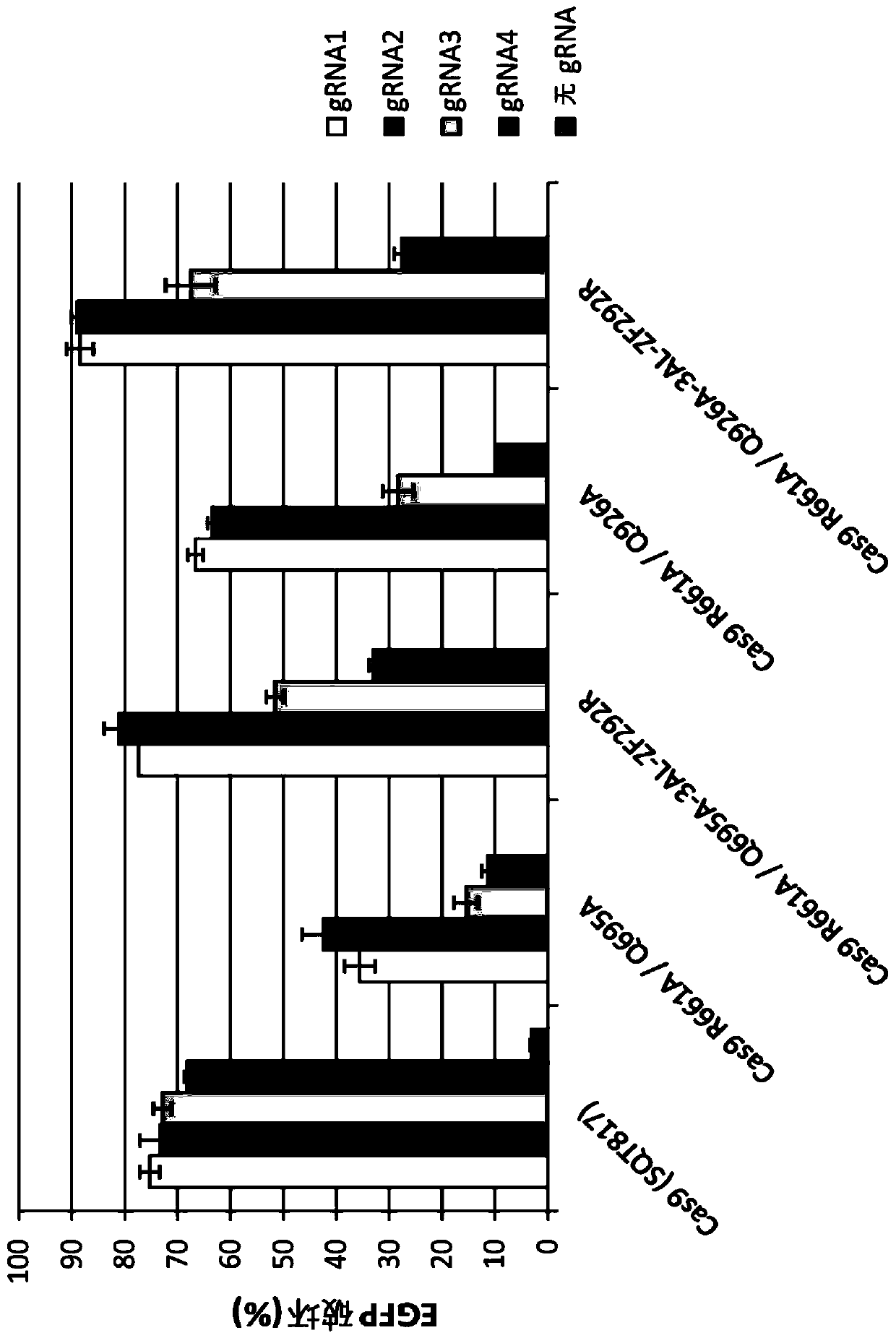
[0122]A system was developed in which SpCas9 variants with R661A and Q695A mutations or with R661A or Q926A mutations were genetically fused to an engineered zinc finger array (ZF292R) targeting genomic integration of a single-copy EGFP reporter gene. Introduction of nuclease-induced DSBs into the EGFP coding region, followed by repair by NHEJ, can result in the introduction of frameshift mutations that result in cells becoming negative for EGFP, a phenotype that can be quantified using flow cytometry. We tested the nuclease activity of these variants with or without the ZF292R zinc finger array and with four different gRNA variants targeting the same site in EGFP: (1) with 20 nt homology to the target site and with Additional 5' gRNA with additional G (gRNA1) wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com