A kind of method and application of preparing graphene oxide based on gelatin
A graphene and gelatin technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, applications, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as high cost, unsafe, complicated process, and achieve low cost, high mechanical strength, safe and controllable process Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
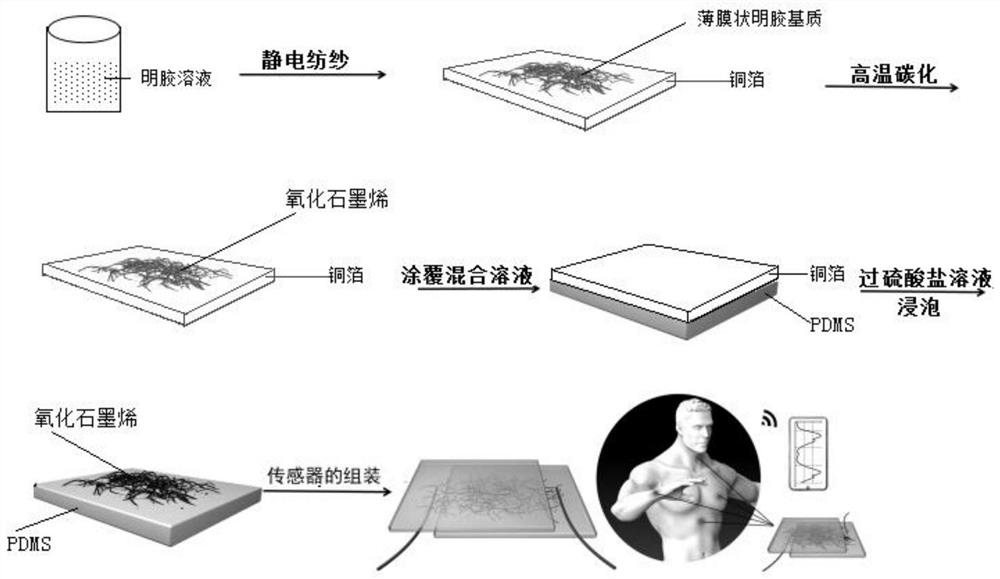
[0046] Step 2, the preparation of graphene oxide
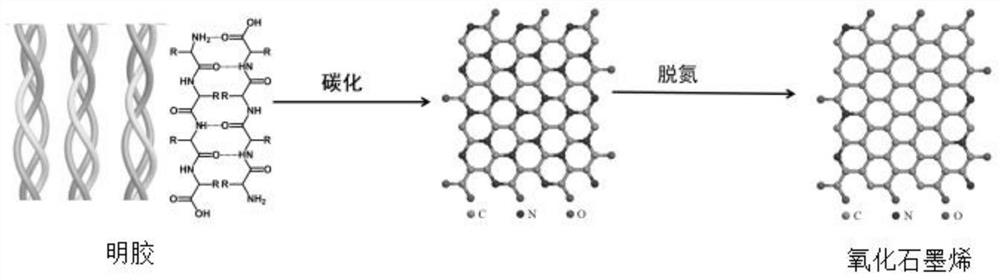
[0047] The gelatin matrix of fixed form obtained in step 1 is carried out high-temperature carbonization treatment under the protection of inert gas atmosphere, is cooled to room temperature, obtains graphene oxide (such as figure 1As shown, this process undergoes carbonization, dehydrogenation, and denitrogenation of gelatin, and finally obtains graphene oxide).
[0048] In the above technical scheme, in step 1, gelatin is an existing technology, which can be obtained commercially without special restrictions, and is preferably a mixture of one or more of edible gelatin, medicinal gelatin, photographic gelatin, and industrial gelatin; the solvent mainly Dissolving effect, on the basis of not changing the gelatin composition, as long as the solvent that can dissolve the gelatin effect can be realized, it is preferably a mixture of one or more of water, glycerol, formic acid or acetic acid; the dissolution condition is preferab...
Embodiment 1
[0061] Step 1. Weigh 2g of gelatin and add it to 5mL of water, heat and magnetically stir until the gelatin is completely dissolved, then filter to obtain a gelatin solution, transfer the gelatin solution to a glass mold with a 5mL inner cavity, and evaporate the solvent in an oven , directly demoulding to obtain a cube block gelatin matrix;
[0062] Step 2. Put the cubic block gelatin matrix obtained in Step 1 in a tube furnace, and calcine it under the protection of argon. First, gradually increase the temperature from room temperature to 200° C. at a rate of 5° C. / min, and keep the temperature constant for 1 hour. Then, Raise the temperature to 400°C at a rate of 5°C / min, hold the temperature for 1 hour, and finally raise the temperature to 600°C at a rate of 5°C / min, hold the temperature for 1 hour, and cool to room temperature to obtain graphene oxide.
Embodiment 2
[0064] Step 1. Weigh 3g of gelatin and add it to 5mL of formic acid. Stir magnetically until the gelatin is completely dissolved. After filtration, the gelatin solution is obtained. Transfer the gelatin solution to a cylindrical glass mold with a cylindrical cavity, evaporate the solvent in an oven, and remove the gelatin directly. The mold obtains the cylindrical gelatin matrix;
[0065] Step 2. Place the cylindrical gelatin matrix obtained in Step 1 in a tube furnace, and calcine it under the protection of argon. First, gradually increase the temperature from room temperature to 100°C at a rate of 2°C / min, and keep the temperature constant for 1h. Then, Raise the temperature to 500°C at a rate of 5°C / min, hold the temperature for 1 hour, and finally raise the temperature to 1000°C at a rate of 10°C / min, hold the temperature for 1 hour, and cool to room temperature to obtain graphene oxide.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength at break | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com