Multi-satellite coordinated real-time tracking method for spatial dynamic target
A dynamic target, real-time tracking technology, applied in the field of satellite scheduling, can solve the problems of insufficient research on resource utilization, ignoring the real-time performance of tracking tasks, and difficult identification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0102] The following is a detailed description of the embodiments of the present invention. This embodiment is carried out based on the technical solution of the present invention, and provides detailed implementation methods and specific operation processes to further explain the technical solution of the present invention.
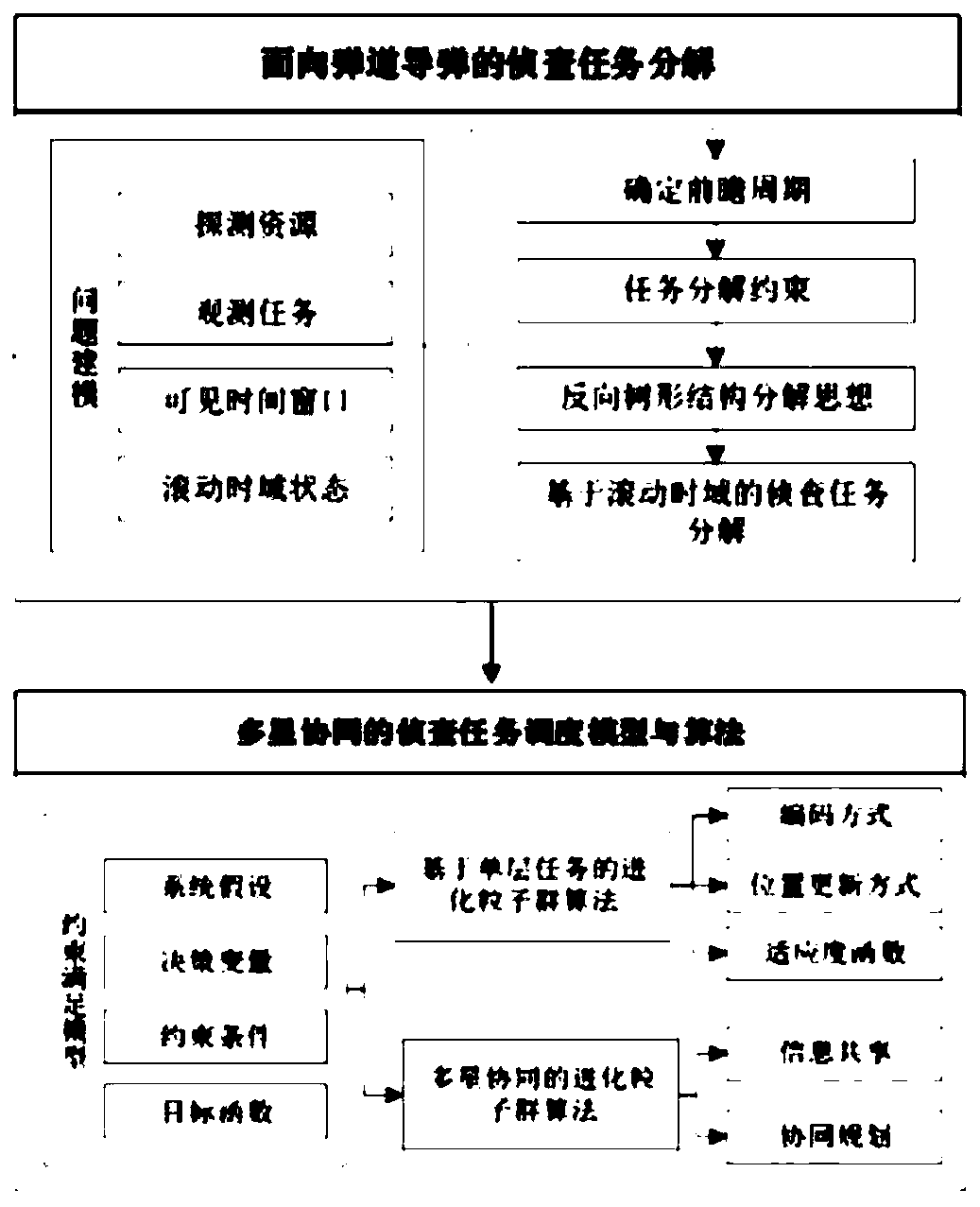
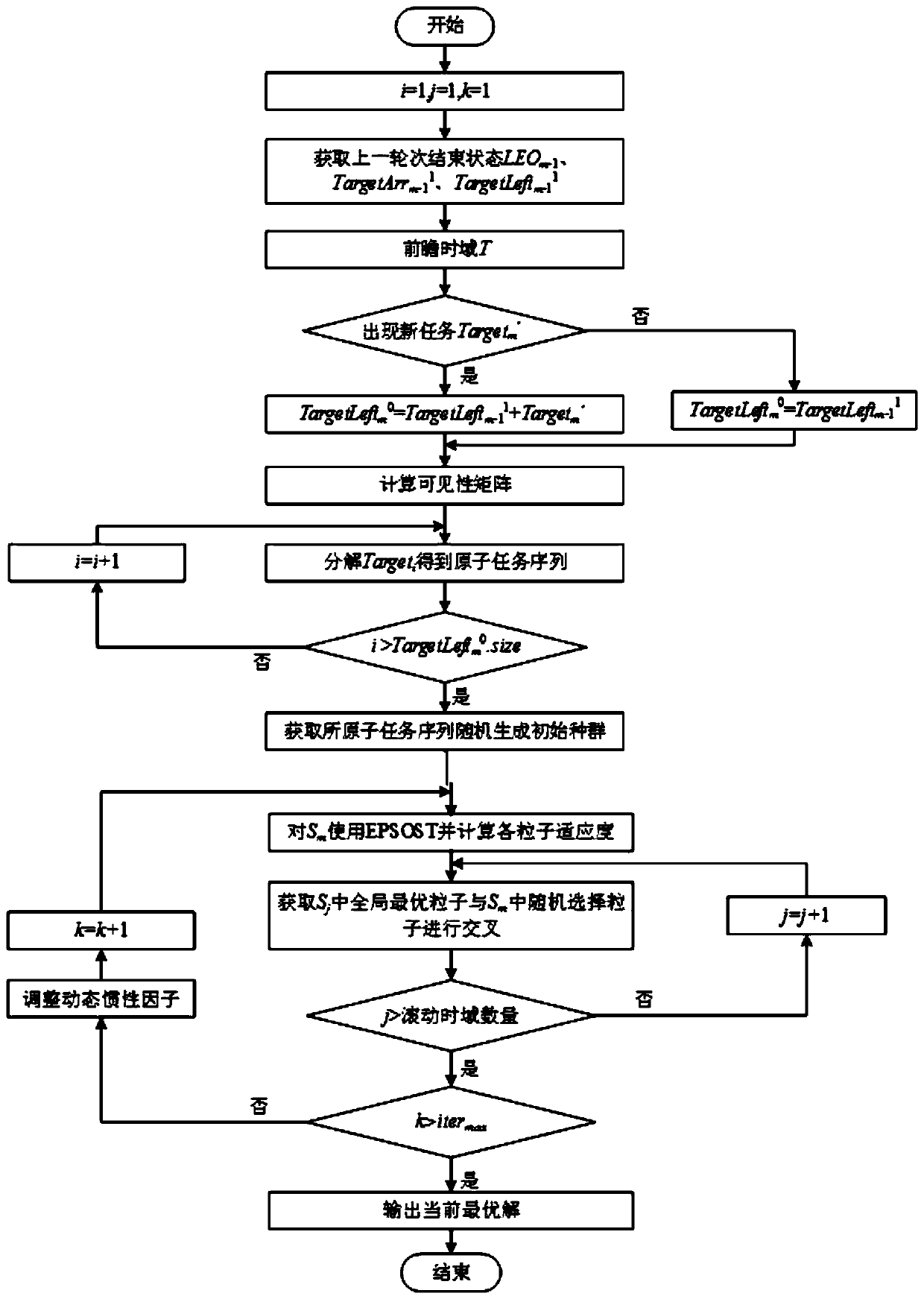
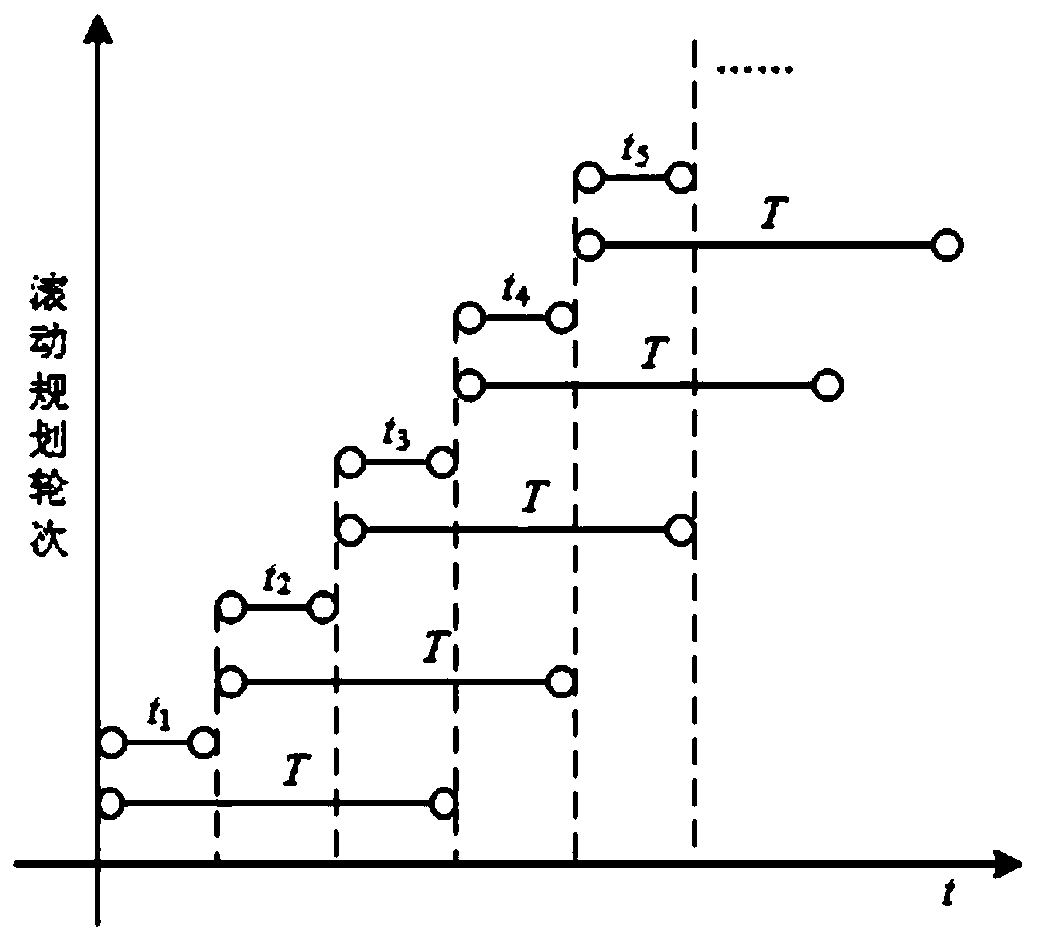
[0103] A multi-satellite coordinated space dynamic target real-time tracking method of the present invention includes two stages: tracking task decomposition based on rolling time domain and multi-satellite coordinated reconnaissance task scheduling, such as figure 1 , 2 As shown, it specifically includes the following steps:
[0104] Step 1, establish a problem model;
[0105] In view of the characteristics of high real-time tracking tasks, difficult recognition, and fine time constraints, in the tracking task decomposition stage, the problem model is first established, including low-orbit satellite and staring detector models, tracking task models, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com