Determining drivable free-space for autonomous vehicles
A technology of free space and vehicles, which is applied in the direction of autonomous decision-making process, vehicle position/route/height control, motor vehicles, etc. Resource consumption, efficiency improvement effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
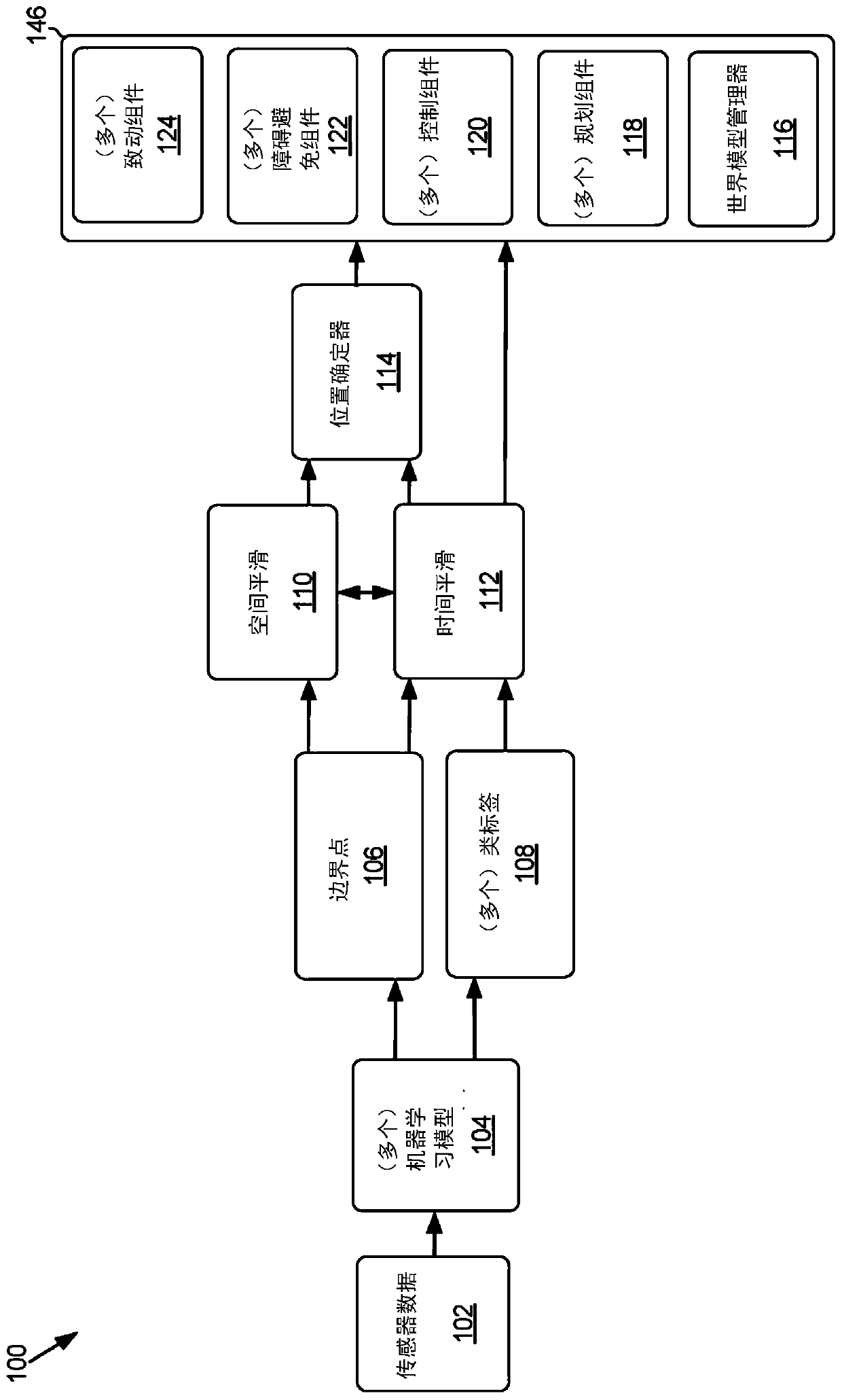
[0024] Systems and methods related to determining drivable free space for an autonomous vehicle are disclosed. The present disclosure may be described with respect to an example autonomous vehicle 700 (alternatively referred to herein as "vehicle 700" or "autonomous vehicle 700"), examples of which are referenced herein Figures 7A-7D described in more detail. However, the present disclosure is not limited to autonomous vehicles, and may be used in advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), robotics, virtual reality (eg, to determine free space for movement of an athlete), and / or in other technical fields. Accordingly, the description herein with respect to the vehicle 700 is for exemplary purposes only and is not intended to limit the present disclosure to any one technical field.
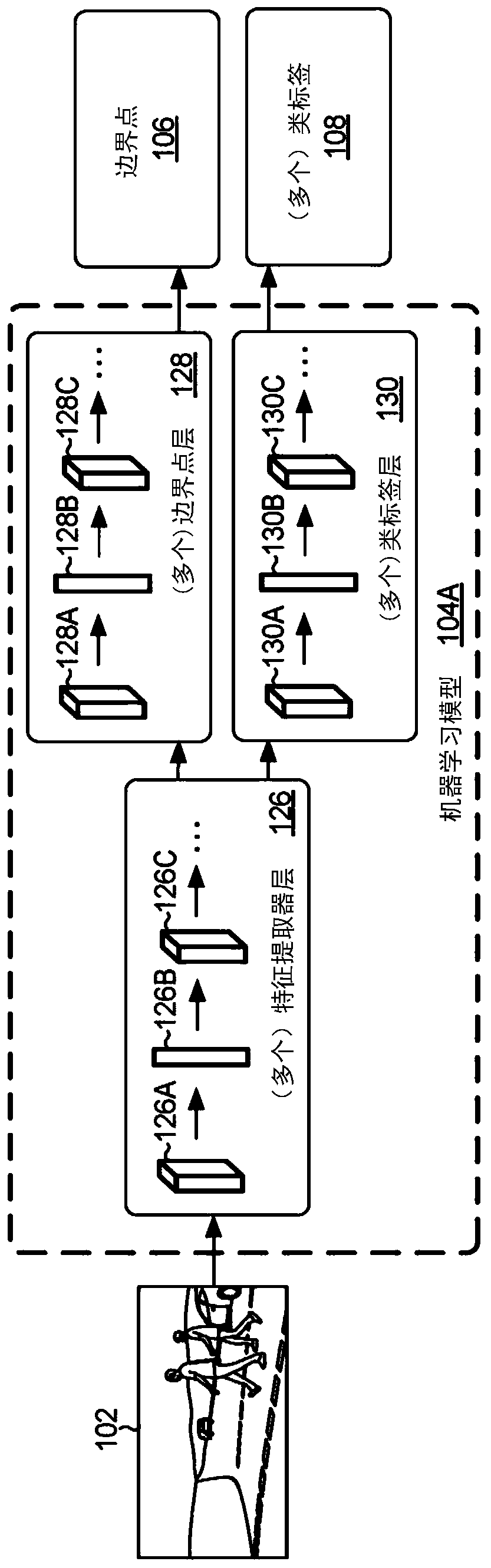
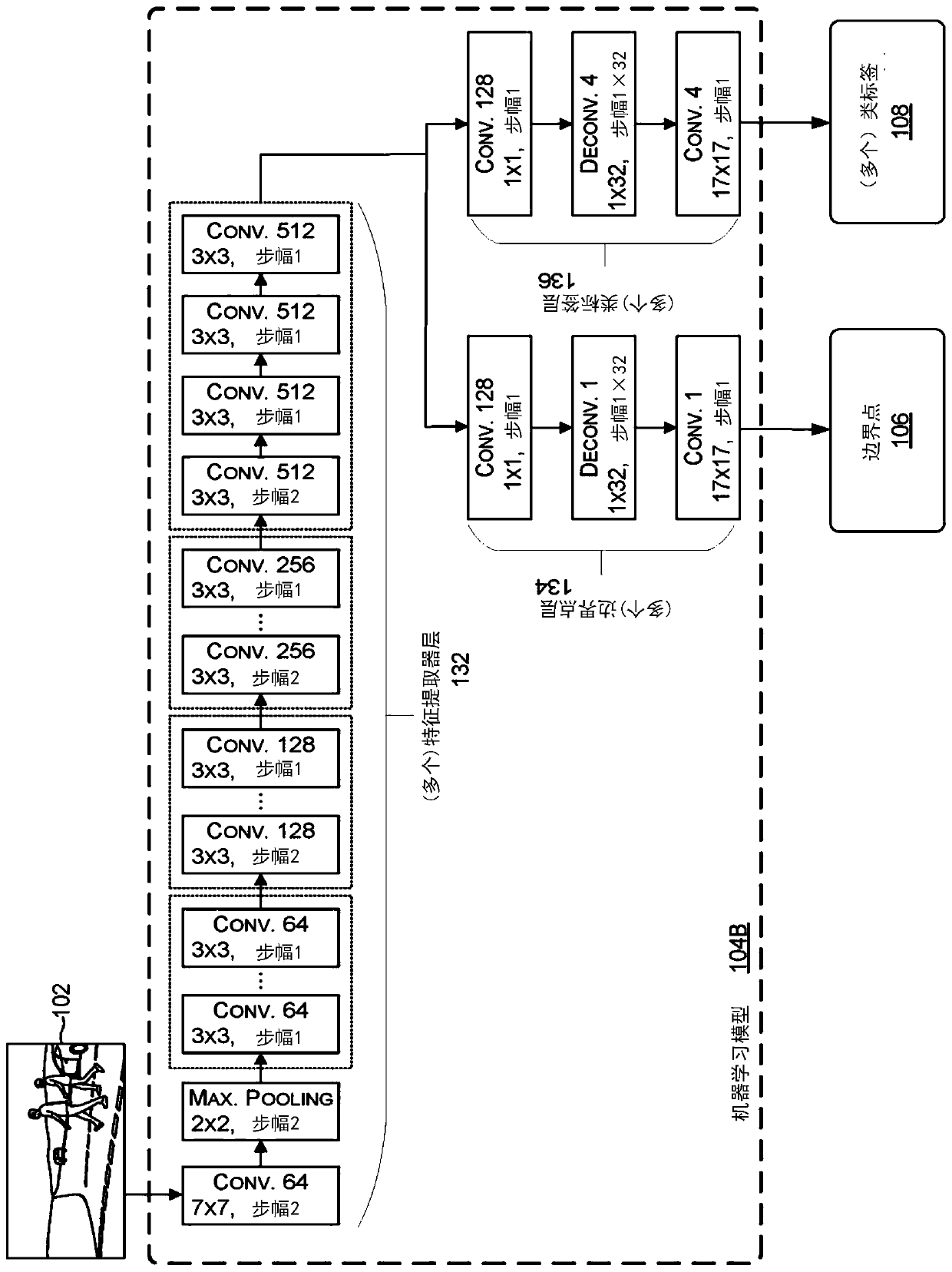
[0025] Boundary point and class label detection system
[0026] As described in this paper, some traditional methods of determining drivable free space can rely on deep neural networks (DNNs) to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com