Biomarker detection method, disease assessment method, biomarker detection device, and biomarker detection program
A technology of biomarker and detection method, applied in the field of biomarker detection, disease judgment, biomarker detection device and biomarker detection program
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
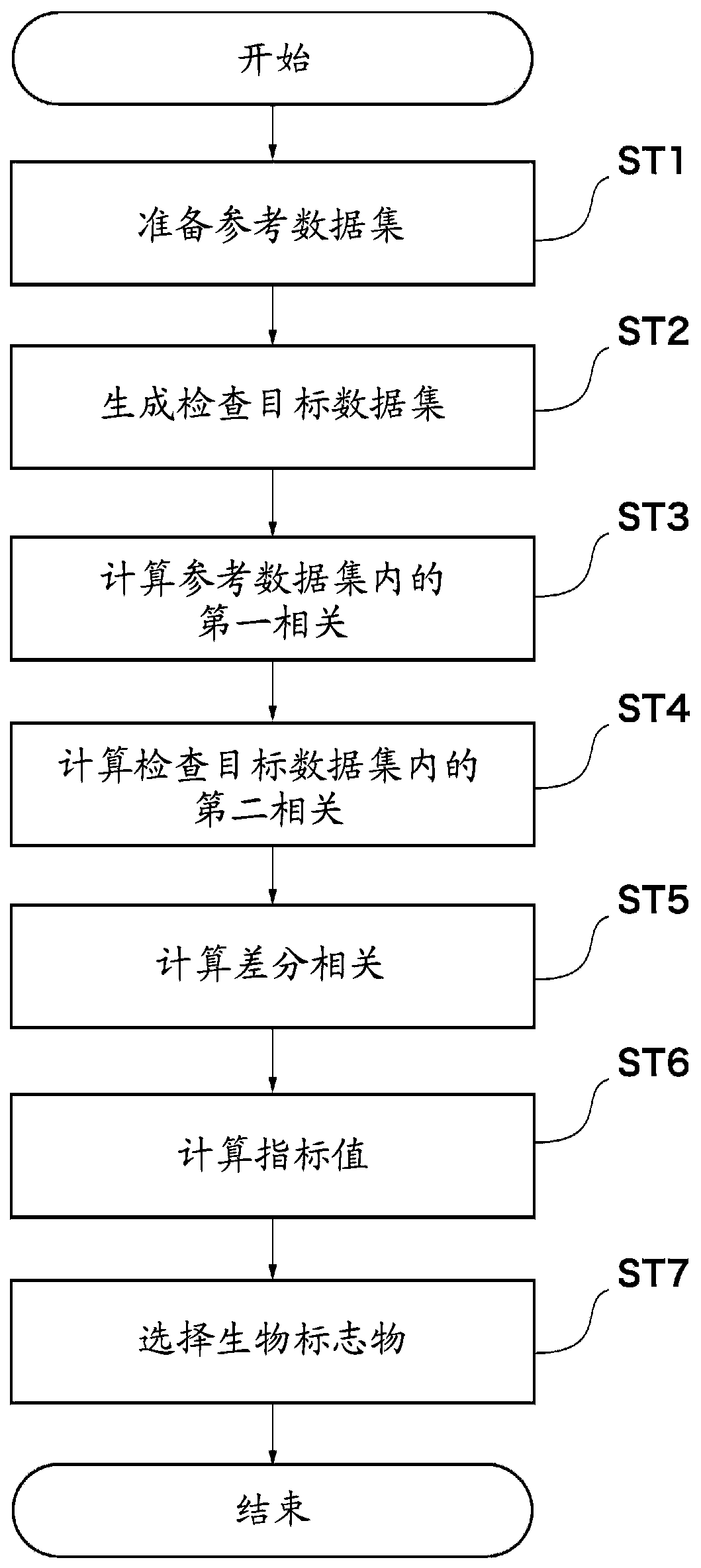
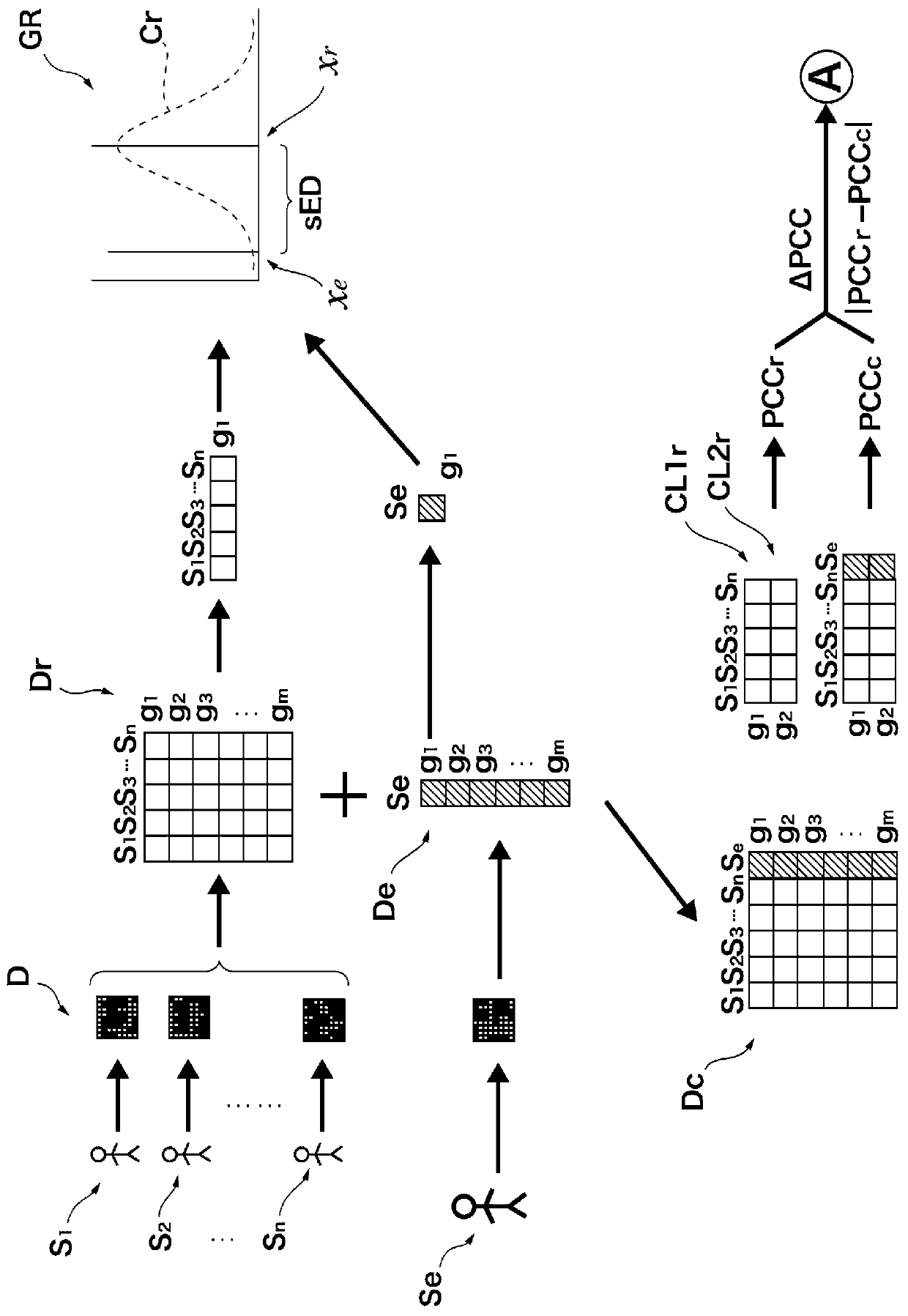
[0032] Below, refer to Figure 2 to Figure 5 The biomarker detection method according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described. figure 2 is a flowchart for explaining the biomarker detection method according to the first embodiment. image 3 and Figure 4 is a schematic diagram showing the biomarker detection method according to the first embodiment.
[0033] Such as figure 2 As shown, the biomarker detection method according to the first embodiment includes: a step of preparing a reference data set (ST1); a step of generating an inspection target data set (ST2); a step of calculating a first correlation coefficient (ST3); The step of two correlation coefficients (ST4); the step of calculating differential correlation coefficients (ST5); the step of obtaining indexes (ST6); and the step of selecting biomarkers (ST7).
[0034]
[0035] First, prepare the reference data set Dr( image 3 ). The reference dataset Dr is a dataset used as reference ...
no. 2 approach
[0067] Next, a biomarker detection device according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figure 6 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the detection device according to the second embodiment. Figure 6 The shown biomarker detection device 1 includes a control unit 10 , a storage unit 11 , a storage unit 12 , an input unit 13 , an output unit 14 and an interface unit 15 .
[0068] The control unit 10 is configured using circuits such as a CPU (Central Processing Unit) and controls the entire detection device 1 . The storage unit 11 includes a magnetic recording device such as HDD (Hard Disk Drive) and a nonvolatile auxiliary recording device such as SSD (Solid State Drive). The storage unit 11 records various programs including the detection program 11a according to the embodiment of the present invention. The detection program 11a includes instructions (codes) for causing the detection device 1 to implement the biomarker detect...
no. 3 approach
[0080] Below, refer to Figure 7 The biomarker detection method according to the third embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figure 7 is a flowchart showing a biomarker detection method according to the third embodiment.
[0081] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the biomarker detection method according to the third embodiment includes a step of acquiring high-throughput data (ST11), a step of selecting differential factors (ST12), a clustering step (ST13) and a step of selecting biomarkers (ST14).
[0082] First, in the step of acquiring high-throughput data (ST11), high-throughput data are obtained from the subject Se at different time points. Specifically, first, living body samples are collected from the subject Se a plurality of times in chronological order. The number of biopsy samples collected is preferably 5 or more, for example. In addition, each time interval may be set to several days, weeks, months or years, or may be, for example, minutes or hour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com