Stability control method and system aiming at space non-cooperative target capturing
A stable control method, non-cooperative target technology, applied in attitude control, sustainable transportation and other directions, can solve the problems of poor controllability of control mode switching process, very sensitive environmental parameter changes, increased system oscillation, etc., to improve the rapid stability capability and position tracking accuracy, reducing sensitivity, and mitigating the effects of collision impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
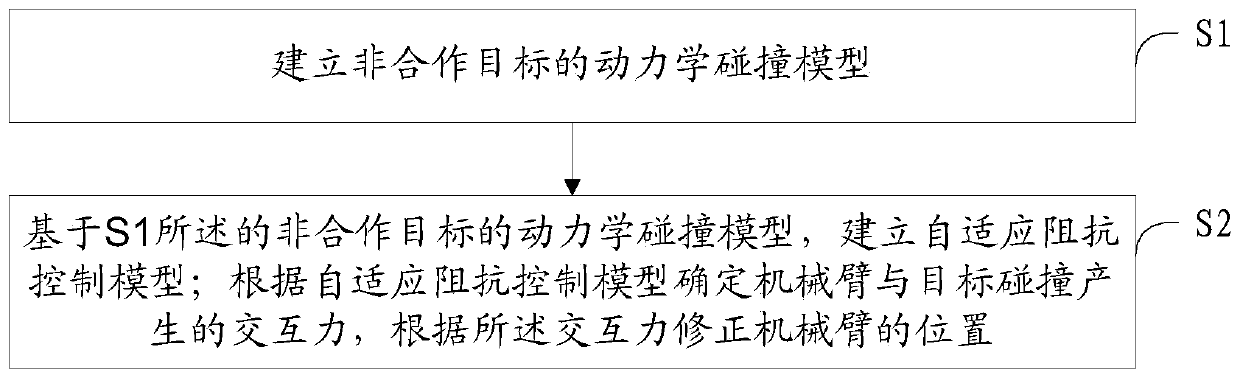
[0050] A stable control method for capturing non-cooperative targets in space, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0051] S1. Establish a dynamic collision model for non-cooperative targets.
[0052] The dynamic collision model for non-cooperative targets is:
[0053]
[0054] In the formula, F ext is the interaction force generated by the collision between the manipulator and the target, D ext and K ext are the damping coefficient of the collision environment and the stiffness coefficient of the collision environment, x t is the actual position of the gripper captured by the manipulator, x target , v target 、a target are the position, velocity and acceleration of the captured target respectively, M target is the mass of the capture target.
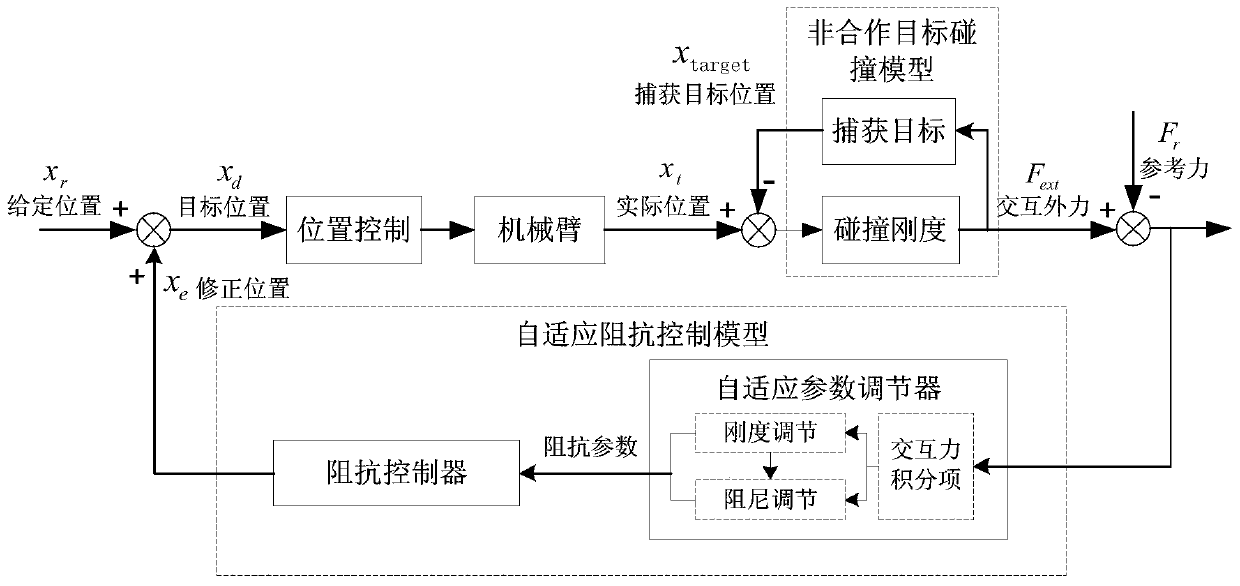
[0055] S2. Based on the dynamic collision model of the non-cooperative target described in S1, determine the interaction force generated by the collision between the manipulator and the target; establish an ...
Embodiment 2
[0066] A stable control system for capturing non-cooperative targets in space, characterized in that it includes a dynamic collision module and an adaptive impedance control module;
[0067] The dynamic collision module is used to establish a dynamic collision model of the non-cooperative target, and then output the dynamic collision model of the non-cooperative target to the adaptive impedance control module.
[0068] The dynamic collision model for non-cooperative targets is:
[0069]
[0070] In the formula, F ext is the interaction force generated by the collision between the manipulator and the target, D ext and K ext are the damping coefficient of the collision environment and the stiffness coefficient of the collision environment, x t is the actual position of the gripper captured by the manipulator, x target , v target 、a target are the position, velocity and acceleration of the captured target respectively, M target is the mass of the capture target.
[007...
Embodiment 3
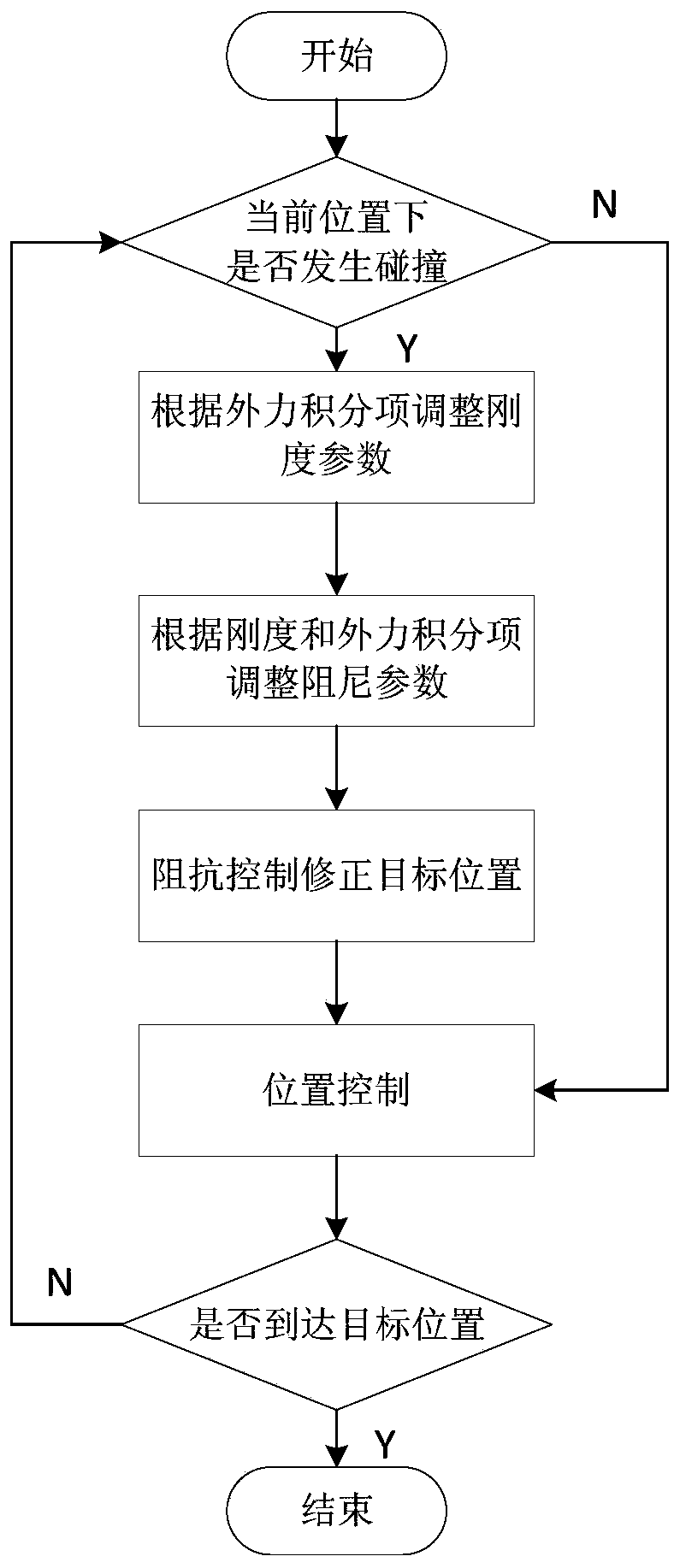
[0082] The capture process flow of this embodiment is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0083] (a) Adaptive impedance controller design
[0084] (a.1) Establish a dynamic collision model for non-cooperative targets
[0085] When a floating non-cooperative target collides with the robotic arm, the capture claws quickly close to capture the target. Therefore, it is first necessary to establish a dynamic collision model of non-cooperative targets to more truly reflect the position constraints and dynamic interactions between the manipulator and the target during the capture process, as shown in formula (1).
[0086]
[0087] Among them, M target is the mass of the capture target, x target , v target , a target are the position, velocity and acceleration of the capture target, respectively. The collision environment is equivalent to a spring-damper system, F ext is the interaction force generated by the collision between the manipulator and the target, D ext and K ext are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com