Medium-wave infrared long-focus lens
A focal length and lens technology, applied in the optical field, can solve the problems of small focal power, long focal length, and inappropriateness, and achieve the effect of light weight, small size, and reduced overall length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
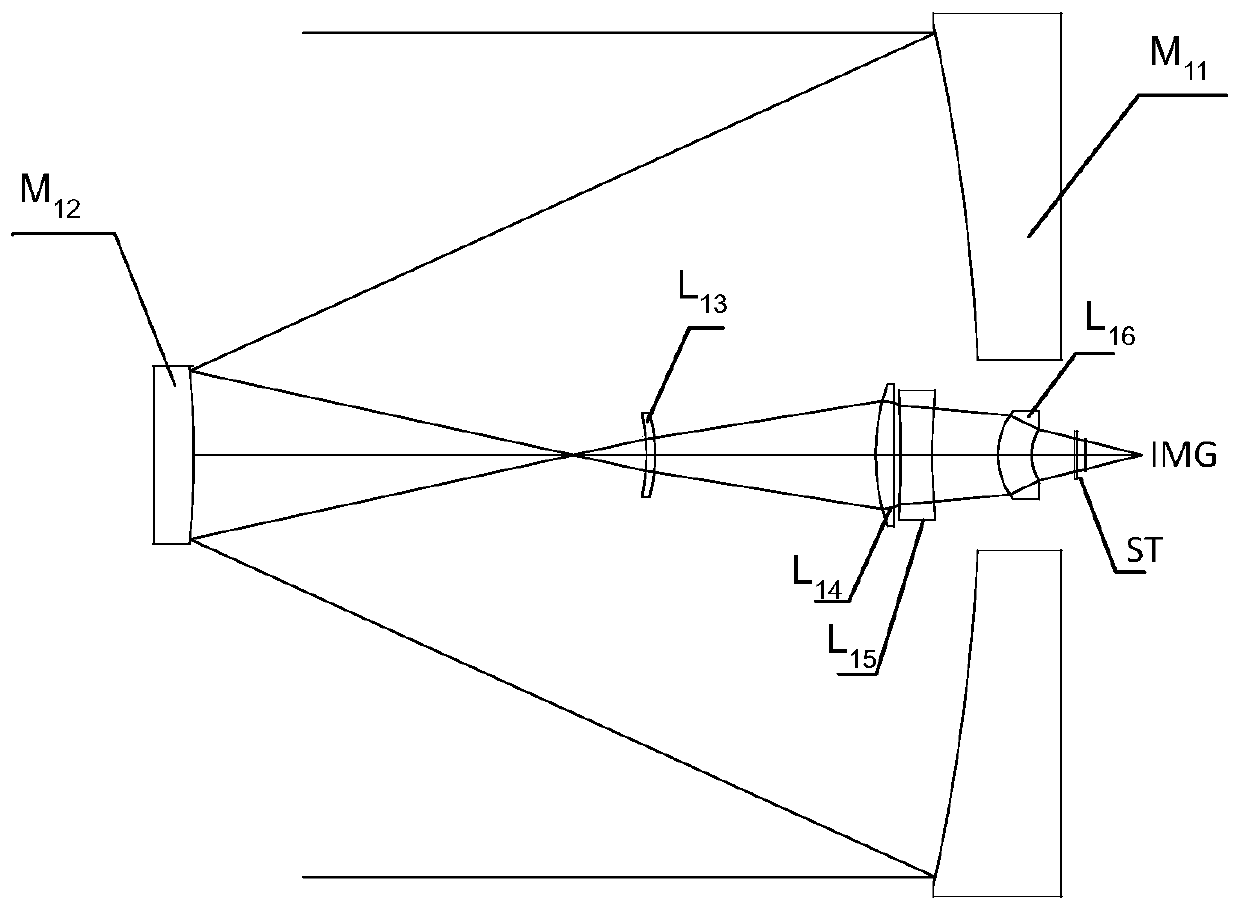
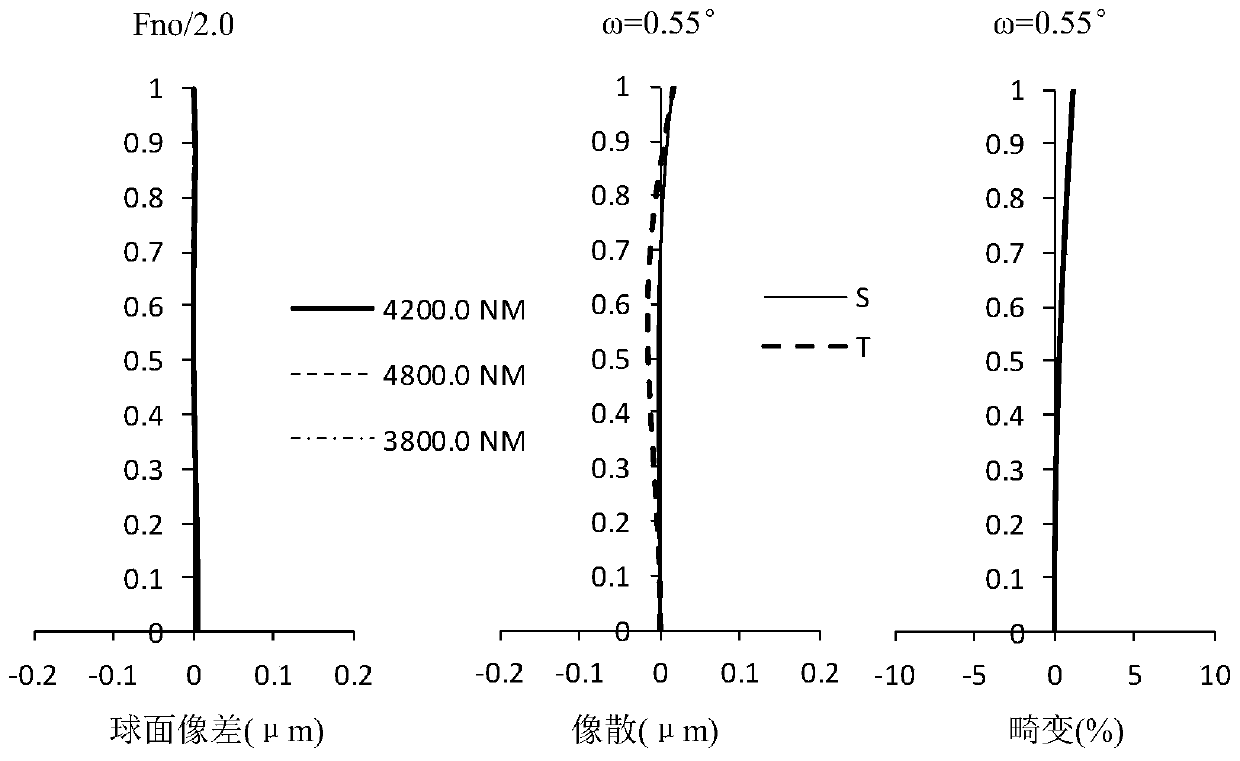
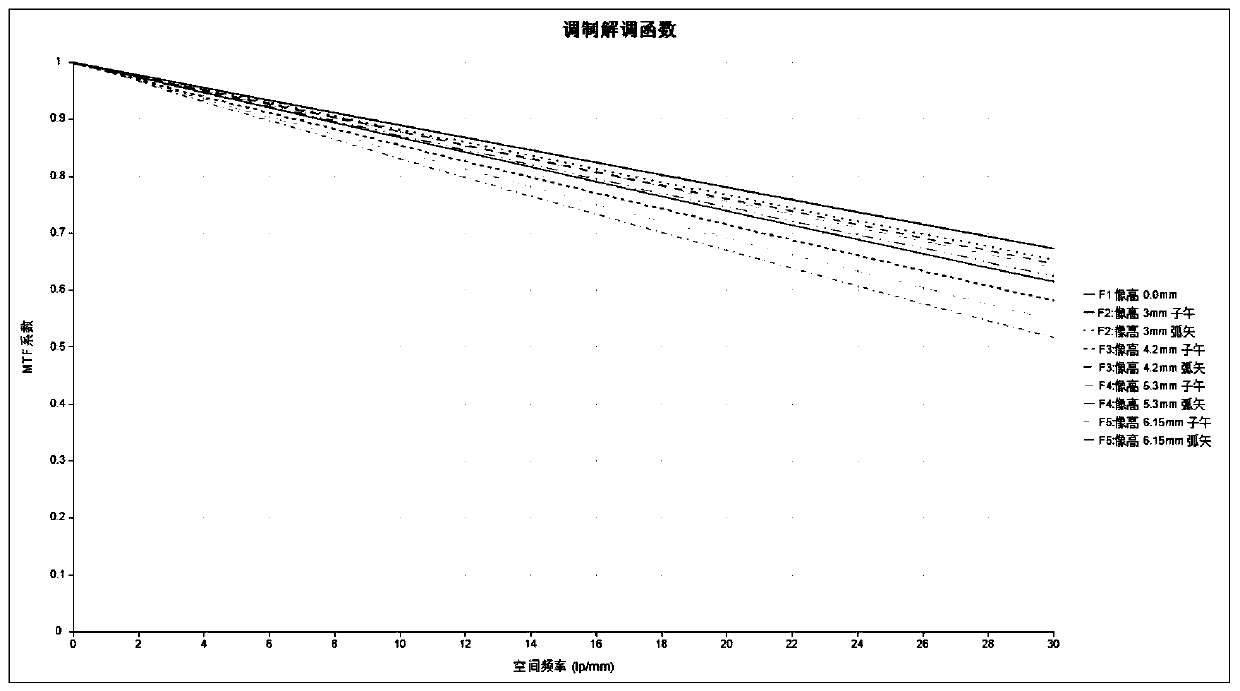
[0054] figure 1It is a sectional view along the optical axis showing the structure of the telephoto lens of Example 1. The long focal length lens is composed of: a reflection mirror group with positive refractive power and a transmission mirror group with positive refractive power. The reflector group is constituted as, the main reflector M 11 , the secondary reflector M 12 ; The lens group is composed of: positive lens L 13 , positive lens L 14 , negative lens L 15 and positive lens L 16 , followed by a cold stop ST and an image plane IMG.
[0055] Various numerical data about the mid-wave infrared telephoto lens of Example 1 are shown below.
[0056] (basic data of the optical system)
[0057] name Face number type radius of curvature thickness Material S0 object side INF INF primary mirror M1 Aspherical -721.32 -290.37 secondary mirror M2 sphere -297.70 167.12 lens 1 S3 sphere -68.43 3.20 silicon ...
Embodiment 2
[0063] Figure 4 It is a sectional view along the optical axis showing the structure of the telephoto lens of Example 2. The long focal length lens is composed of: a reflection mirror group with positive refractive power and a transmission mirror group with positive refractive power. The reflector group is constituted as, the main reflector M 21 , the secondary reflector M 22 ; The lens group consists of: negative lens L 23 , positive lens L 24 , negative lens L 25 and positive lens L 26 , followed by a cold stop ST and an image plane IMG.
[0064] Various numerical data about the mid-wave infrared telephoto lens of Example 2 are shown below.
[0065] (basic data of the optical system)
[0066] name Face number type radius of curvature thickness Material S0 object side INF 0.000 primary mirror M1 Aspherical -632.94 -225.00 secondary mirror M2 sphere -586.07 173.72 lens 1 S3 Aspherical 55.99 8.00 germa...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Figure 7 It is a sectional view along the optical axis showing the structure of the telephoto lens of Example 3. The long focal length lens is composed of: a reflection mirror group with positive refractive power and a transmission mirror group with positive refractive power. The reflector group is constituted as, the main reflector M 31 , the secondary reflector M 32 ; The transmission lens group is composed of: negative lens L 33 , positive lens L 34 and positive lens L 35 , followed by a cold stop ST and an image plane IMG.
[0071] Various numerical data about the mid-wave infrared telephoto lens of Example 3 are shown below.
[0072] (basic data of the optical system)
[0073] name Face number type radius of curvature thickness Material S0 object side INF 0.000 primary mirror M1 Aspherical -492.01 -173.63 secondary mirror M2 Aspherical -422.29 61.73 S3 INF 61.73 lens 1 S4 Aspheric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com