A variable stiffness wrist structure and surgical robotic arm of a surgical robot
A surgical robot and variable stiffness technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of harmfulness to the human body, large size, and bloated mechanism, and achieve the effect of reasonable strength requirements, good biological affinity, and reduced geometric size
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Attached below Figure 1-Figure 10 The present invention is described in detail, specifically, the structure is as follows:
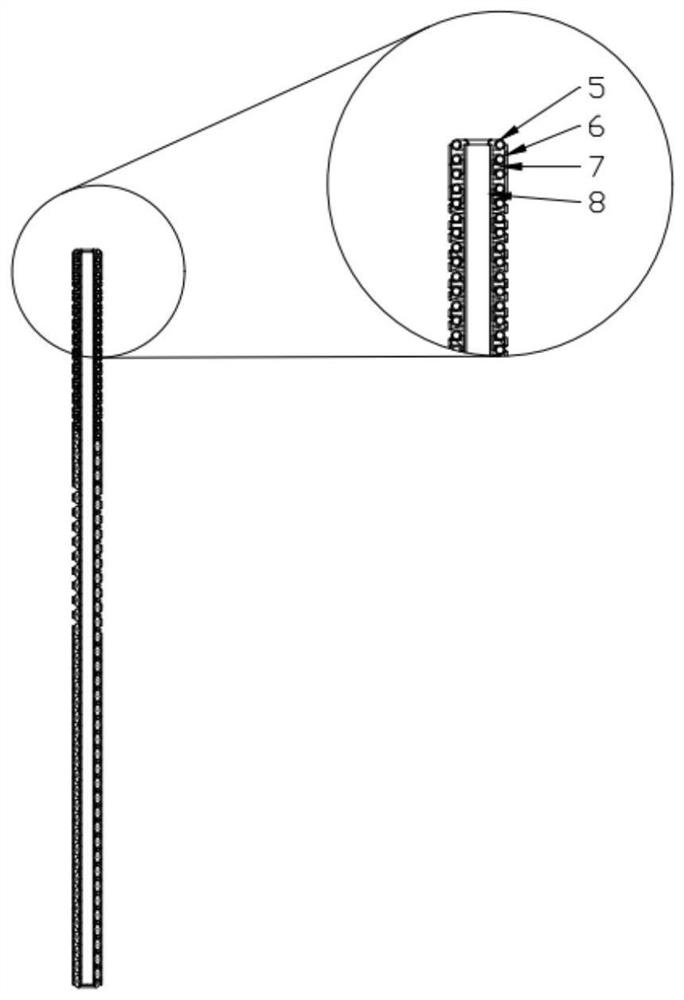
[0039] This embodiment provides a variable stiffness wrist structure of a surgical robot, including an elastic skeleton 8, a notched shape memory alloy tube 6, and a flexible temperature control tube 5. The elastic skeleton 8 is located in the middle, and it adopts a hollow structure to facilitate subsequent terminal execution. The wire driver is required to drive the wire through. A chuck mechanism is installed on the elastic skeleton 8 so as to relatively fix the driving wire 11 to the driven part for easy driving.
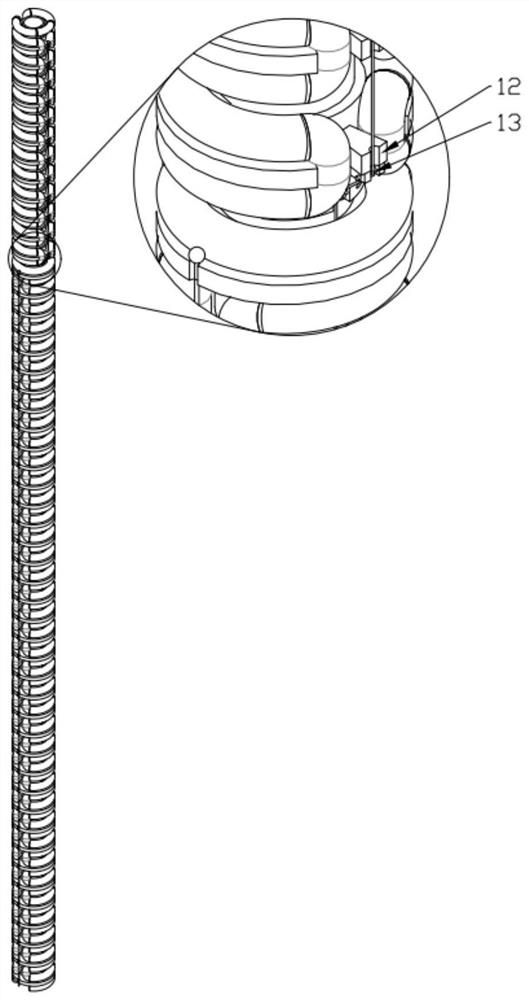
[0040] Such as figure 1 As shown, the elastic skeleton 8 is provided with a flexible temperature control tube 5 on the outer side of the circumference, and the outer side of the flexible temperature control tube 5 is provided with a notched shape memory alloy tube 6 . The flexible temperature control tube 5 adopts a new winding ...
Embodiment 2
[0051] Such as Figure 11-Figure 13 As shown, this embodiment provides a surgical robot arm, including a drive unit and the variable stiffness wrist structure described in Embodiment 1. The drive unit is connected to the variable stiffness wrist structure through a driving wire 11, so that the variable stiffness wrist structure The internal structure can move axially and rotate in two vertical directions, and cooperate with the end effector to meet the overall degree of freedom requirements of the robotic arm of the surgical robot. The variable stiffness wrist structure is driven by the drive unit, which is smaller and more flexible.
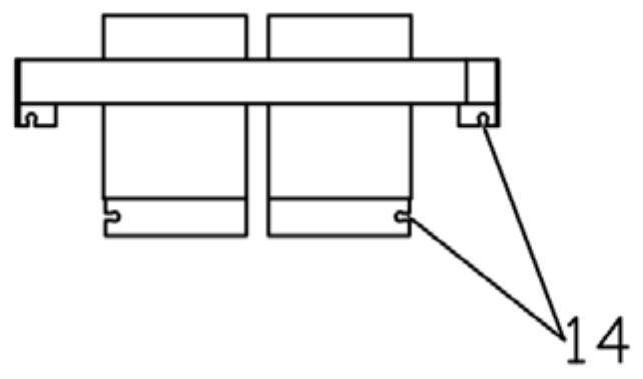
[0052] Specifically, the drive unit includes a gusset box 2, a gusset cover 1 and multiple sets of motors, the gusset box 2 and the gusset cover 1 form a closed structure; In this embodiment, a rectangular installation space is formed inside the gusset box 2 and the gusset cover 1 . It can be understood that in other embodiments, the closed st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com