Infrared target detection method
A technology of infrared target and detection method, which is applied in the field of multi-scale infrared target detection, can solve the problems of slow speed and low detection accuracy, achieve effective results and reduce computing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
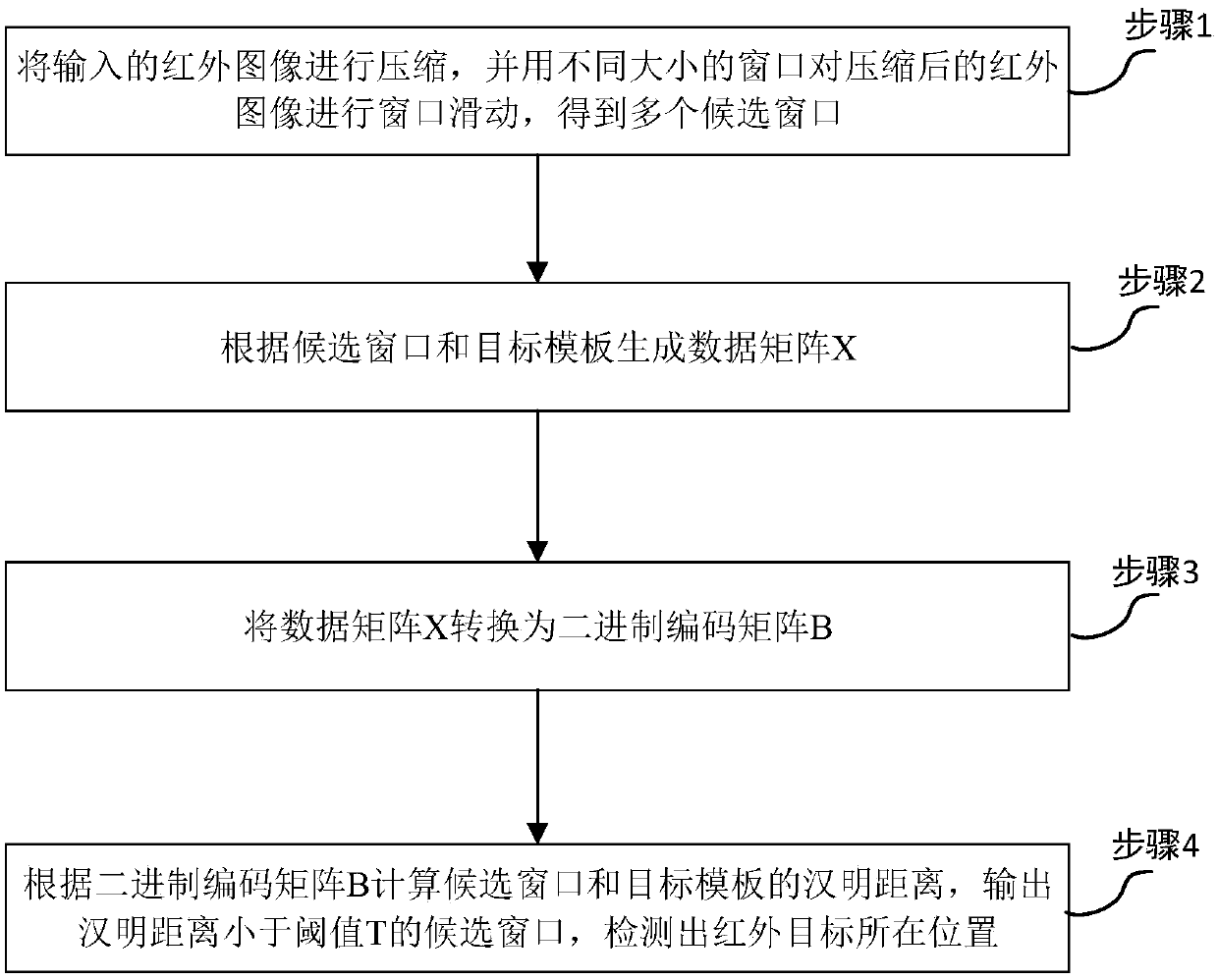
[0047] Refer to attached figure 1 , a multi-scale infrared target detection method based on iterative quantization-locality sensitive hashing, including the following steps:
[0048] Step 1. Compress the input infrared image, and use windows of different sizes to perform window sliding on the compressed image to obtain multiple candidate windows;
[0049] Step 2, generate a data matrix X according to the candidate window and the target template;
[0050] Specifically, when detecting and recognizing an infrared target, under the condition of ensuring correct detection and recognition of the target, the number of candidate windows can be reduced by compressing the image, thereby shortening the detection time. Since the objects to be detected have different sizes and shapes in the infrared image, windows of different sizes should be used to slide the infrared image to obtain candidate windows.
[0051] Set windows of different sizes, and then slide the multiple windows sequenti...
Embodiment 2
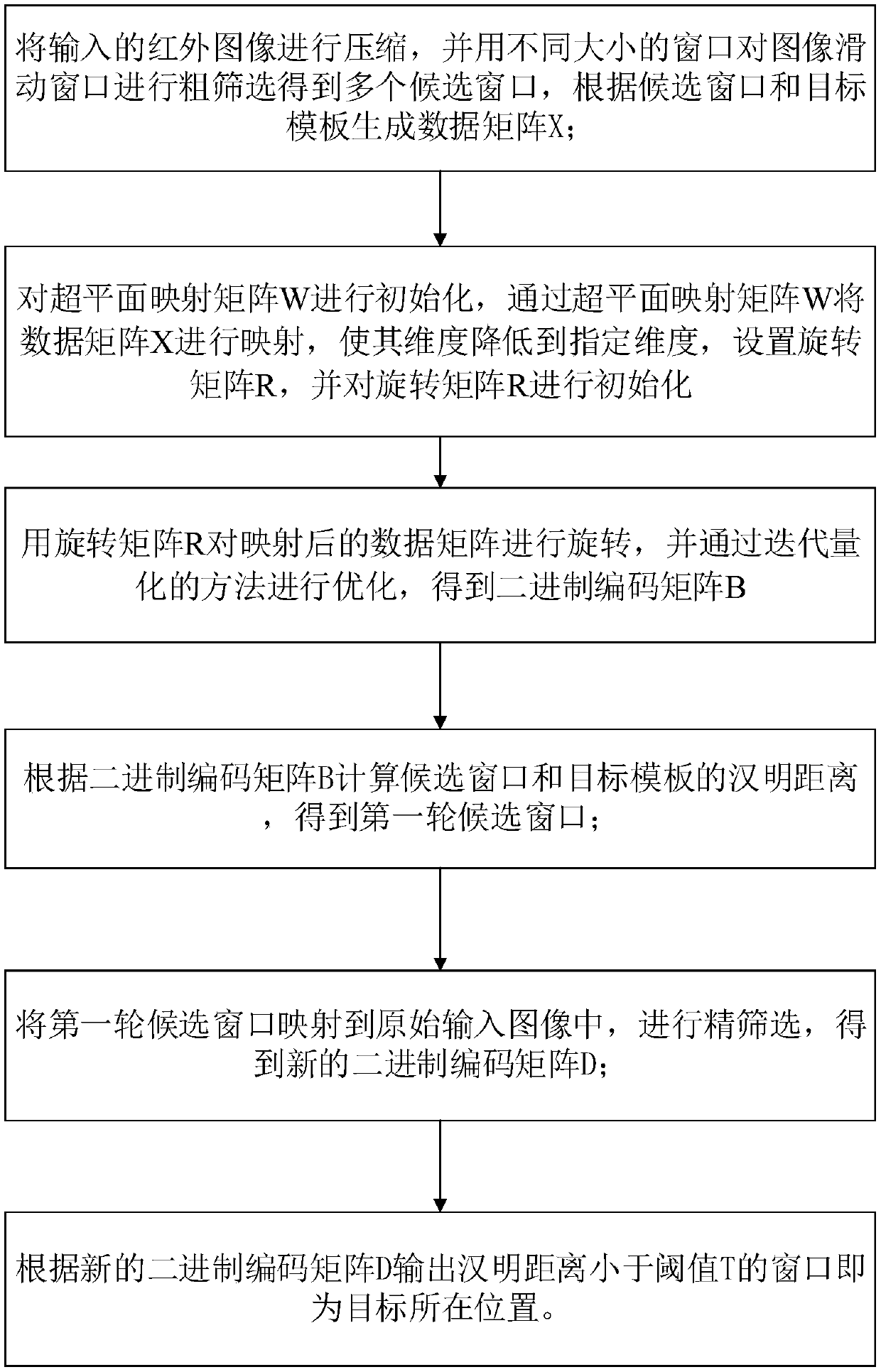
[0066] On the basis of the first embodiment above, in order to reduce the quantization error that occurs during the conversion of the data matrix X into the binary coding matrix B and improve the target detection hit rate, this embodiment adopts an iterative quantization method to obtain the optimal rotation matrix R, and correspondingly calculate the optimal binary coding matrix B, the process is as follows:
[0067] On the basis of the binary coding matrix B in embodiment one, set transition matrix C=XWB ', carry out singular value decomposition to C'C and CC ', make C'C=U 1 ΣU' 1 , CC'=U 2 ΣU' 2 , let the rotation matrix R=U 1 u 2 , where B' is the transposition of the binary coding matrix B, and C' is the transposition of the transition matrix C; by transposing the binary coding matrix B and bringing it into the transition matrix C, a new rotation matrix R is obtained, that is, from the step The initial rotation matrix R in step 312 obtains a new rotation matrix after...
Embodiment 3
[0070] In the second embodiment, in order to speed up the speed of target detection, the input infrared image is compressed, causing the image to lose some information, so more accurate fine screening is required. This embodiment is further improved on the basis of embodiment two, see figure 2 Shown specifically as follows:
[0071] Calculate the Hamming distance between each candidate window and the target template according to the binary coding matrix B, and select the 10 candidate windows closest to each target template as the first round of candidate windows.
[0072] The Hamming distance refers to the number of different codes in each bit of the same position in two binary codes of the same length, which can measure the similarity of the two binary codes. The smaller the distance, the more similar the candidate window and the target template are. Possibly where the target is located. The binary coding matrix B contains the binary coding of the candidate window and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com