A kind of Aspergillus producing monacolin j and its construction method and application
A technology for producing monacolin and constructing a method is applied in the field of biopharmaceuticals, which can solve the problems of large difference in yield, easy degradation and accumulation of lovastatin, and achieve the effects of enhancing fermentation stability, simplifying production process and reducing environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0074] Example 1, Aspergillus genetic transformation
[0075] 1. Preparation of protoplasts
[0076] The spores of Aspergillus HZ01 were inoculated into 50 mL of IPM liquid medium so that the spore concentration was about 10 7 cells / mL, cultured at 200rmp and 32°C for 12-18h. The growing mycelia were collected by filtration through a sterile monolayer of 500-mesh nylon cloth and washed with sterile 0.6M MgSO. 4 The solution was rinsed three times, dried and placed in a sterile 50ml conical flask. An appropriate amount of enzymolysis solution was added according to the weight of mycelium (10ml of enzymolysis solution was added per 1g of mycelium), and treated at 30°C and 60rpm for 1-3h. The mixed solution after the enzymolysis was first filtered with 8 layers of lens-wiping paper, and the filtrate was collected. Protoplasts were collected by centrifugation at 4°C, 4000 rpm, washed once with pre-cooled 1.0 M sorbitol solution, and then pre-cooled with STC (STC composition: 1....
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2. Complete knockout of lovF gene
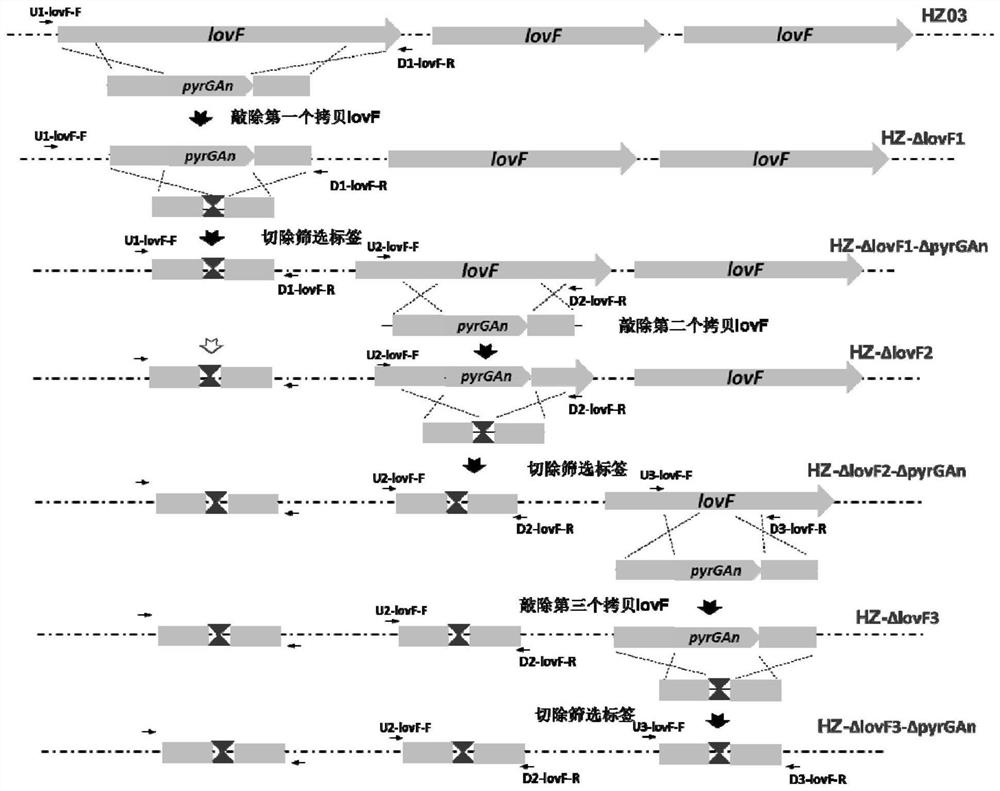
[0080] Knock out the lovF gene to complete the knockout of all copies. All primer positions and gene knockout strategies are as follows figure 1 shown.
[0081] 1. Knock out the first copy of lovF
[0082] (1) Construction of lovF gene targeting element lovF-KO1
[0083] According to Aspergillus terreus NIH2624 genome information (GenBank: AAJN00000000.1) and Aspergillus terreus HZ01 lovastatin synthesis gene cluster information, the following primers were designed and synthesized:
[0084] U1-lovF-F: 5'-gctcccatagctatggttggc-3' (SEQ ID No. 1);
[0085] U1-lovF-R: 5'-GTTCAATCACCATCTCCCTTAgagtcttcaagacgatcgcagc-3' (SEQ ID No. 2);
[0086] D1-lovF-F: 5'-CGTATTTCTCCGCCTGTGTGatctgcgagtggctggtcgatc-3' (SEQ ID No. 3);
[0087] D1-lovF-R: 5'-gcatctcagaacgggatgctg-3' (SEQ ID No. 4).
[0088] Using Aspergillus HZ01 genomic DNA as a template, pfu DNA polymerase (Fermentas, catalog number: EP0501) was used for PCR amplification, an...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3. Construction of LovE strains overexpressing specific transcriptional regulators
[0145] 1. Design and synthesize the following primers:
[0146] Uku80-F: 5'-agcacaaacatattgatcagc-3' (SEQ ID No. 31);
[0147] pyrGAn-R: 5'-GGATCCTCCCAGAGTGTAAgcatcaaatcgtcgtaccgca-3' (SEQ ID No. 32);
[0148] TtrpC-F3: 5'-aagcttgagatccacttaacgttactgaaatcatc-3' (SEQ ID No. 33);
[0149] Dku80-R: 5'-gaaggcgaaaagtagtctcgtg-3' (SEQ ID No. 34).
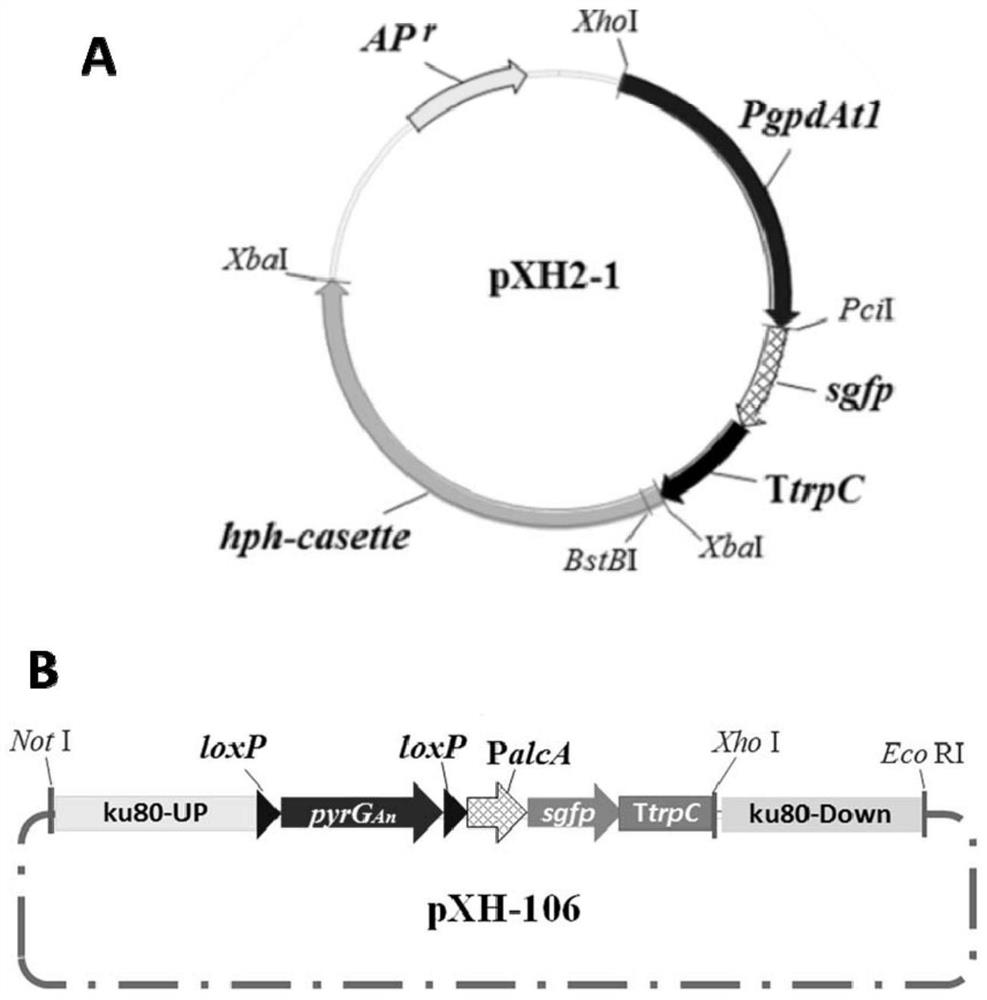
[0150] Using plasmid pXH-106 as a template, PCR amplification was performed with primer pairs Uku80-F / pyrGAn-R and TtrpC-F3 / Dku80-R to obtain the upstream homology arm Uku80-pyrGAn and the downstream homology arm TtrpC-Dku80.
[0151] 2. Design and synthesize the following primers:
[0152] lovE-F: 5'-ACAACTCATCAATCATCACatggctgcagatcaaggtat-3' (SEQ ID No. 35);
[0153] lovE-R: 5'-GTTAAGTGGATCTCAAGCTTcatggaggaatattgttga-3' (SEQ ID No. 36).
[0154] Using Aspergillus HZ01 genomic DNA as a template, the lovE gene fragment was obtained by...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com