Method and system for predictive maintenance of integrated circuits
An integrated circuit, predictive technology, applied in the direction of digital circuit testing, electronic circuit testing, using electrical devices, etc., can solve problems such as time-consuming and cost-effective, and achieve the effect of avoiding downtime, saving costs, and reducing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
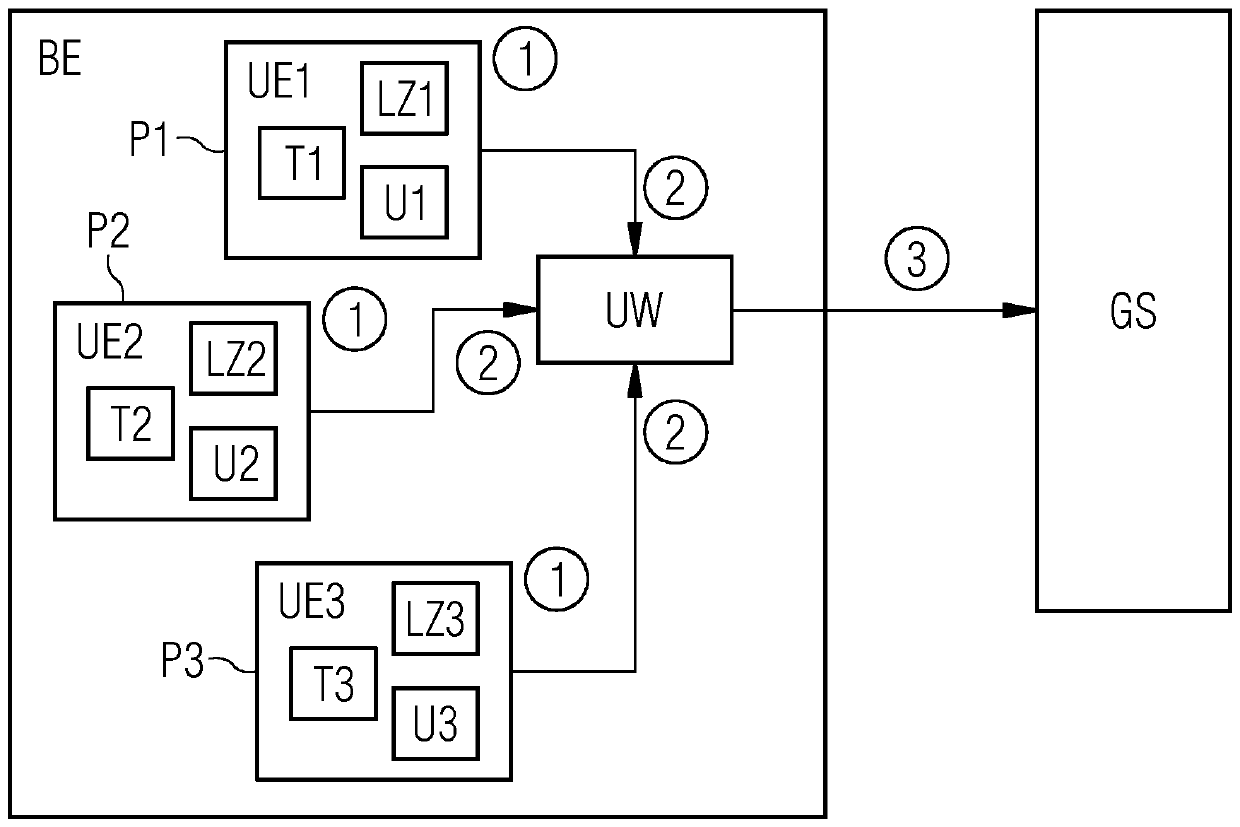
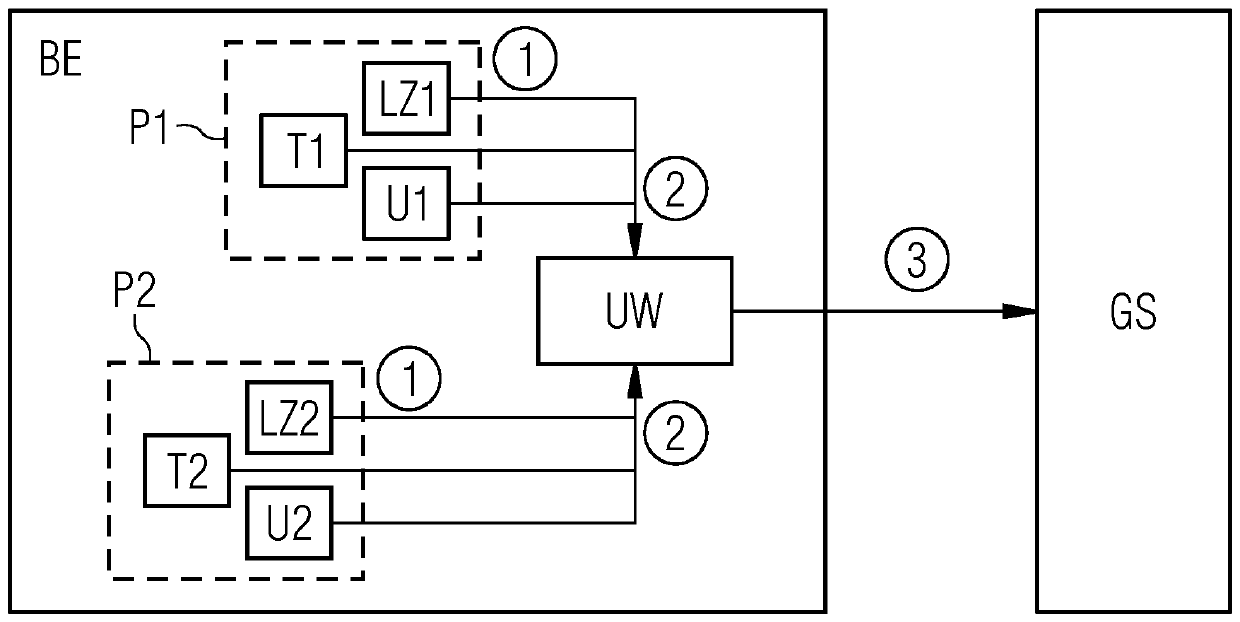
[0033] figure 1 An exemplary electronic device BE is shown schematically. The device BE is implemented as an integrated circuit, for example as an application specific integrated circuit or ASIC. Alternatively, however, the electronics BE can also be embodied as a so-called Field Programmable Gate Array (Field Programmable Gate Array) or FPGA. The electronics BE can be, for example, a system component or a part of a system component in the overall system GS, which serves as a superordinate layer and is designed, for example, as an embedded system GS.
[0034] Among other things for simplicity in figure 1 Outside of units not shown, the figure 1 The electronic device BE shown in exemplarily has a plurality of sensors T1, U1, LZ1, T2, U2, LZ2 at two exemplary positions P1, P2, these sensors are mounted for example on the semiconductor material of the electronic device BE or integrated circuit middle. Current values of system parameters, such as temperature and voltage as ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com