Rigid-flexible composite robot based on minimum energy structure of dielectric elastomer
A dielectric elastomer and robot technology, applied in the field of flexible robots, can solve the problems of low overall deformation, insufficient driving force, unstable movement, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, improved initial tension, and simple structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The technical solution of the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the description of the drawings and specific embodiments.
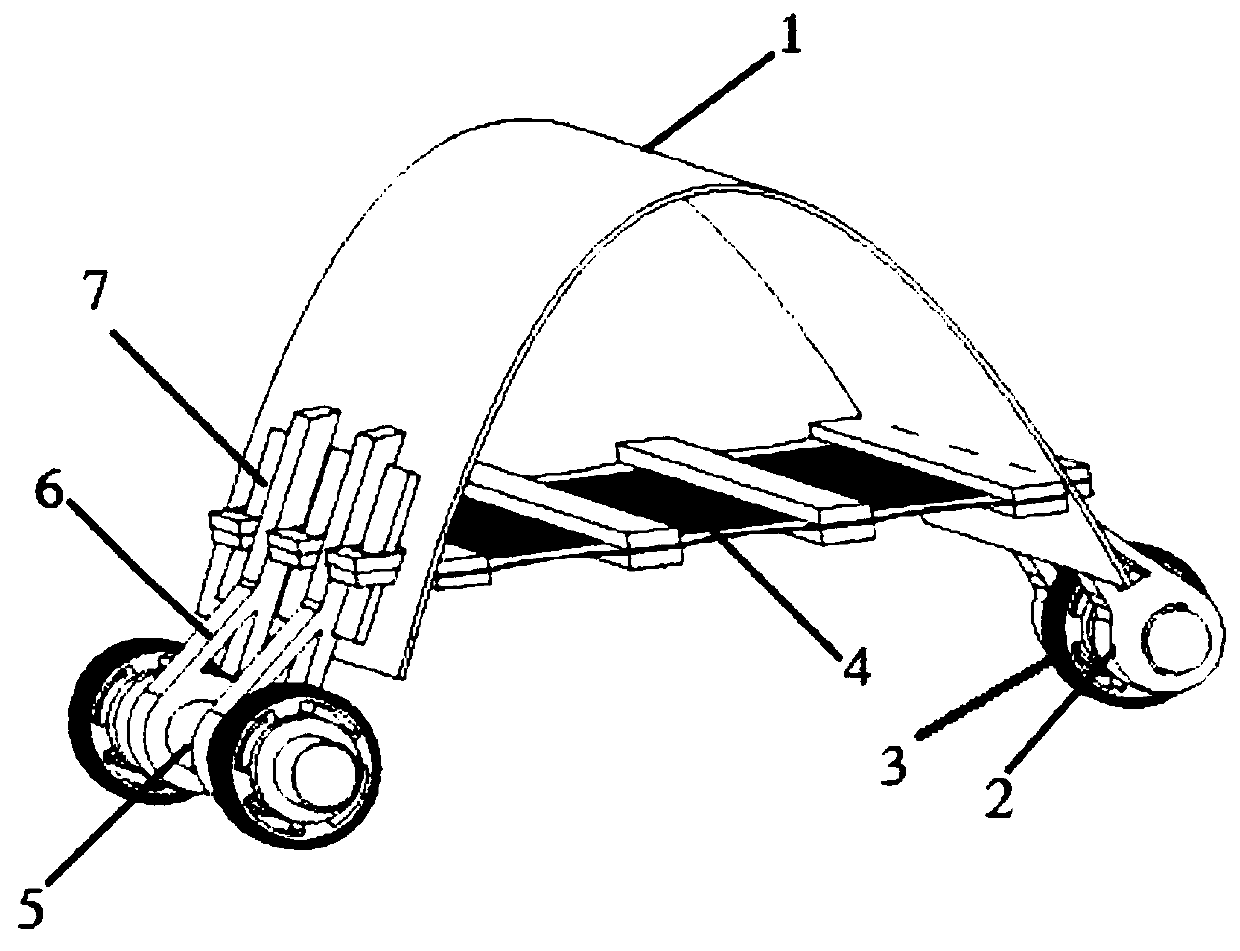
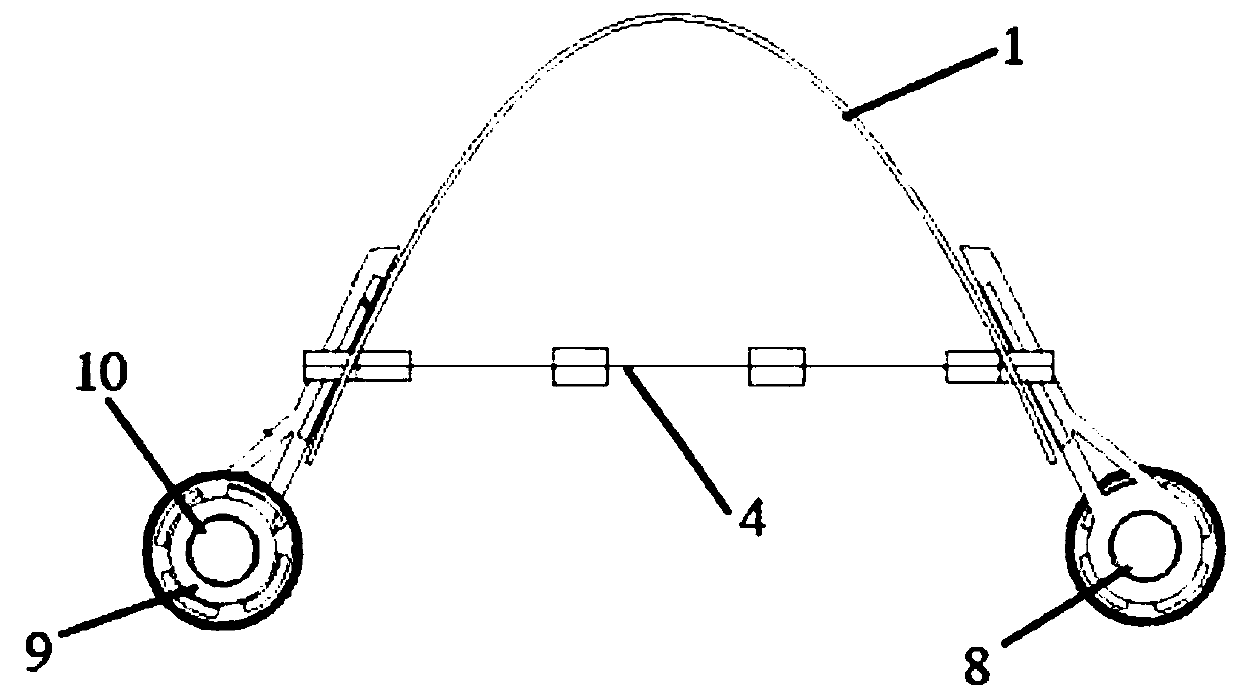
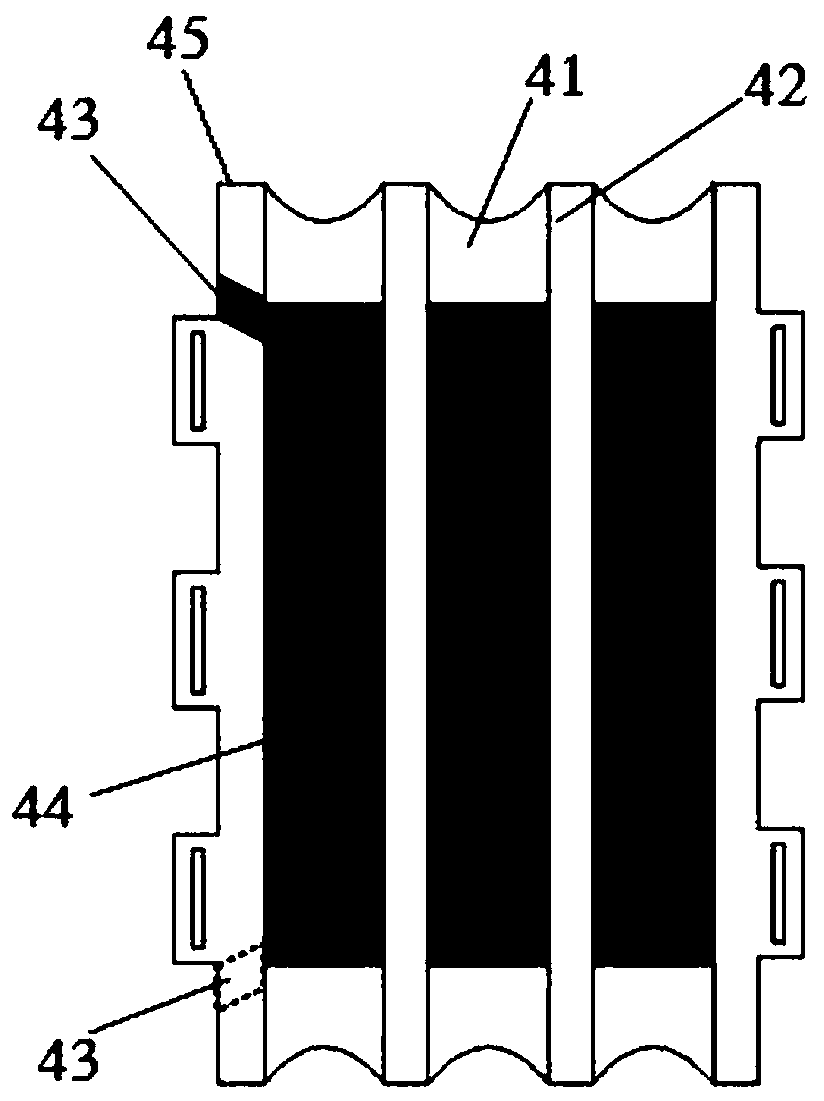
[0021] Such as figure 1 As shown, a rigid-flexible composite robot based on a dielectric elastomer minimum energy structure of the present invention includes a bow-shaped and bendable support element 1, and a drive element 4 that is deformable after voltage is applied to both sides is arranged below the support element 1. The driving element 4 is connected with a control circuit. The two ends of the driving element 4 protrude from the front side and the rear side of the supporting element 1 respectively and are fixed by pins 7. The front side of the supporting element 1 is provided with a front axle connecting rod 2, and the front axle is connected to The rod 2 is connected with the front actuator 3 , the rear side of the support element 1 is provided with the rear axle connecting rod 6 , and the rear a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com