Patents
Literature
504 results about "Dielectric elastomers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
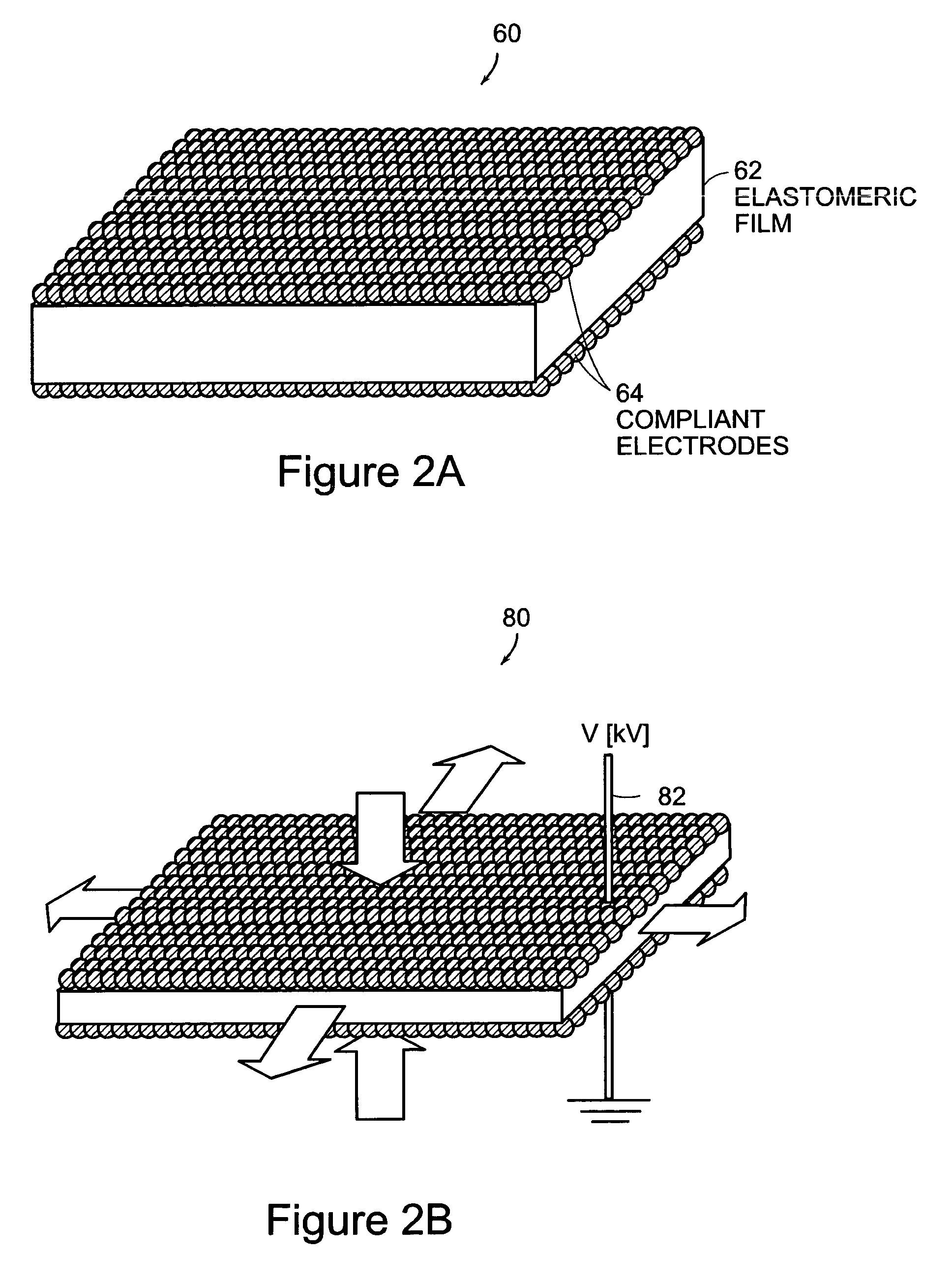
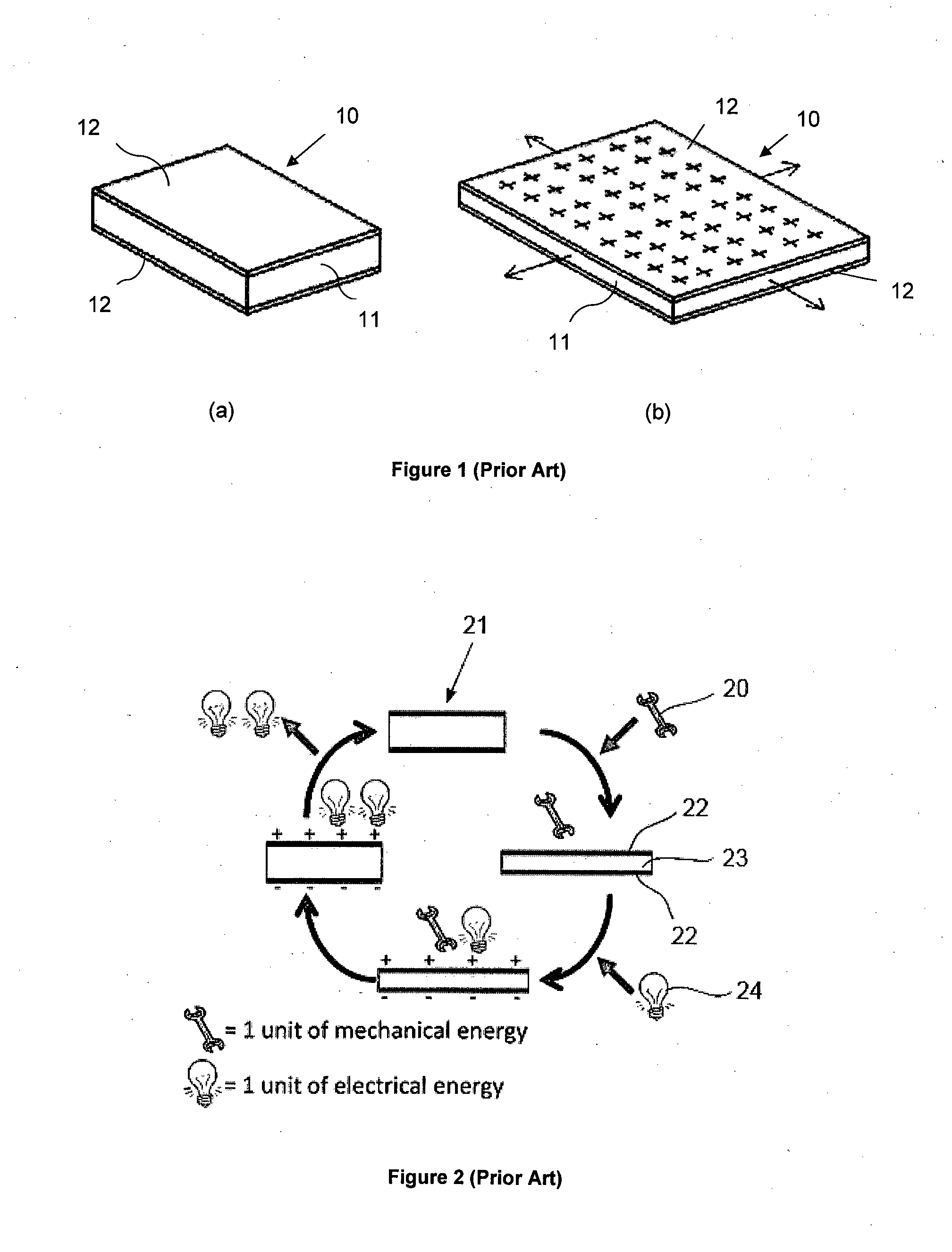
Dielectric elastomers (DEs) are smart material systems that produce large strains. They belong to the group of electroactive polymers (EAP). DE actuators (DEA) transform electric energy into mechanical work. They are lightweight and have a high elastic energy density. They have been investigated since the late 1990s. Many prototype applications exist. Every year, conferences are held in the US and Europe.
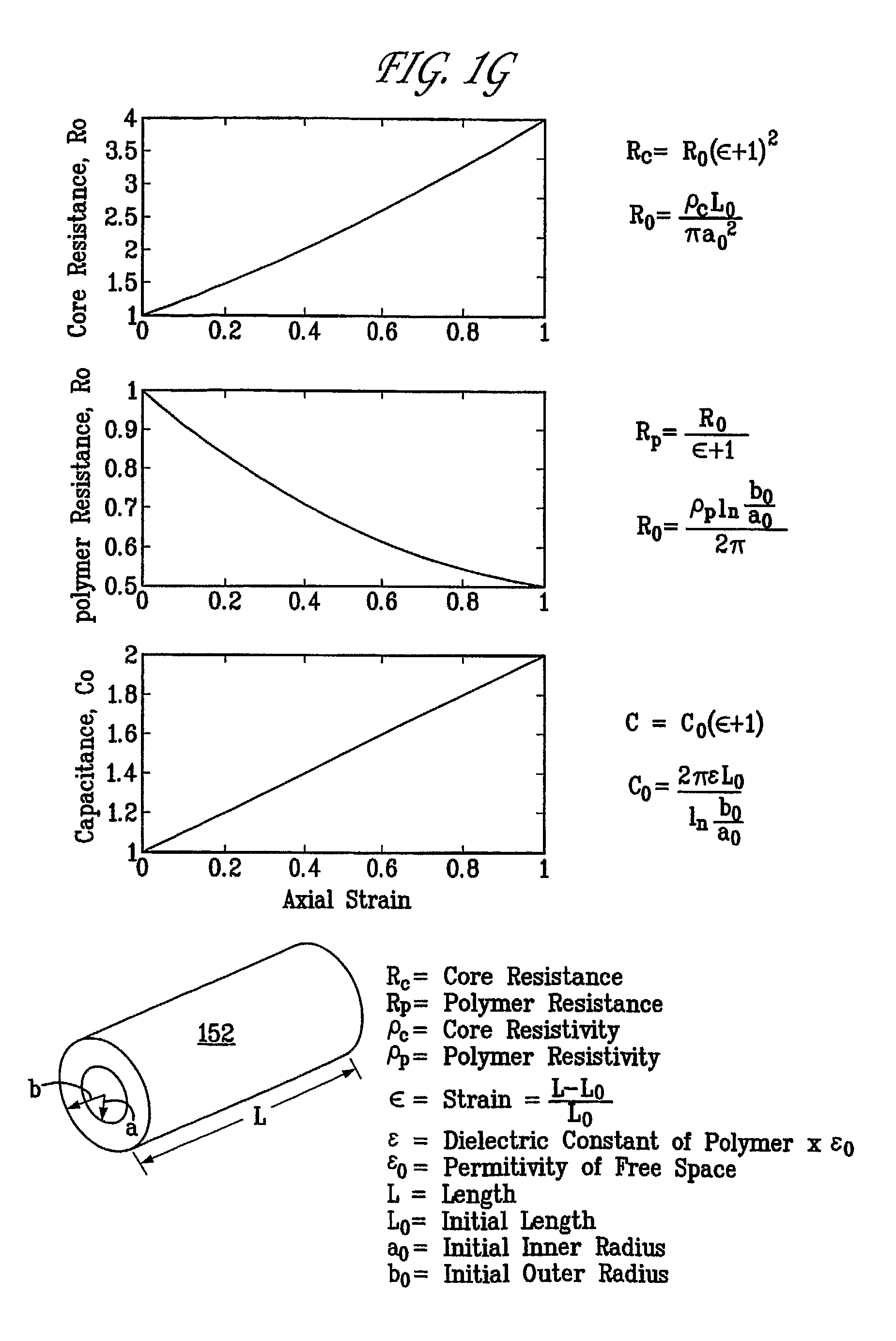
Dielectric elastomer fiber transducers
ActiveUS20090085444A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesTransducerPolymer chemistry
Disclosed are electroactive polymer fibers, processes of preparing electroactive polymer fibers, and devices containing electroactive polymer fibers. Devices can be used as actuators and sensors, generators and transducers. Applications include inter alia artificial muscles, prosthetics and robotics.
Owner:WOODCOCK WASHBURN +1
Bistable electroactive polymers
ActiveUS20100171393A1Improve mechanical energySpeed up the conversion processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device material selectionHigh energyShock resistance
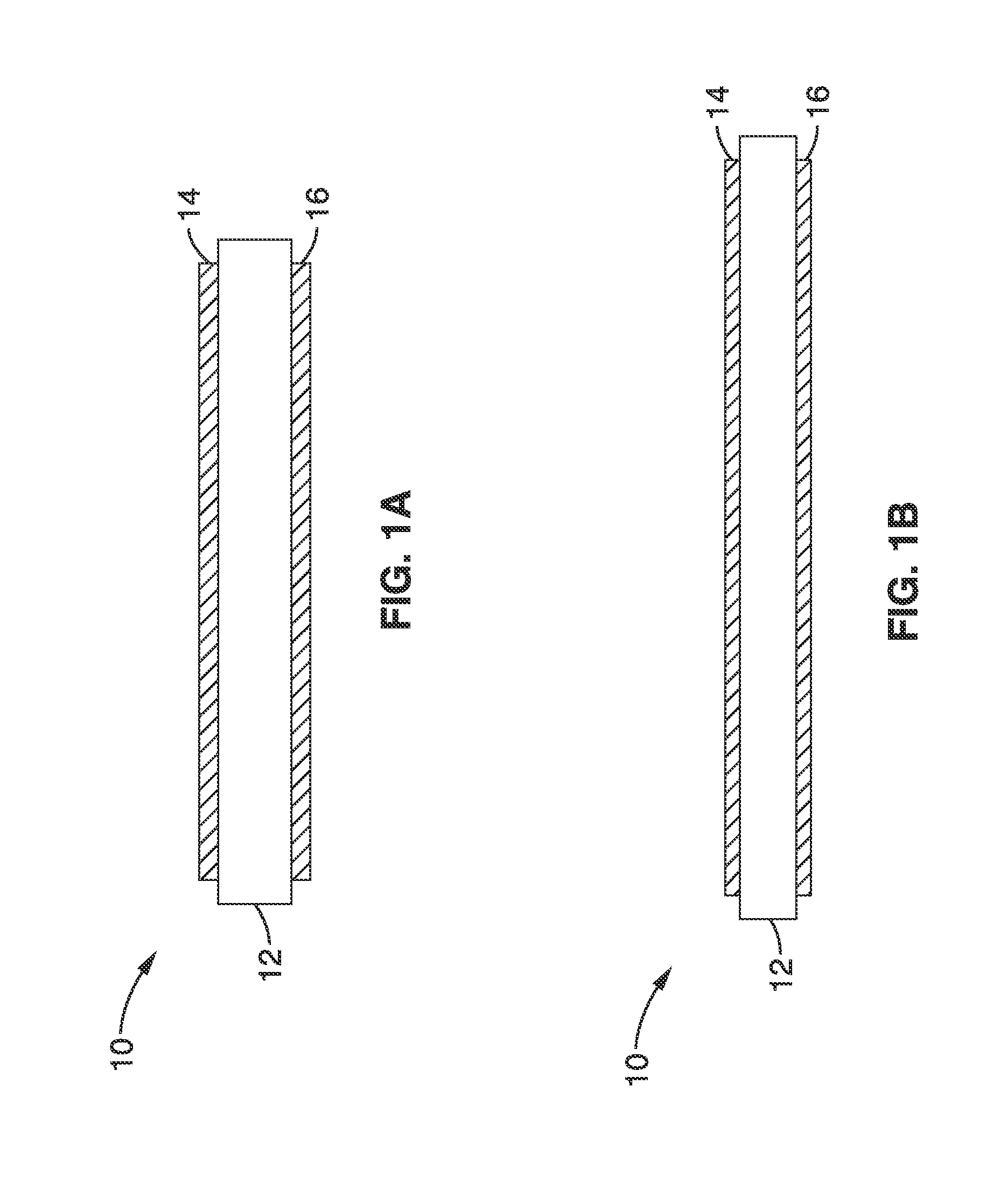
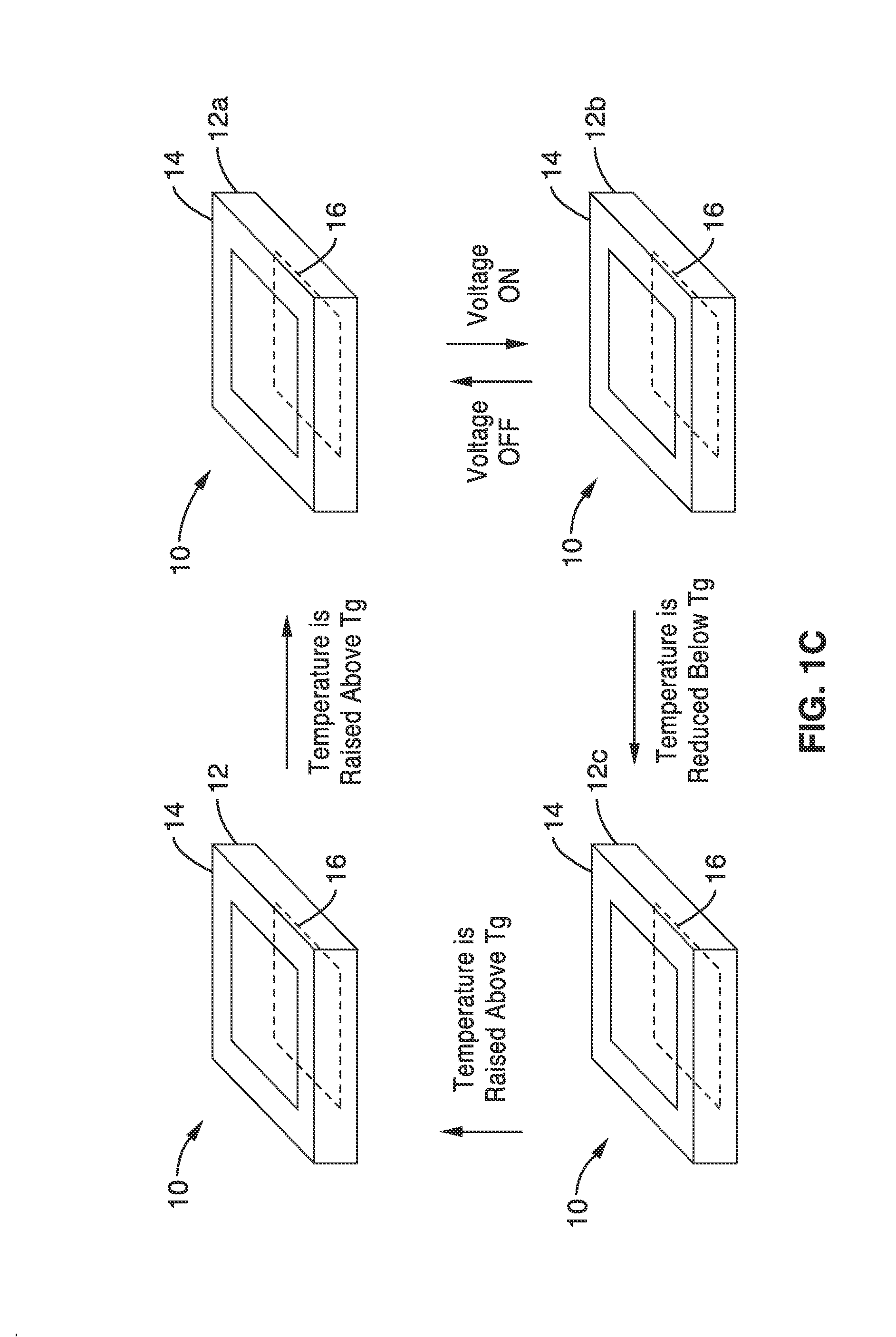
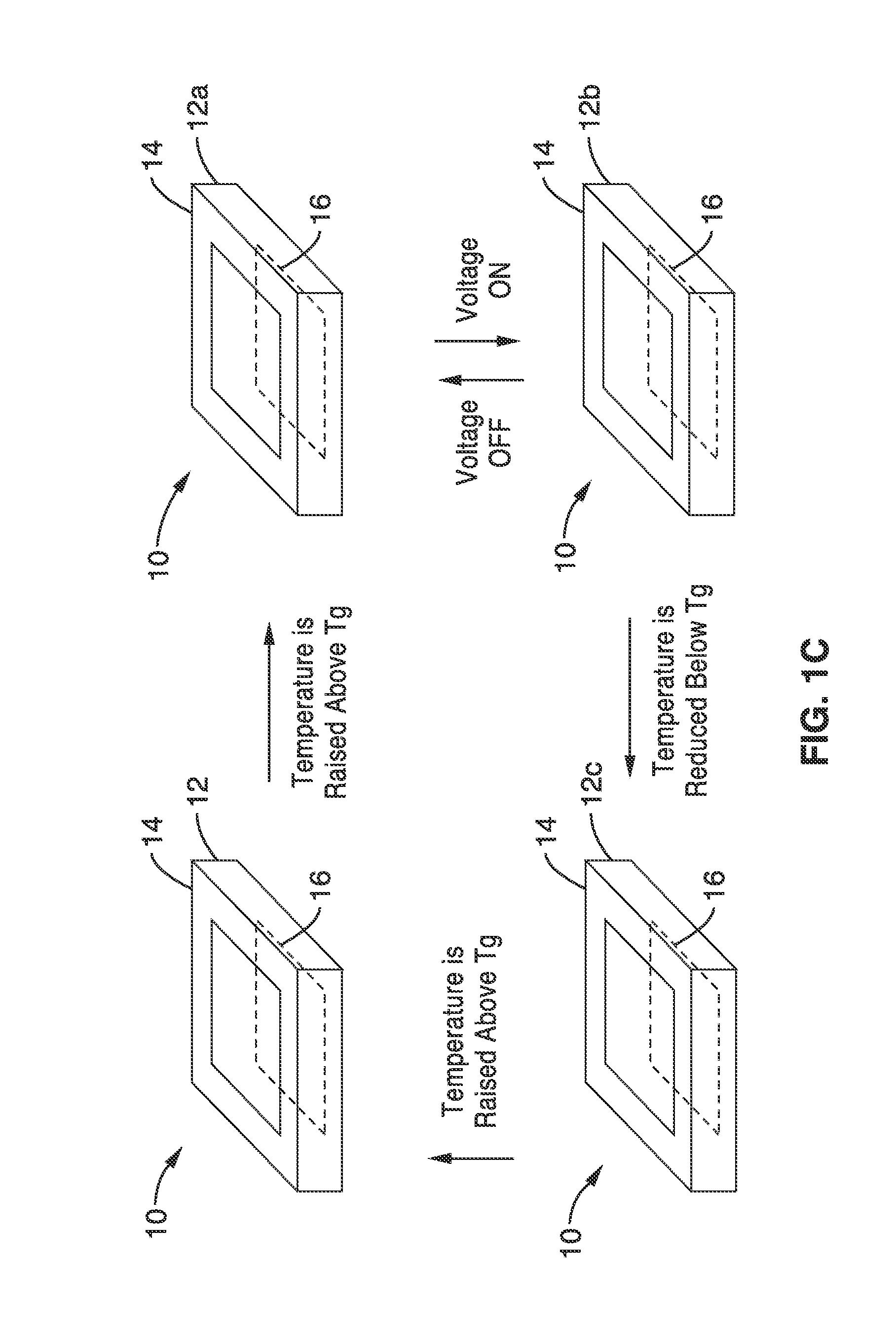
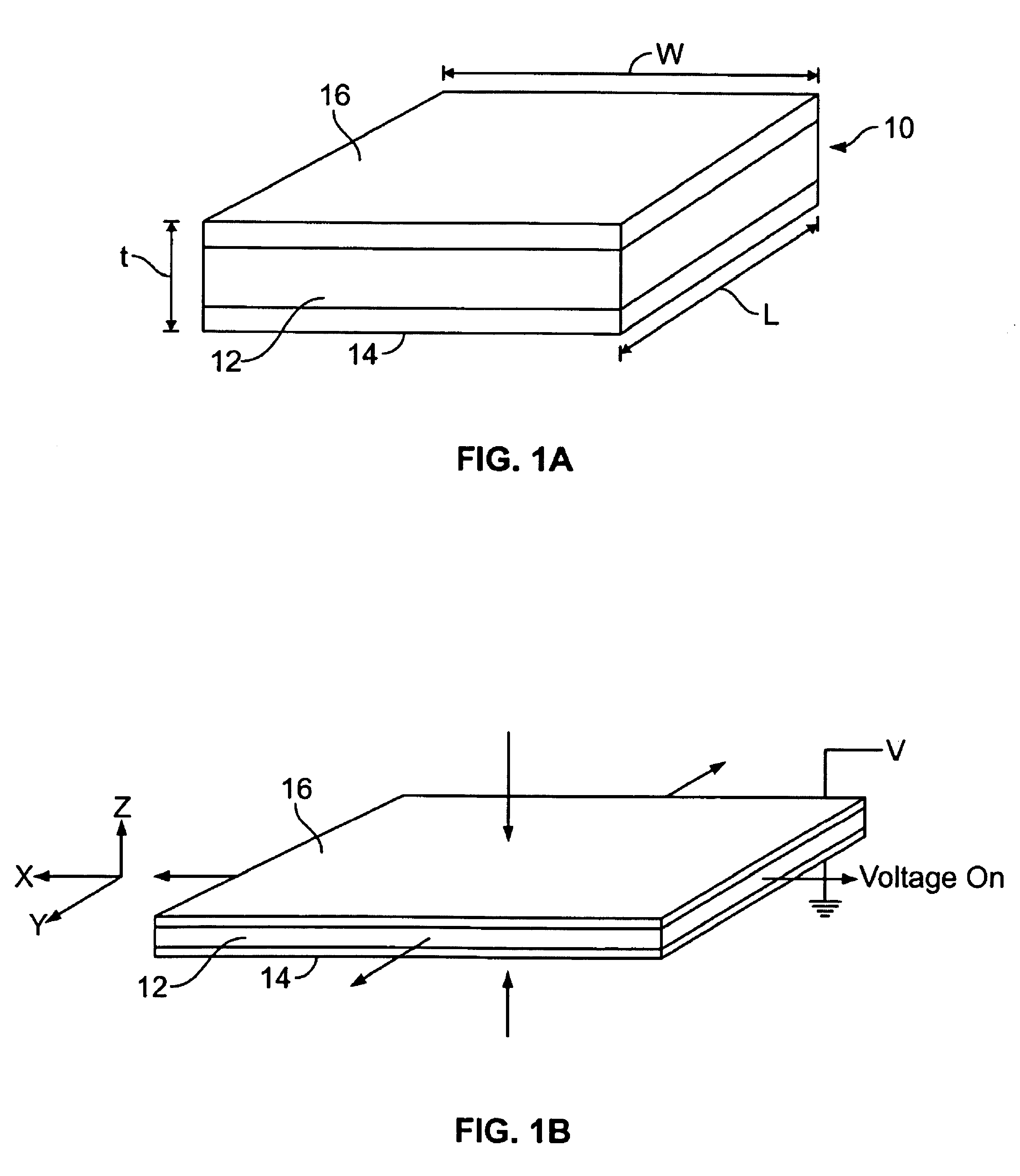
A bistable electroactive polymer transducer is provided for electrically actuated deformation of rigid electroactive polymer members. The polymers have glass transition temperatures (Tg) above ambient conditions and turn into rubbery elastomers above Tg and have high dielectric breakdown strength in the rubbery state. They can be electrically deformed to various rigid shapes with maximum strain greater than 100% and as high as 400%. The actuation is made bistable by cooling below Tg to preserve the deformation. The dielectric actuation mechanism includes a pair of compliant electrodes in contact with a dielectric elastomer which deforms when a voltage bias is applied between the pair of electrodes. In some of the transducers of the present invention, the dielectric elastomer is also a shape memory polymer. The deformations of such bistable electroactive polymers can be repeated rapidly for numerous cycles. The polymer transducers have such advantages as high energy and power densities, quietness, mechanical compliancy (for shock resistance and impedance matching), high efficiency, lightweight, and low cost.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bistable electroactive polymers
ActiveUS8237324B2Improve mechanical energySpeed up the conversion processPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesVitrificationActive polymer
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dielectric elastomer fiber transducers
ActiveUS7834527B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsTransducerArtificial muscle
Disclosed are electroactive polymer fibers, processes of preparing electroactive polymer fibers, and devices containing electroactive polymer fibers. Devices can be used as actuators and sensors, generators and transducers. Applications include inter alia artificial muscles, prosthetics and robotics.
Owner:WOODCOCK WASHBURN +1
Energy harvesting system
InactiveUS20100244457A1Generation and useAuxillary drivesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesVibrational energyElectroactive materials
Energy harvesting systems are described in which electroactive materials, such as dielectric elastomers, may be utilized to absorb the shocks, bumps, and vibrations from the road or path to generate energy which is captured and stored for use in the vehicle to provide additional power for any number of uses. Other devices and systems, such as household appliances which dissipate vibrational energy, may also incorporate any number of the dielectric elastomer generators.
Owner:BHAT NIKHIL +1
Electroactive polymer transducers
ActiveUS20090154053A1Minimize corona effectMinimize partial dischargePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyCapacitance correctionTransducerDielectric elastomers
Dielectric elastomer or electroactive polymer film transducers configured to minimize high electrical field gradients that can lead to partial discharge and corona.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Flexible polymer conductor, and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN105238007AImprove conductivityImprove flexibilityAdditive manufacturing apparatusSelective laser sinteringPolymer science
The invention discloses a flexible polymer conductor, and a preparation method and applications thereof. According to the preparation method, 0.01 to 20 parts of a nano conductive filler is uniformly dispersed in an aqueous solution or an ethanol solution containing 0 to 1 part of a surfactant via ultrasonic dispersion; 100 parts of a flexible polymer powder is added, full stirring is carried out so as to coat the surfaces of the flexible polymer particles with the nano conductive filler uniformly; the flexible polymer powder coated with the nano conductive filler is obtained via filtering, drying, and screening, and is dispersed onto a selective laser sintering device workbench for 3D printing so as to obtain the flexible polymer conductor. The flexible polymer conductor possesses excellent mechanical properties and electrical conductivity; electrical conductivity can be as high as 5.06S / m; cyclic tension can be carried out for one thousand times under deformation of 50%, and electrical conductivity is maintained to be essentially constant; the flexible polymer conductor can be applied to the fields such as electronic skin, flexible electrode, flexible implantable device, wearable devices, flexible display screen, artificial blood vessel, or dielectric elastomer drivers.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Electroactive actuators
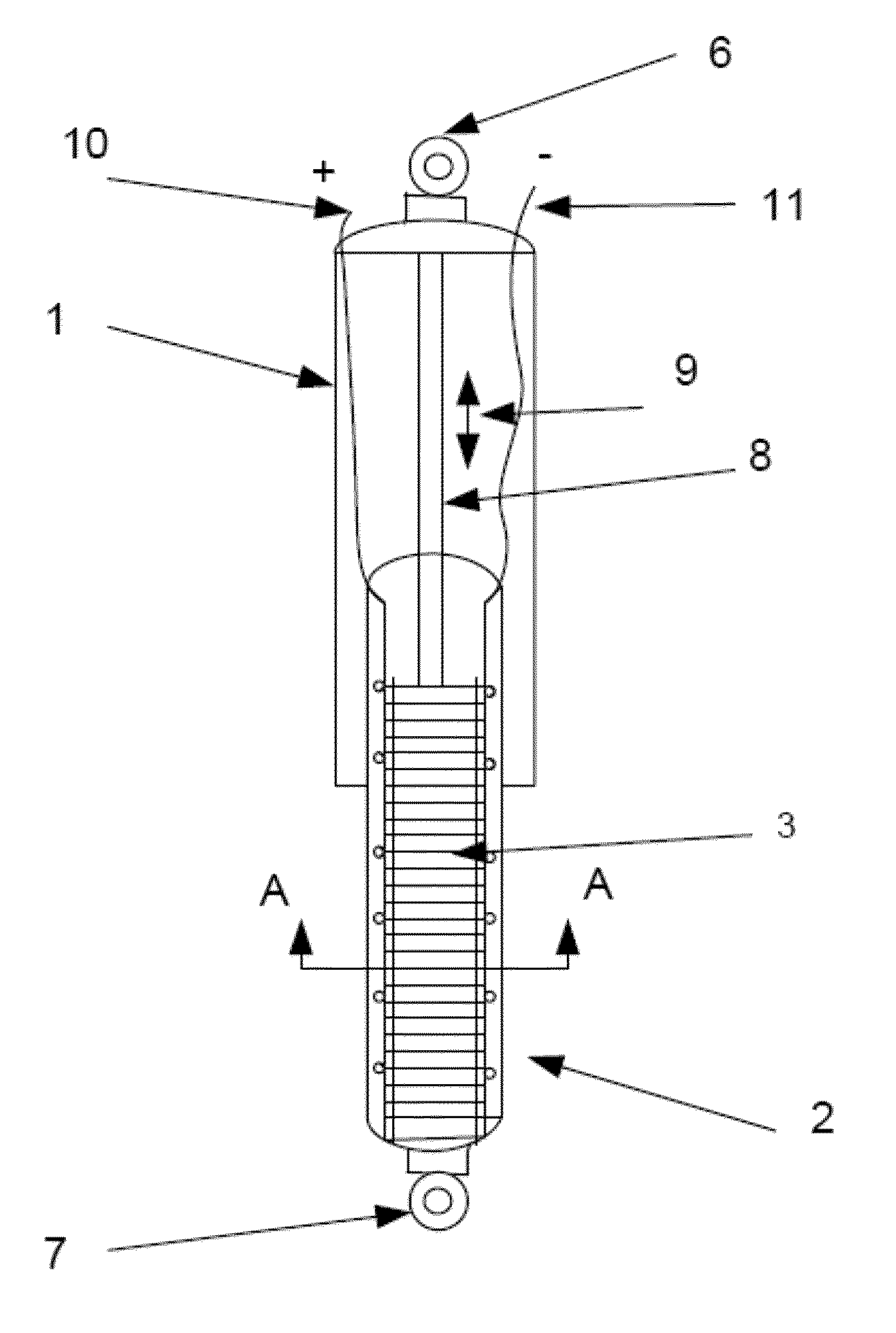
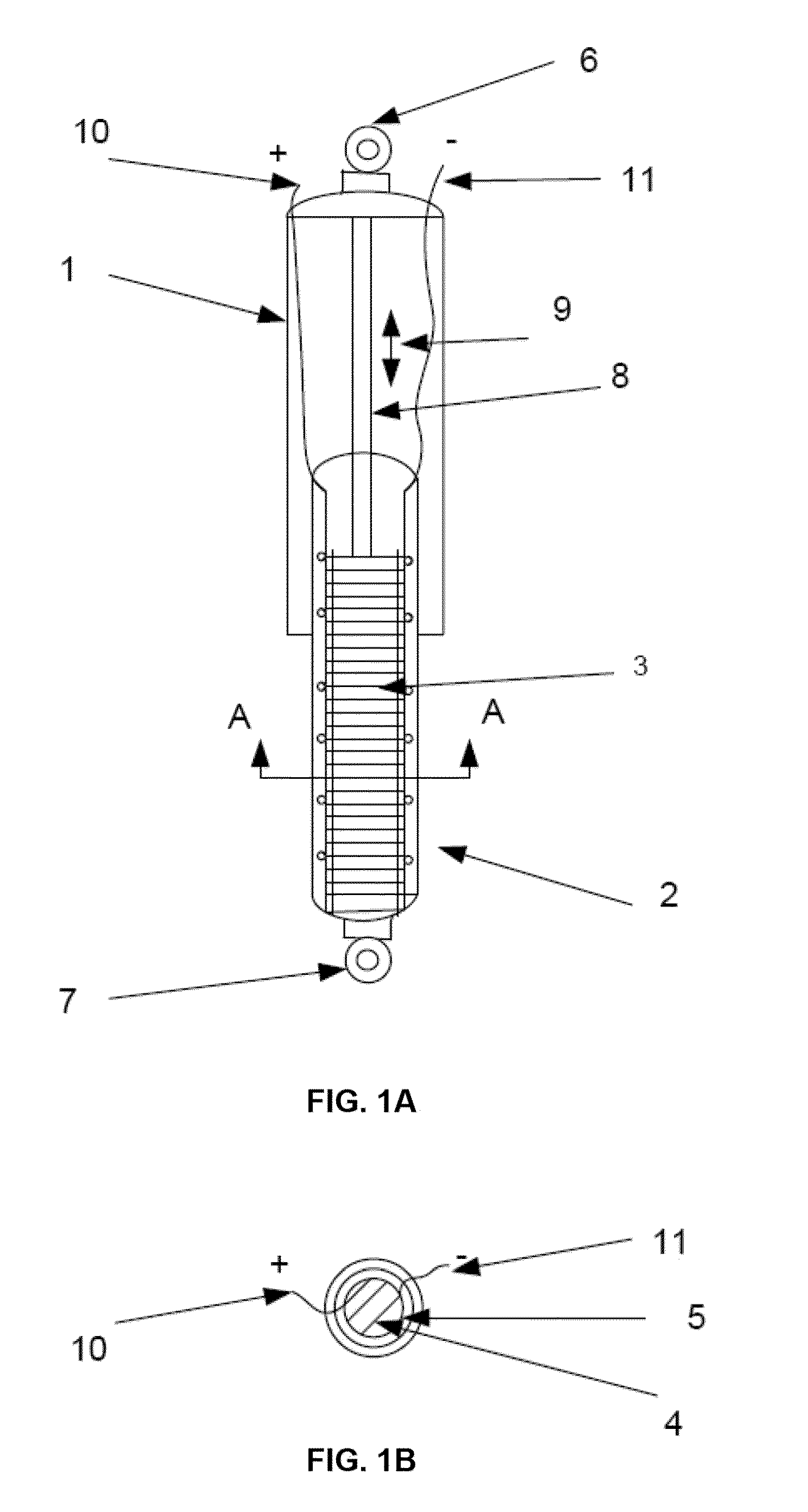
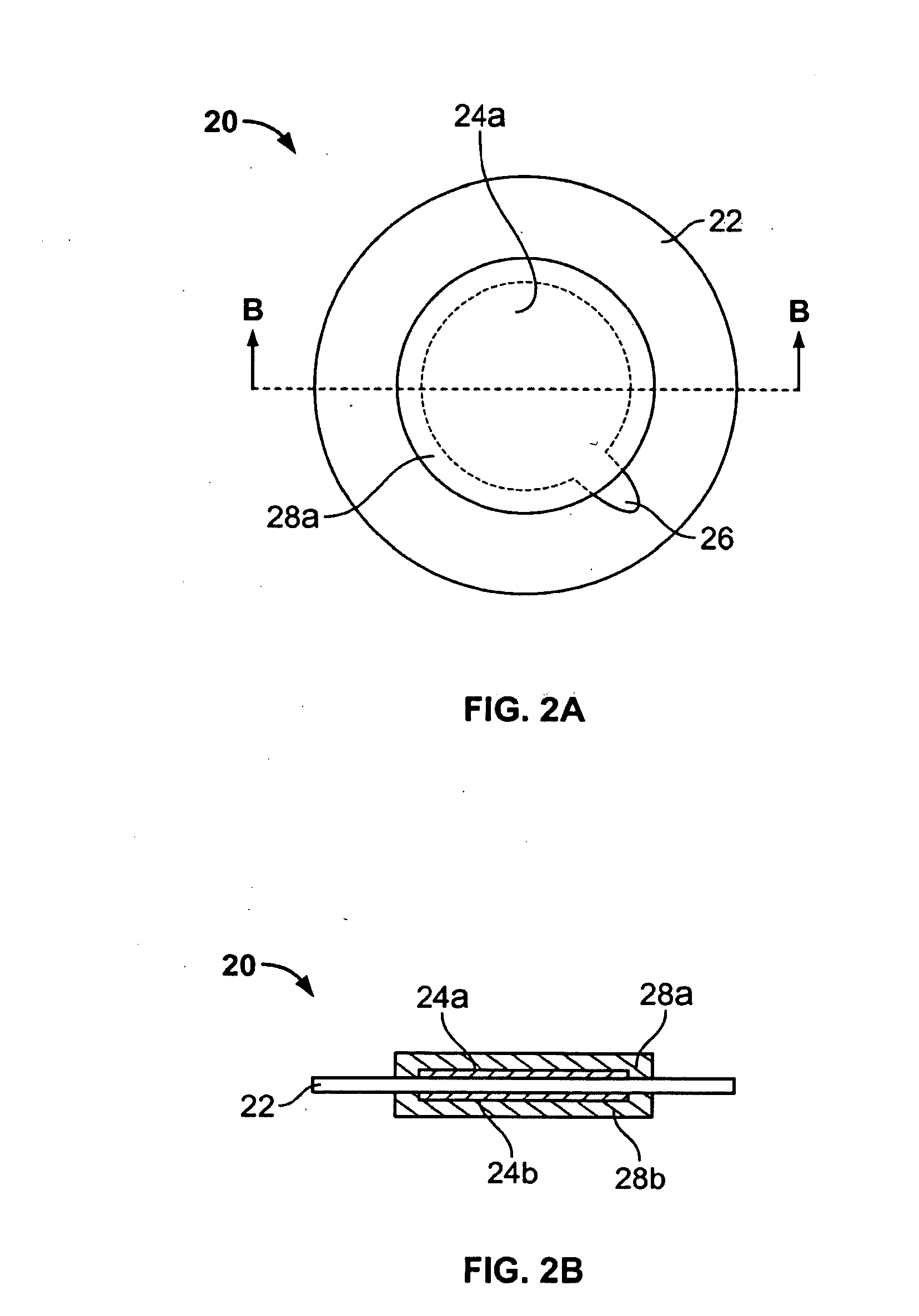
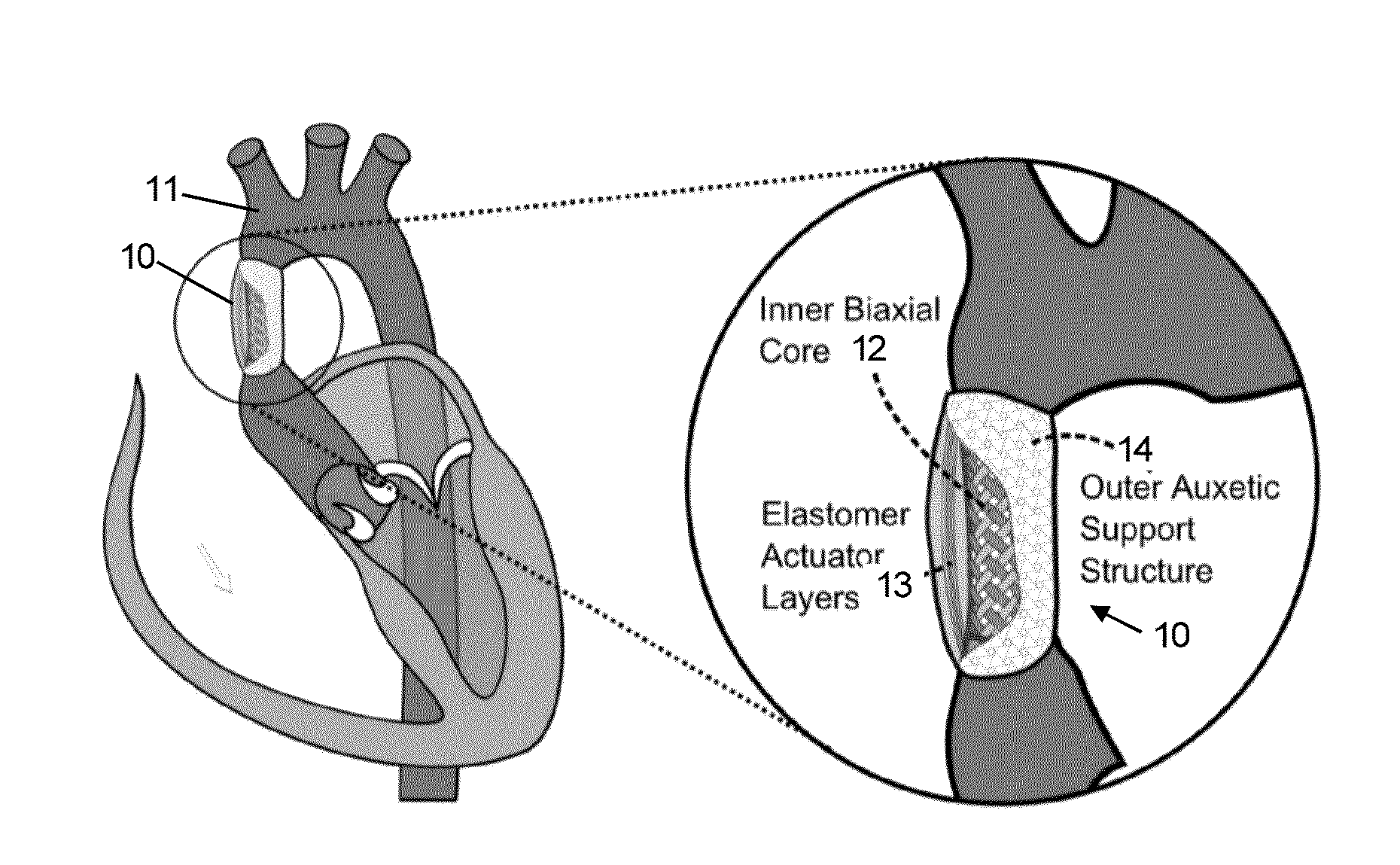
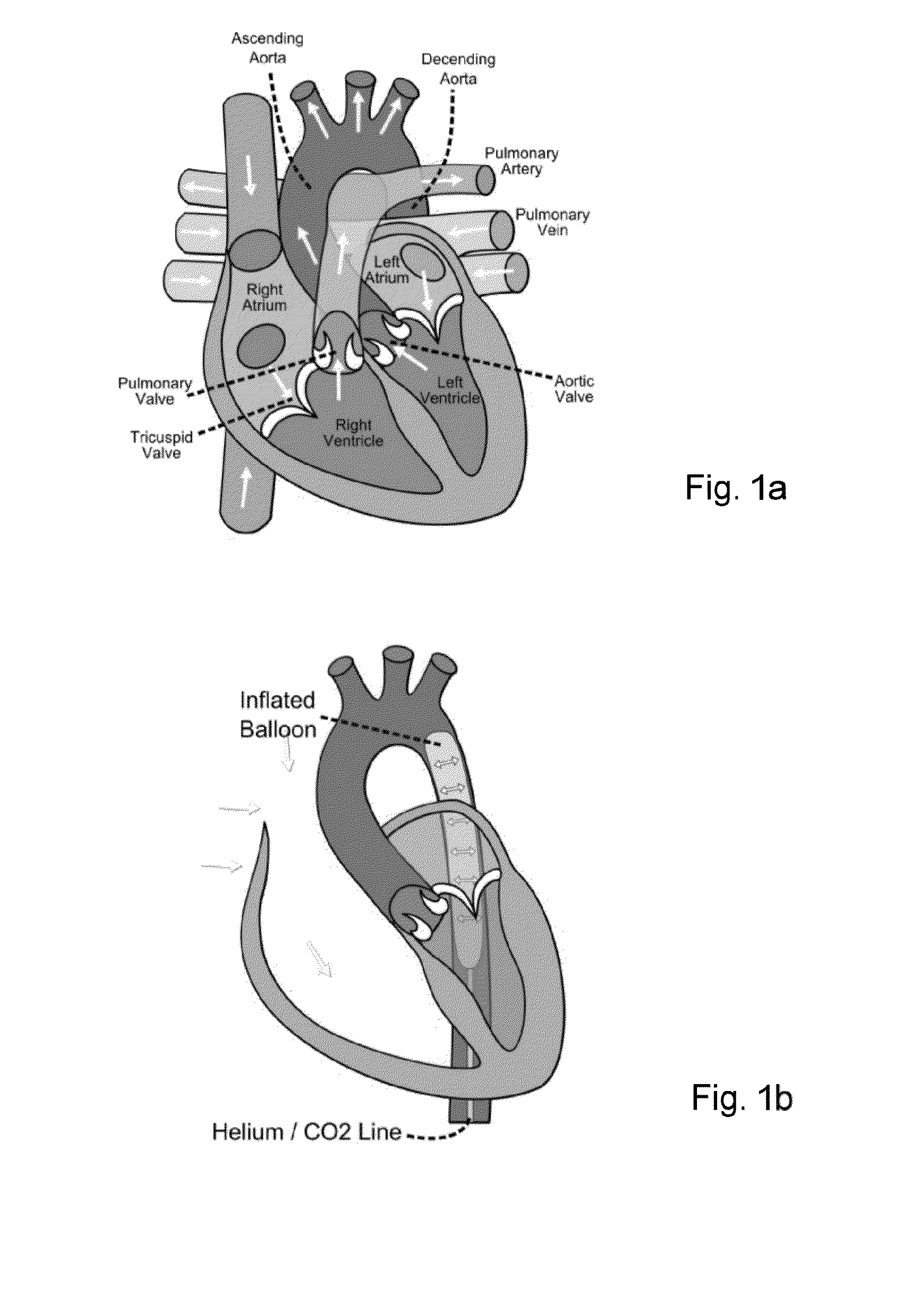
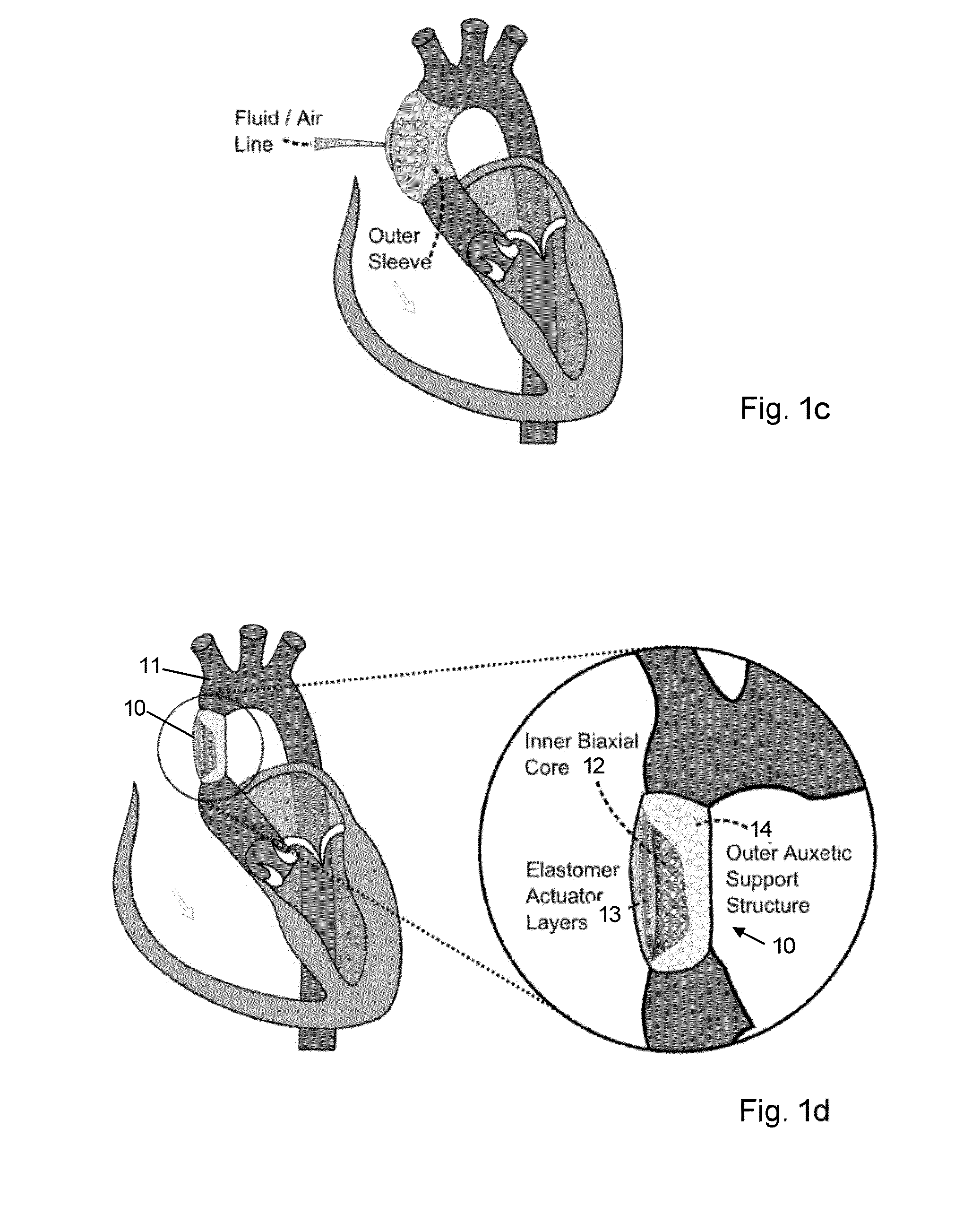
The invention relates to actuators based on electroactive polymeric materials for use in pumping fluids or in other applications where a contractile actuation is required, in particular although not necessarily exclusively for use in vascular pulsation devices such as a variable aortic tension device. Embodiments disclosed include an actuator (10) comprising: an inner tubular structure (15, 12); an outer tubular structure (13, 14) surrounding the inner tubular structure (15, 12) and comprising a plurality of layers of a dielectric elastomeric material (13) and a tubular elastic support structure (14), the elastic support structure (14) configured to maintain a pre-stress in the layers of the dielectric elastomeric material (13), wherein the outer tubular structure (13, 14) is configured to contract in a radial direction around the inner tubular structure (12, 15) upon application of an actuation voltage signal across the dielectric elastomeric material layers (13).
Owner:NOTTINGHAM TRENT UNIVERSITY +1
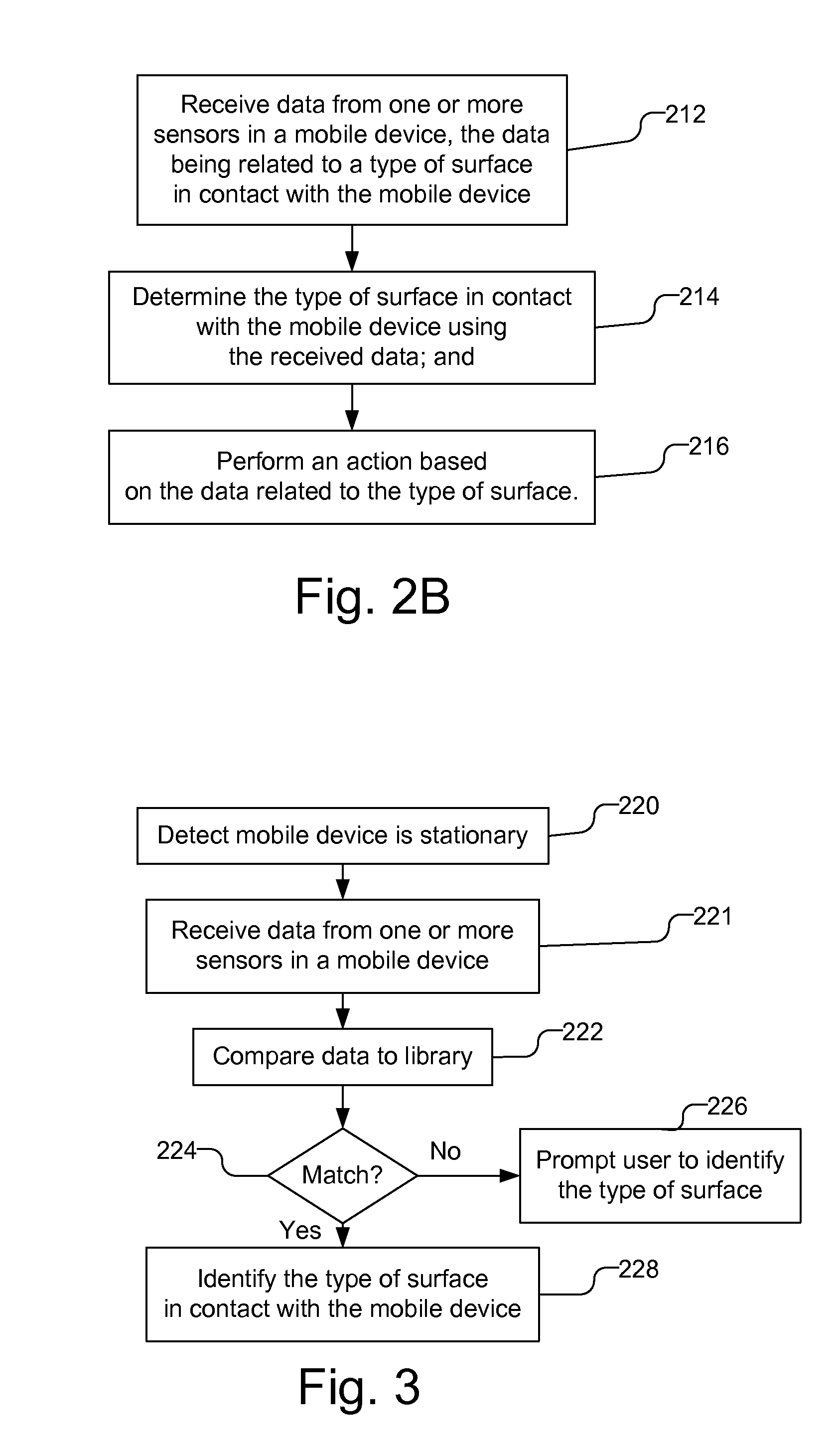
Mobile device control based on surface material detection
ActiveUS20130297926A1Material analysis by optical meansDevices with sensorProximity sensorEngineering
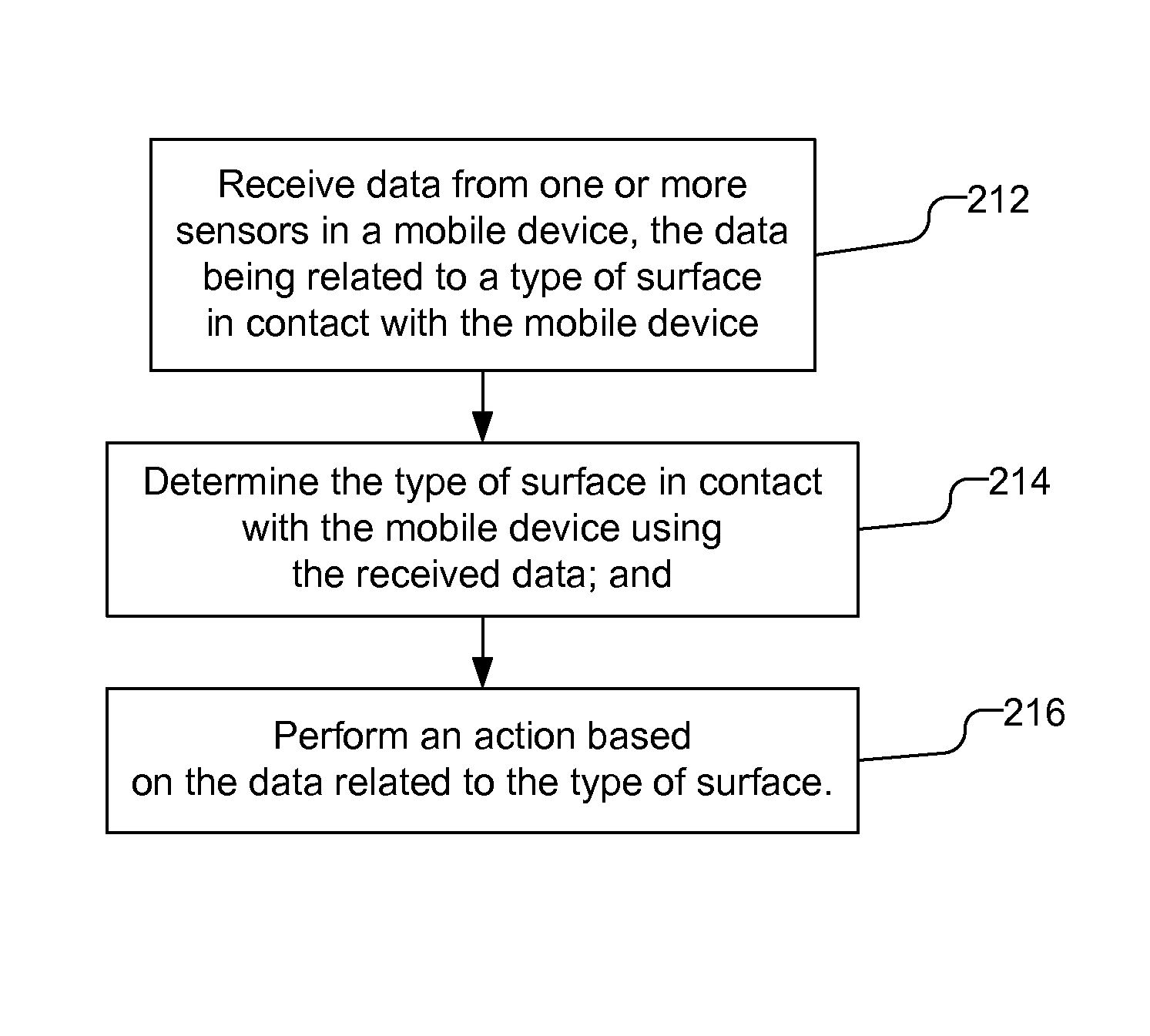
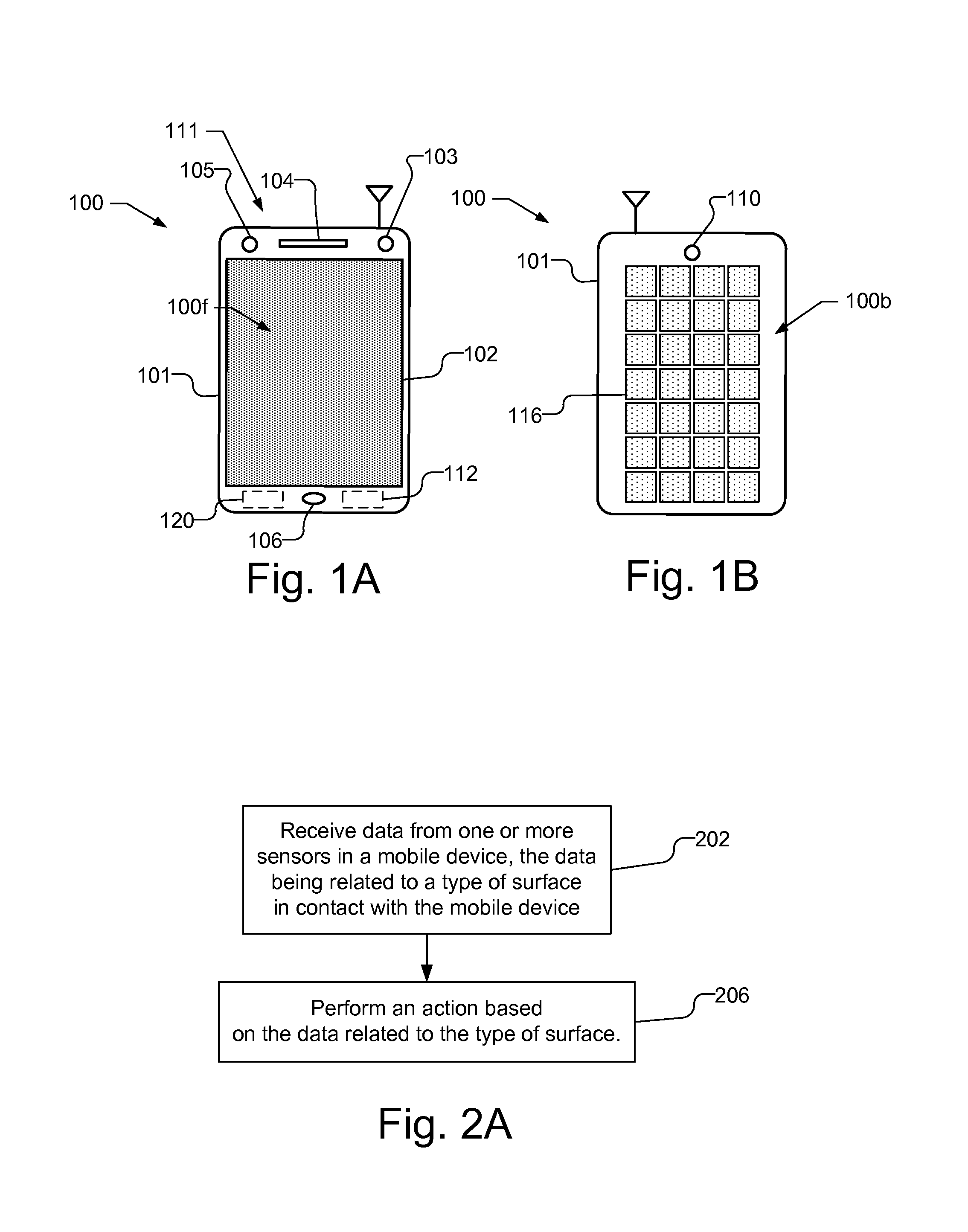
A mobile device uses sensor data related to the type of surface in contact with the mobile device to determine an action to perform. The sensors, by way of example, may be one or more of a microphone and noise generator, a light based proximity sensor, and pressure sensors, such as dielectric elastomers, configured to detect a texture of the surface, and / or pressure waves produced by setting the mobile device down or by a noise generator and reflected by the surface. The mobile device may identify the type of surface and perform the action based on the type of surface. The mobile device may further determine its location based on the sensor data and use that location to identify the action to be performed. The location may be determined using additional data, e.g., data not related to determining the type of surface with which the mobile device is in contact.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Fluorosilicone-Based Dielectric Elastomer and Method for its Production
InactiveUS20130236730A1Increased dielectric permittivityHigh modulusPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsPolymer scienceThin membrane
A dielectric elastomer has a film that contains a fluorinated silicone elastomer and has two faces. A coating of a stretchable electrode material is applied to each one of the two faces. The fluorinated silicone elastomer has a modulus of elasticity of maximally 450 kPa. The fluorinated silicone elastomer is a three-dimensionally crosslinked, fluorinated, alkyl group-containing polysiloxane in combination with a fluorinated silicone oil. Alternatively, or in addition, the fluorinated silicone elastomer is a three-dimensional wide-mesh crosslinked, fluorinated, alkyl-group containing polysiloxane whose wide mesh property has been effected by a chain length extension by addition of a chain-shaped silicone molecule containing two Si—H groups to an alkenyl group-containing polysiloxane molecule.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Roll-to-roll manufacturing processes for producing self-healing electroactive polymer devices
ActiveUS20150034237A1Avoid catastrophic failureDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingPolymer scienceConductive materials
A process for producing a corrugated electrode for use in an electroactive polymer cartridge is disclosed. A laminated web comprising a support sheet laminated to a dielectric elastomer film is positioned. The support sheet defines areas exposing portions of the dielectric elastomer film. A force is applied to the positioned laminated web to stretch the laminated support sheet-dielectric elastomer film web in a direction that is orthogonal to a plane defined by the web. An electrically conductive material is applied to the laminated support sheet-dielectric elastomer film web while the laminated support sheet-dielectric elastomer film web is in a stretched state. The laminated support sheet-dielectric elastomer film web is relaxed to form the corrugated electrode on the dielectric elastomer film portion of the web.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
Electroactive polymer transducers
ActiveUS8248750B2Minimize corona effectMinimize partial dischargePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyFixed capacitor electrodesTransducerDielectric elastomers
Dielectric elastomer or electroactive polymer film transducers configured to minimize high electrical field gradients that can lead to partial discharge and corona.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Dielectric elastomer actuated systems and methods
InactiveUS7411331B2Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesControl theoryCurved beam
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
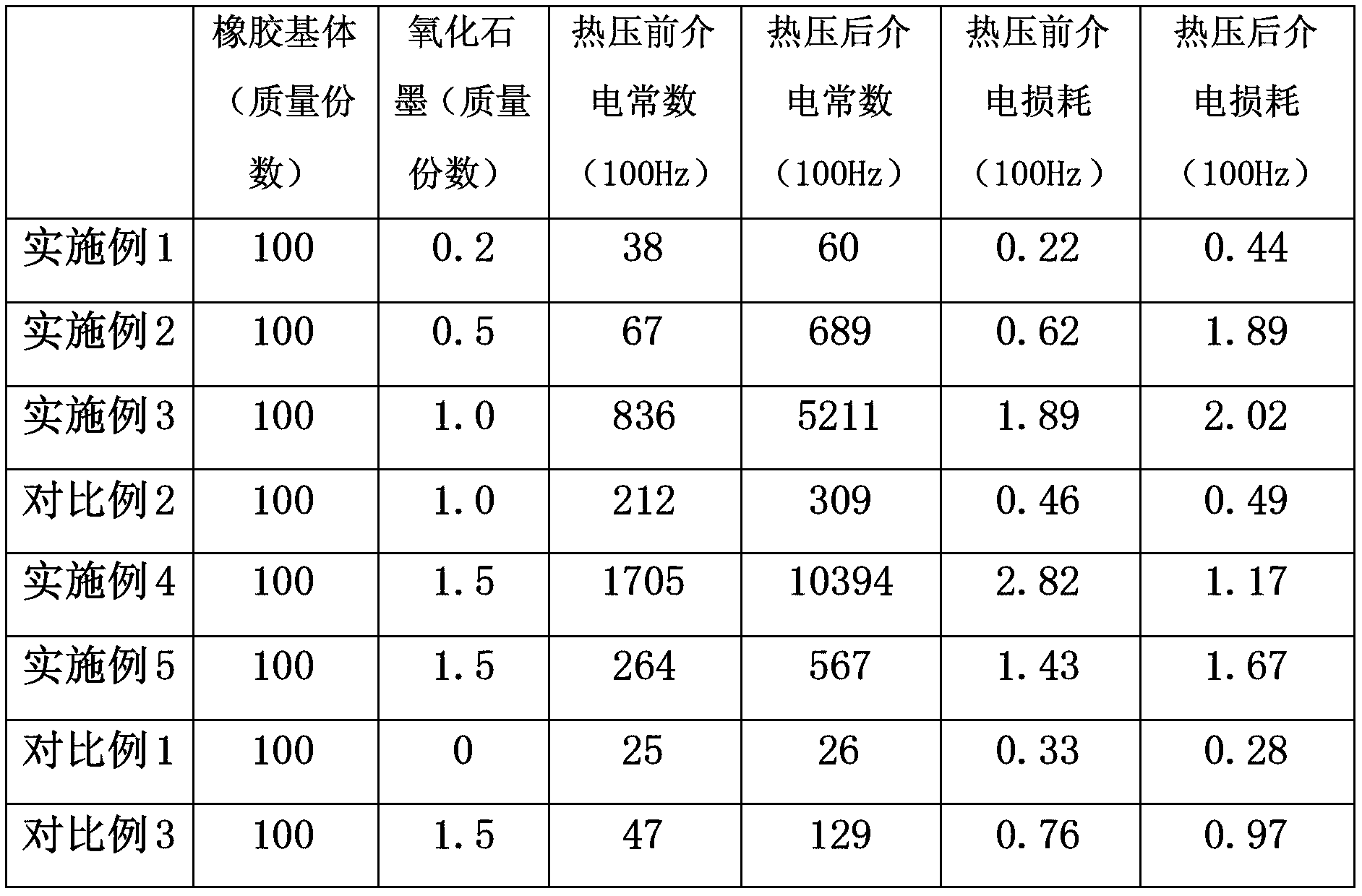
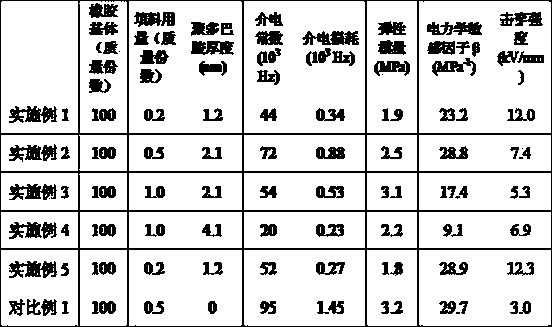
Graphene elastomer nano composite material with high dielectric constant and low dielectric loss and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103183847ALarge specific surface areaExcellent dielectric propertiesElectrical conductorLatex particle
The invention discloses a graphene elastomer nano composite material with low filling quantity and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of preparation of dielectric elastomer. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding an aqueous solution of graphene oxide into water-soluble rubber latex so that the graphene oxide is dispersed in rubber matrix on molecular level, reducing the graphene oxide into graphene by adopting an in-situ hot-pressing reduction method, and thus forming a network structure that graphene flake layers wrap latex particles. The obtained composite material has high dielectric constant under low filling quantity, keeps low dielectric loss, and has low percolation value. The composite material solves the problem that the performance of the composite material is reduced because the filling quantity required when an inorganic conductor is filled with rubber and the dielectric constant and the dielectric loss are simultaneously improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Graphene-based dielectric elastomer composite material and preparing method thereof
The invention relates to a graphene-based dielectric elastomer composite material and a preparing method thereof. The composite material comprises an elastomer matrix, graphene oxide dielectric padding and a crosslinking system, wherein the graphene oxide dielectric padding is oxidation graphene with the surface wrapped by a poly-dopamine organic layer and is scattered in the elastomer matrix in a nanometer horizontal layer mode, and an isolation network structure that an oxidized graphene slice layer which is wrapped by the poly-dopamine organic layer wraps latex particles. According to the preparing method, the dopamine bionic ornament oxidization graphene is adopted, the dielectric loss is obviously reduced, the electric breakdown strength is improved, the organic layer thickness of the poly-dopamine can be regulated through the parameters of the modification process of the dopamine, the dielectric constant, the dielectric loss and the electric breakdown strength of the composite material can be adjusted according to the demands, and the graphene-based dielectric elastomer composite material meeting the safety requirement in the biology medical field can be prepared.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Dielectric elastomer membrane feedback apparatus, system and method
InactiveUS20140232646A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsElectricityEngineering
A feedback enabled system, module, and method are disclosed. The feedback enabled system comprises a first feedback module. The first feedback module comprises a membrane (thin film); a frame; a motion coupling, wherein when a voltage is applied to the membrane (thin film), the motion coupling exerts a force on the frame to provide feedback; and a user interface, wherein the first feedback module is configured to provide feedback through the user interface. The method comprises applying a first voltage with a first waveform to a first feedback module, the first feedback module comprising a dielectric elastomer membrane (thin film), a frame, and a motion coupling, wherein, when the first voltage is applied to the dielectric elastomer membrane (thin film), the motion coupling exerts a force on the frame.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Repeatable and flexible capture structure based on dielectric elastomer and shape memory polymer and method for capturing space debris
InactiveCN105416613AThe overall structure is simple and reliableImprove stabilityCosmonautic vehiclesGripping headsEngineeringStructure based
The invention provides a repeatable and flexible capture structure based on dielectric elastomer and shape memory polymer and a method for capturing space debris. According to the repeatable and flexible capture structure based on the dielectric elastomer and the shape memory polymer and the method for capturing the space debris, the problems that traditional aerospace machines and motor driving capture structures are complex and large in weight are solved. The repeatable and flexible capture structure based on the dielectric elastomer and the shape memory polymer is mainly composed of the unfolding structure of a shape memory polymer composite material sheet layer, namely a three-wing type unfolding beam, and the dielectric elastomer. The structure constituted by the shape memory polymer composite material sheet layer is used for driving and controlling the capture structure to the designated spot, and the structure constituted by the shape memory polymer and the dielectric elastomer is used for capturing the space debris. The repeatable and flexible capture structure based on the dielectric elastomer and the shape memory polymer is simple in structure and high in reliability, and is applied to repeatable and flexible capture structures.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Silicon rubber based porous dielectric elastomer composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a silicon rubber based porous dielectric elastomer composite material, in particular to a silicon rubber based porous dielectric elastomer composite material having high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss and low Young modulus and a preparation method thereof. The silicon rubber based porous dielectric elastomer composite material comprises polydimethylsiloxane, curing agent, polyethylene glycol and conductive filler, a mass ratio of polydimethylsiloxane to the curing agent is 5:1-40:1, a mass ratio of polydimethylsiloxane to polyethylene glycol is 17:10-88:1, and the conductive filler accounts for higher than 0 and lower than or equal to 2.7% of total mass of polydimethylsiloxane / polyethylene glycol / curing agent. The composite material has a uniform microporous structure, and the conductive filler is selectively distributed at an interface of polydimethylsiloxane and polyethylene glycol. The silicon rubber based porous dielectric elastomer composite material has the advantages of high dielectric constant, low dielectric loss and low Young modulus.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Dielectric elastomer composites and actuators using the same
InactiveUS20130049530A1Improve propertiesEnhancing dispersibility of fillerPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyNanotechnologyPolymer scienceBarium titanate
The present invention relates to an actuator which is one of the energy conversion devices, and is characterized by improving the ability to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy by way of using a dielectric elastomer composite comprising a filler with an efficient dispersibility. In case of using a conventional resilient dielectric layer, there was a problem in that the operating voltage is high, while advantageously exhibiting a fast response and a high strain. The present invention can provide dielectric elastomer composite actuators that show excellent electromechanical conversion properties, by adding a dispersing agent such as a pyrene derivative or a polymeric compound having an amine end group when preparing the composite wherein carbon-based conductive fillers such as carbon blacks, single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs), double-walled carbon nanotubes (DWCNTs), multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and graphenes, or high dielectric fillers such as copper phthalo-cyanine (CuPc), MOFs (metal organic frameworks) and barium titanate (BaTiO3) are comprised in a thermoplastic resilient dielectric layer to enhance the dispersibility of the fillers.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Electroactive polymer energy converter
InactiveUS20140145550A1Piezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesConvertersActive polymer
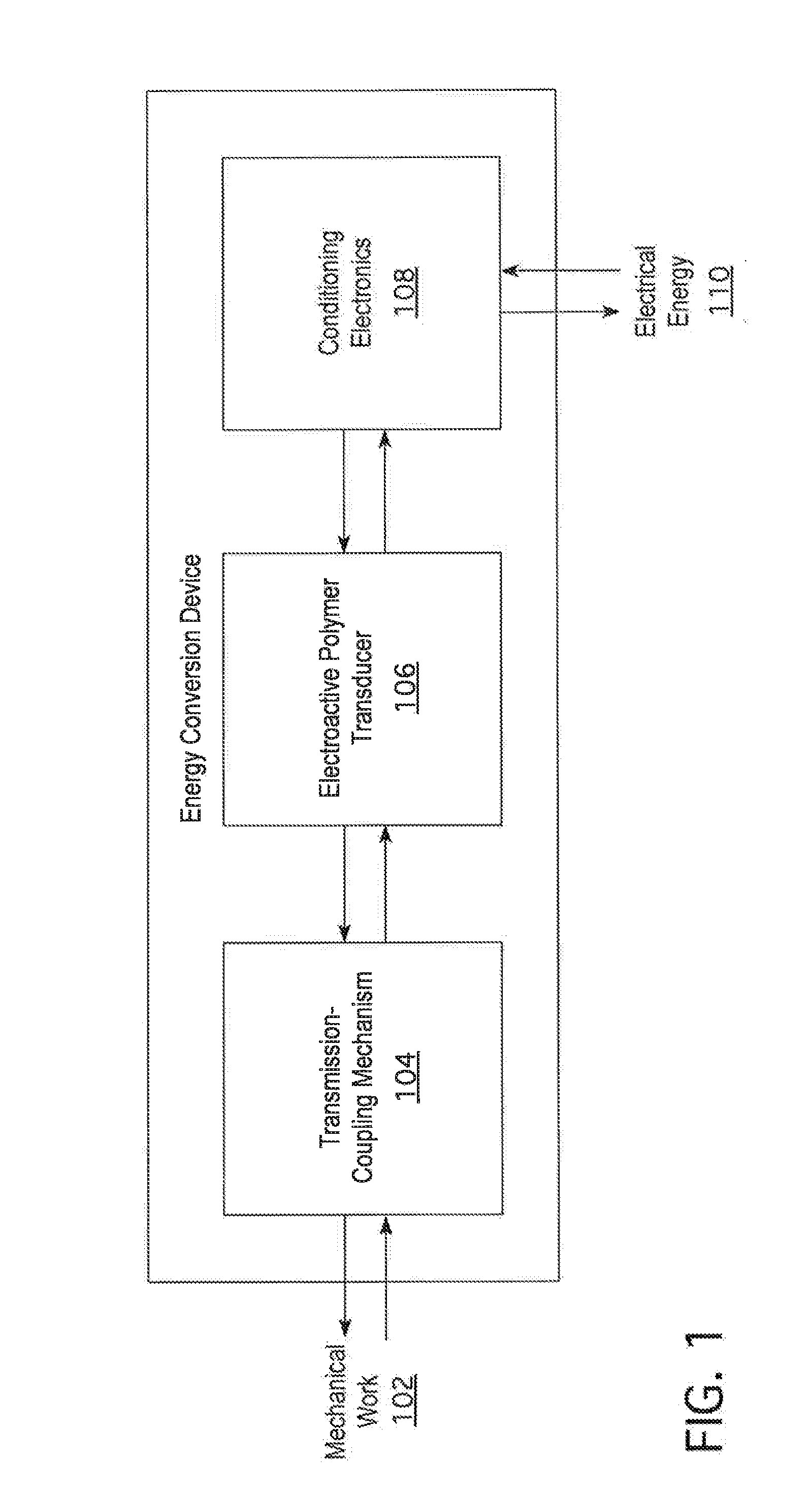
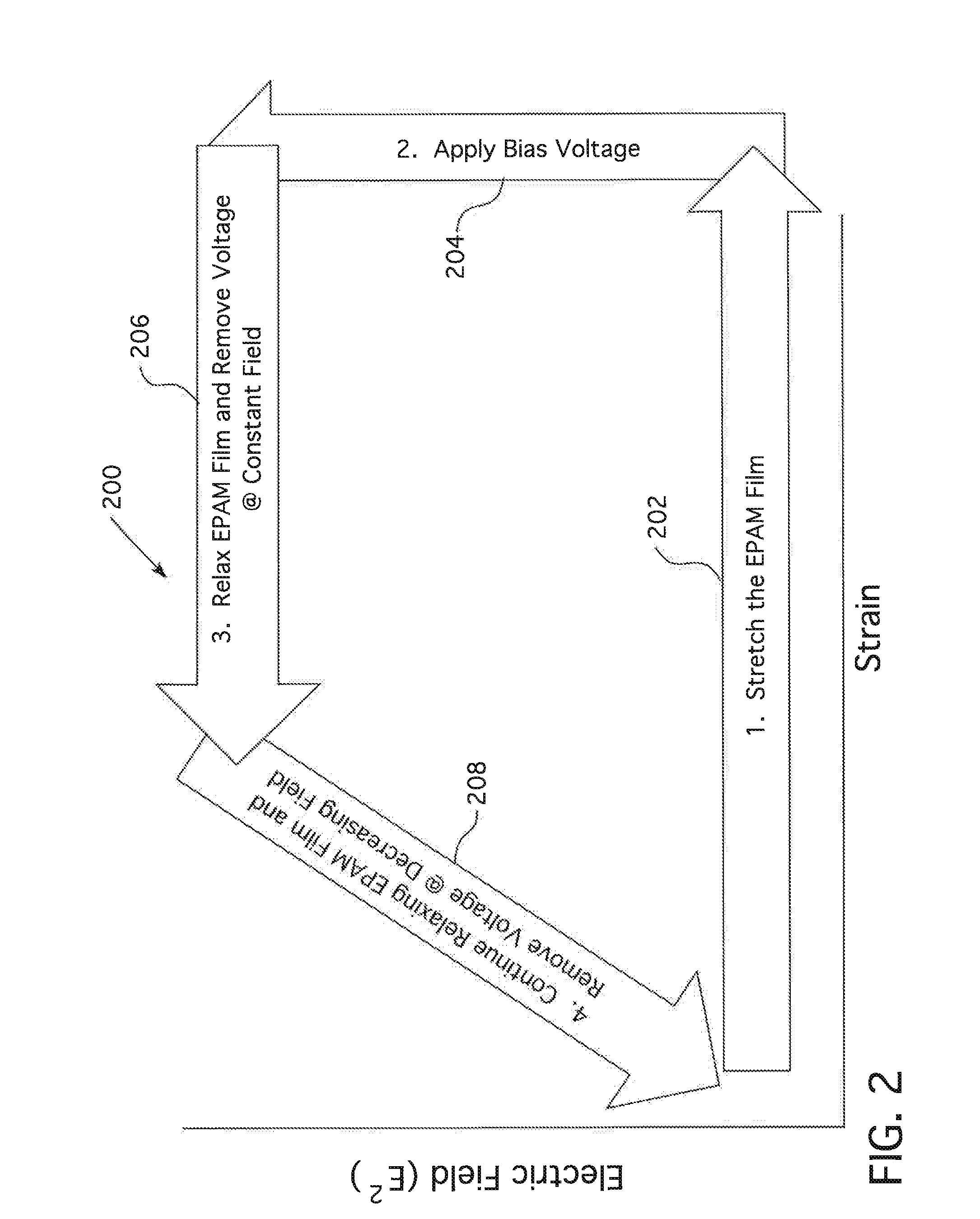
An energy conversion apparatus configured to convert energy from a mechanical energy source into electrical energy is provided. The energy conversion apparatus includes a transducer comprising a dielectric elastomer module made of stretchable electroactive polymer material. The dielectric elastomer module comprising at least one dielectric elastomer film layer is disposed between at least first and second electrodes. A transmission coupling mechanism is configured to couple the mechanical energy source and is operatively attached to the transducer to cyclically strain and relax the transducer in response to the mechanical energy acting on the transmission coupling mechanism. A conditioning circuit is coupled to the at least first and second electrodes and configured to apply an electric charge to the dielectric elastomer film when the dielectric elastomer film is in a strained state, to disconnect from the dielectric elastomer film when the dielectric elastomer film transitions from the strained state to a relaxed state, and to remove electrical charge from the dielectric elastomer film when the dielectric elastomer film reaches a relaxed state.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Actuator
InactiveUS20080238258A1Simple processLarge displacementPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsControl theoryDielectric elastomers
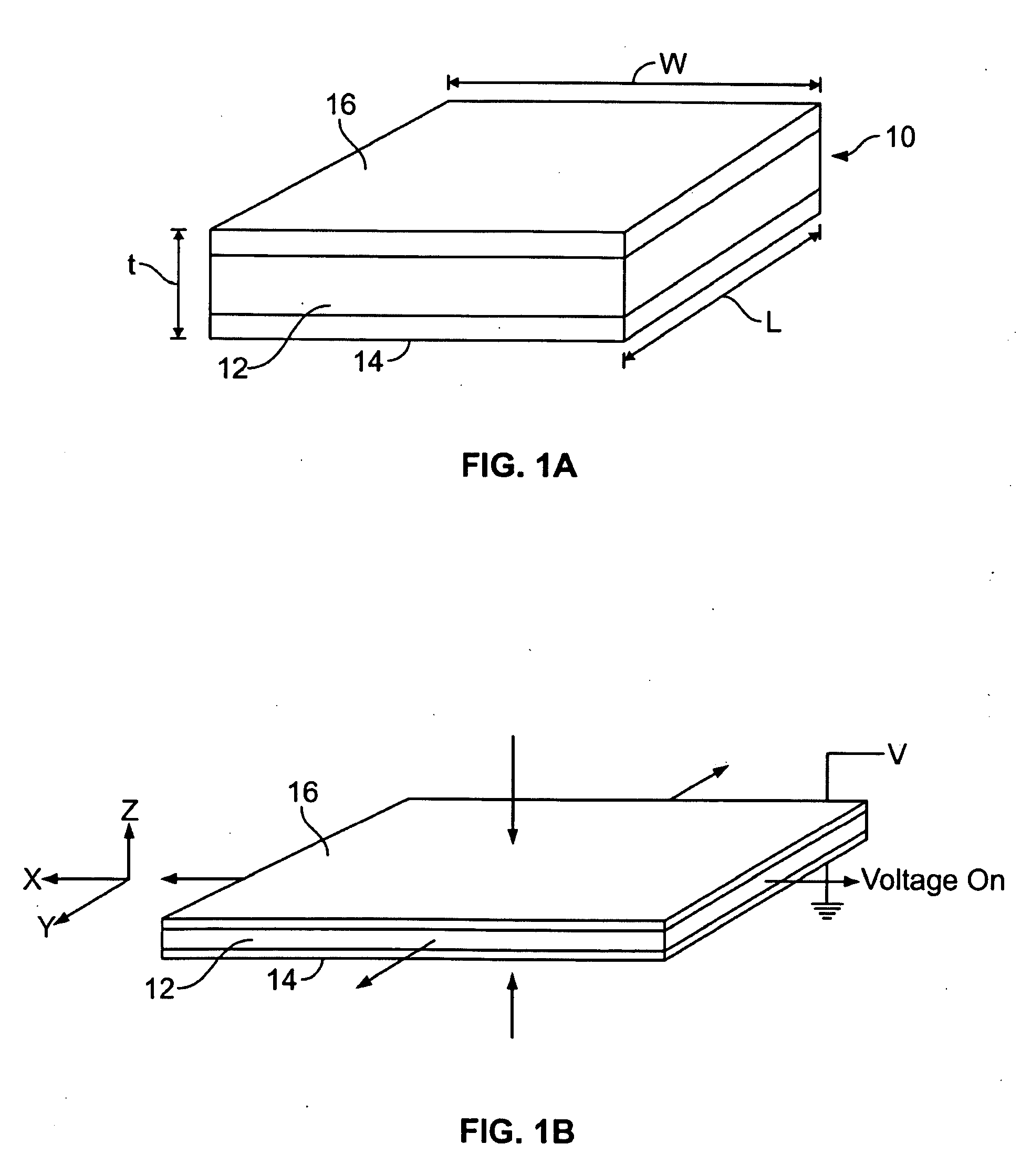
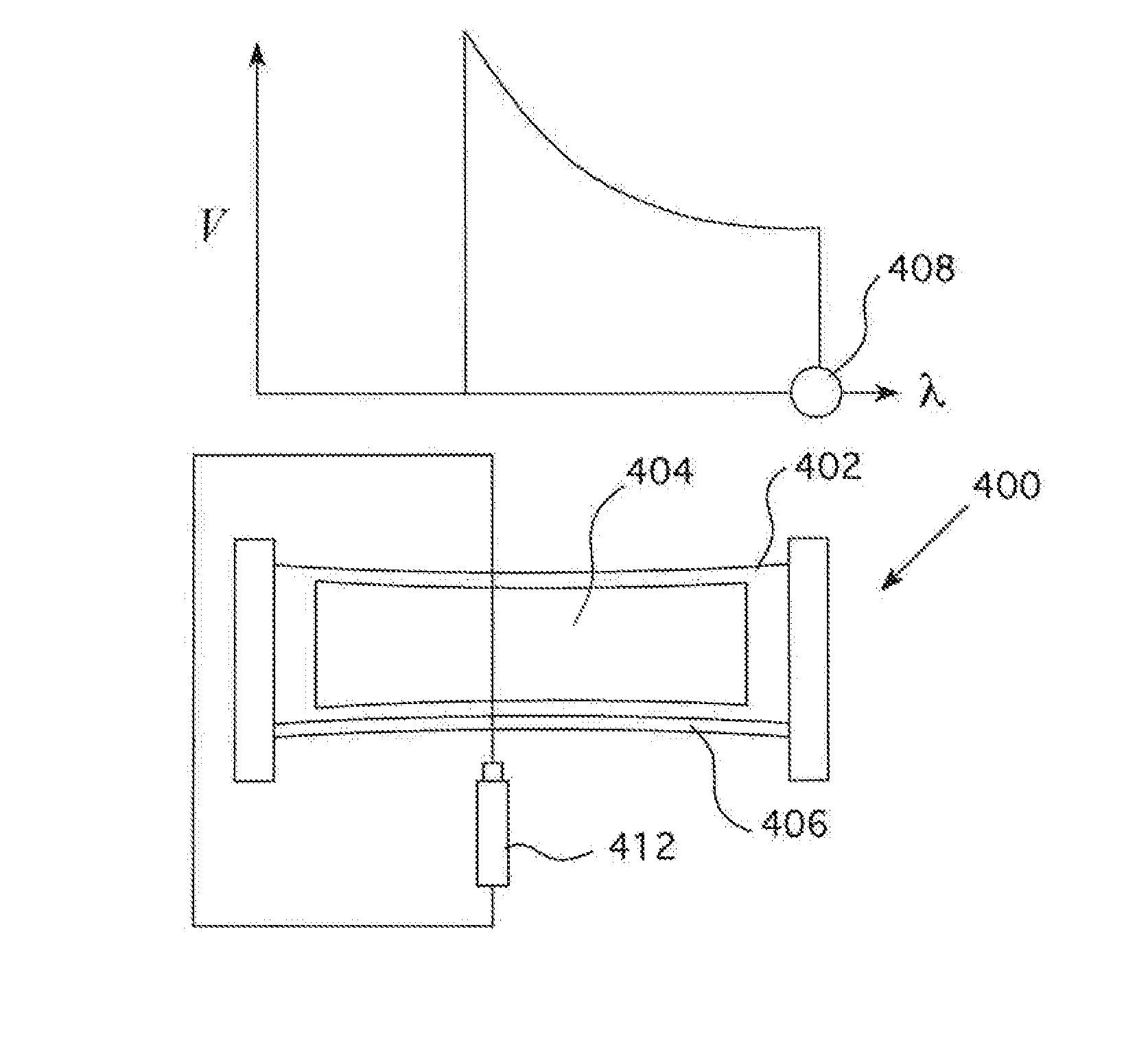
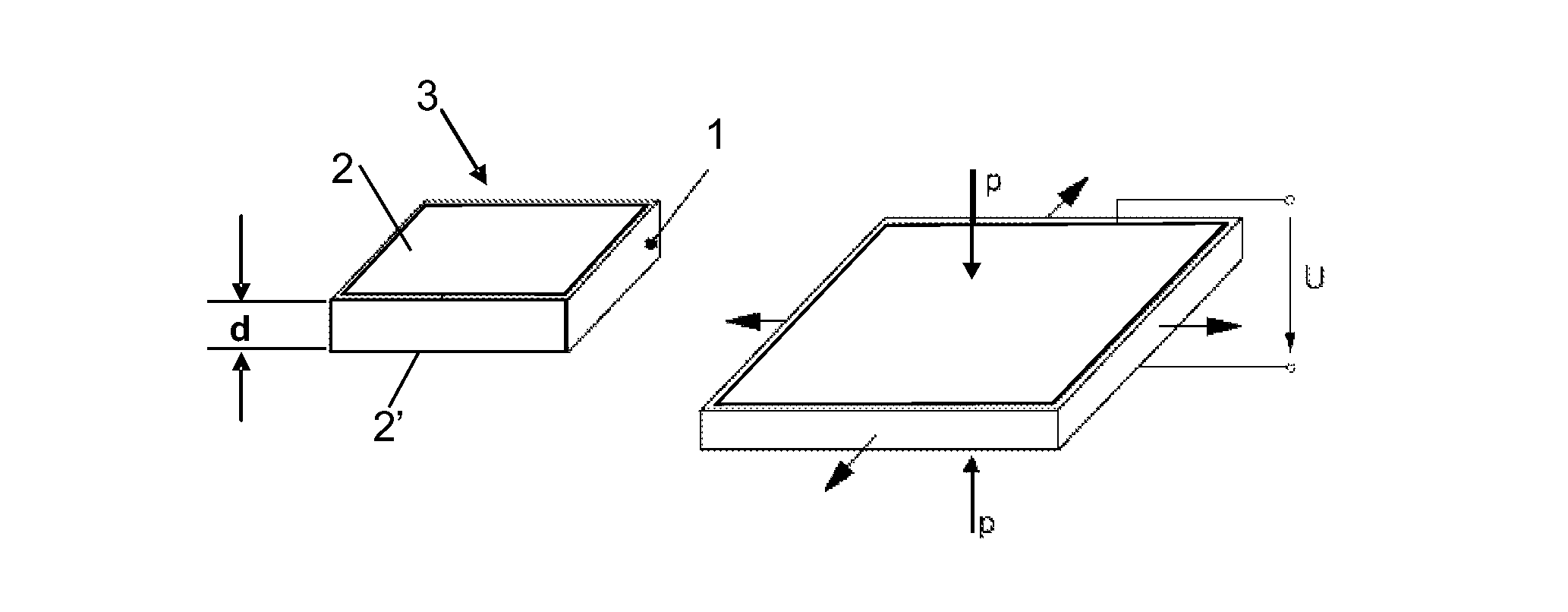
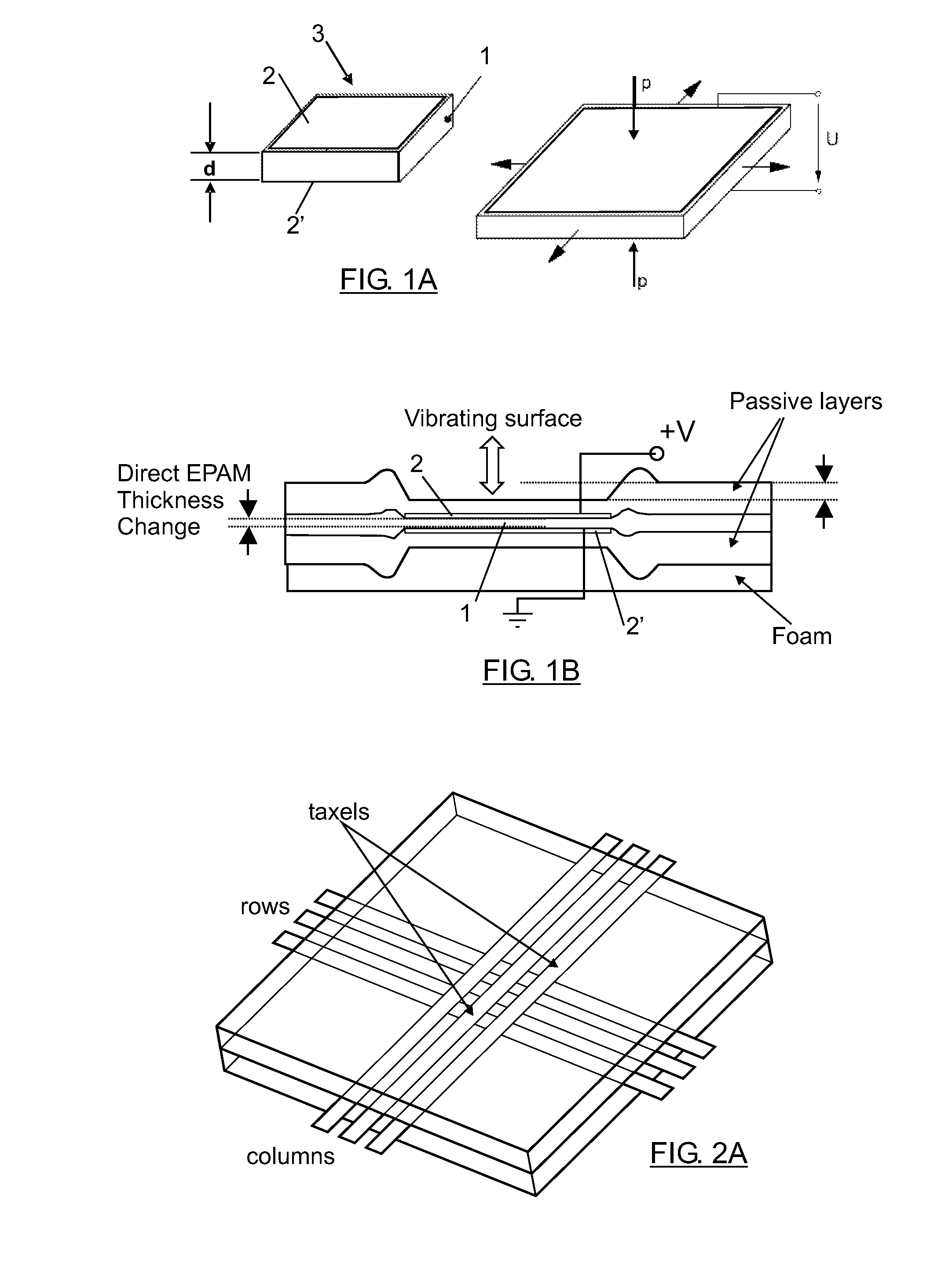
To provide an actuator which is easily made a small size and flexible, and has a large displacement. The actuator comprises a rod-shaped actuator element, having one axial end thereof fixed, including a dielectric film made of a dielectric elastomer and a plurality of electrodes arranged via the dielectric film, in the actuator element, the dielectric film extends as a voltage applied across the electrodes becomes large, and a load member connected to the other axial end of the actuator element and fixed in a state in which the actuator element is permitted to be extended axially, characterized in that making large the voltage applied across the electrodes causes the dielectric film to be extended, whereby the actuator element is extended axially according to the tension of the load member.
Owner:SUMITOMO RIKO CO LTD
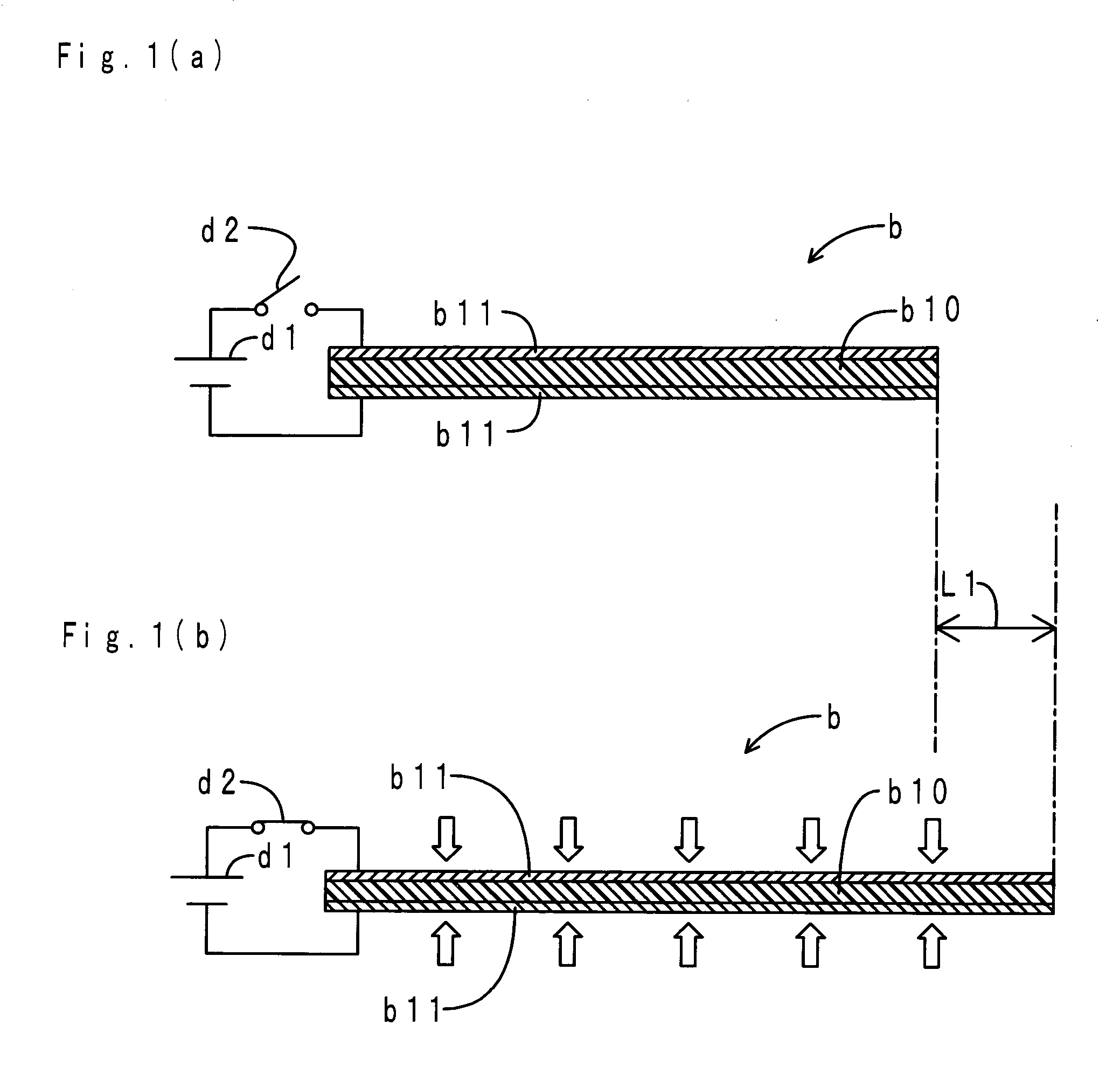
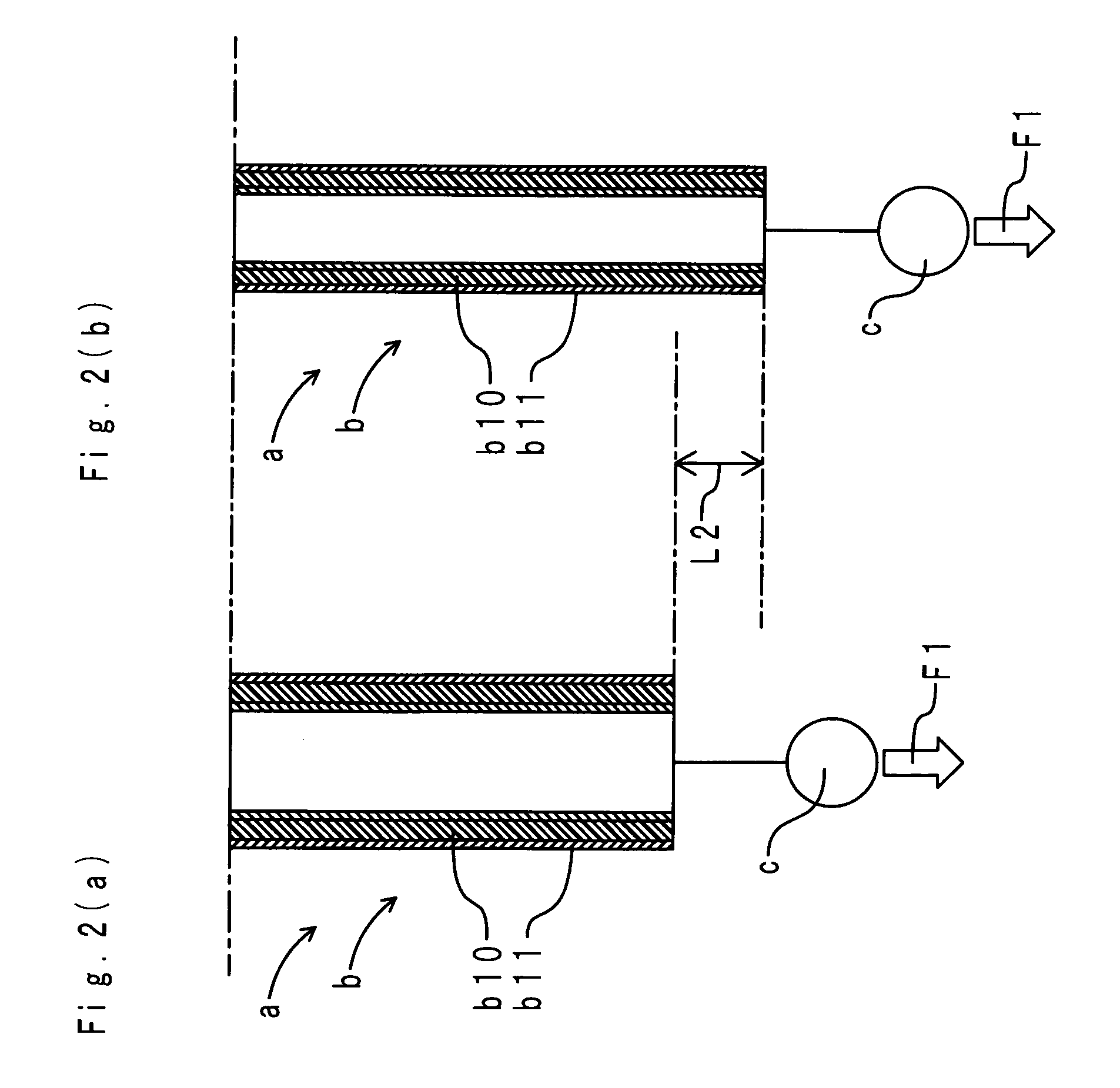
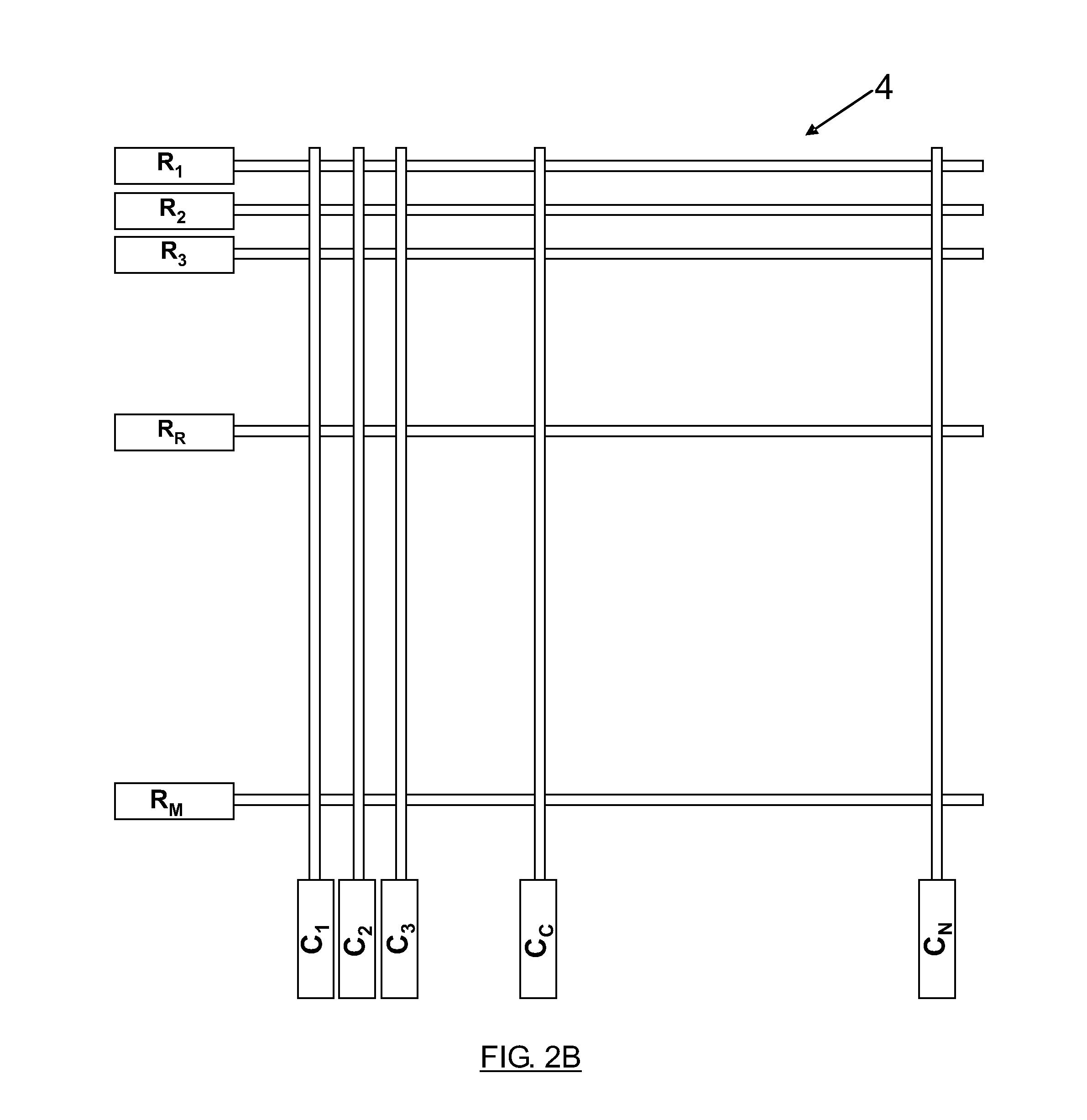
Method and apparatus for driving a dielectric elastomer matrix avoiding crosstalk
A method for driving a matrix of elements responding to the absolute value of the activation voltage avoiding crosstalk, the matrix (4) composed of elements (3) arranged in M rows and N columns with a first (2) and second (2′) electrodes to apply the activation voltage. When elements (E3C,E6C,E8C) located on a common activation column (CC) and on activation rows (R3,R6,R8) are to be excited, the method including applying a row activation voltage (V3) to the first electrode (2) of the elements (3) located on activation rows (R3,R6,R8); applying a column activation voltage (V0) to the second electrode (2′) of the elements (3) located on common activation column (C); applying a common row voltage (V1) to the first electrode (2) of the elements (3) located on all the rows of the matrix (4) except for the activation rows (R3,R6,R8); applying a common column voltage (V2) to the second electrode (2′) of the elements (3) located on all the columns of the matrix (4) except for the common activation column (C).
Owner:VISION TACTIL PORTABLE
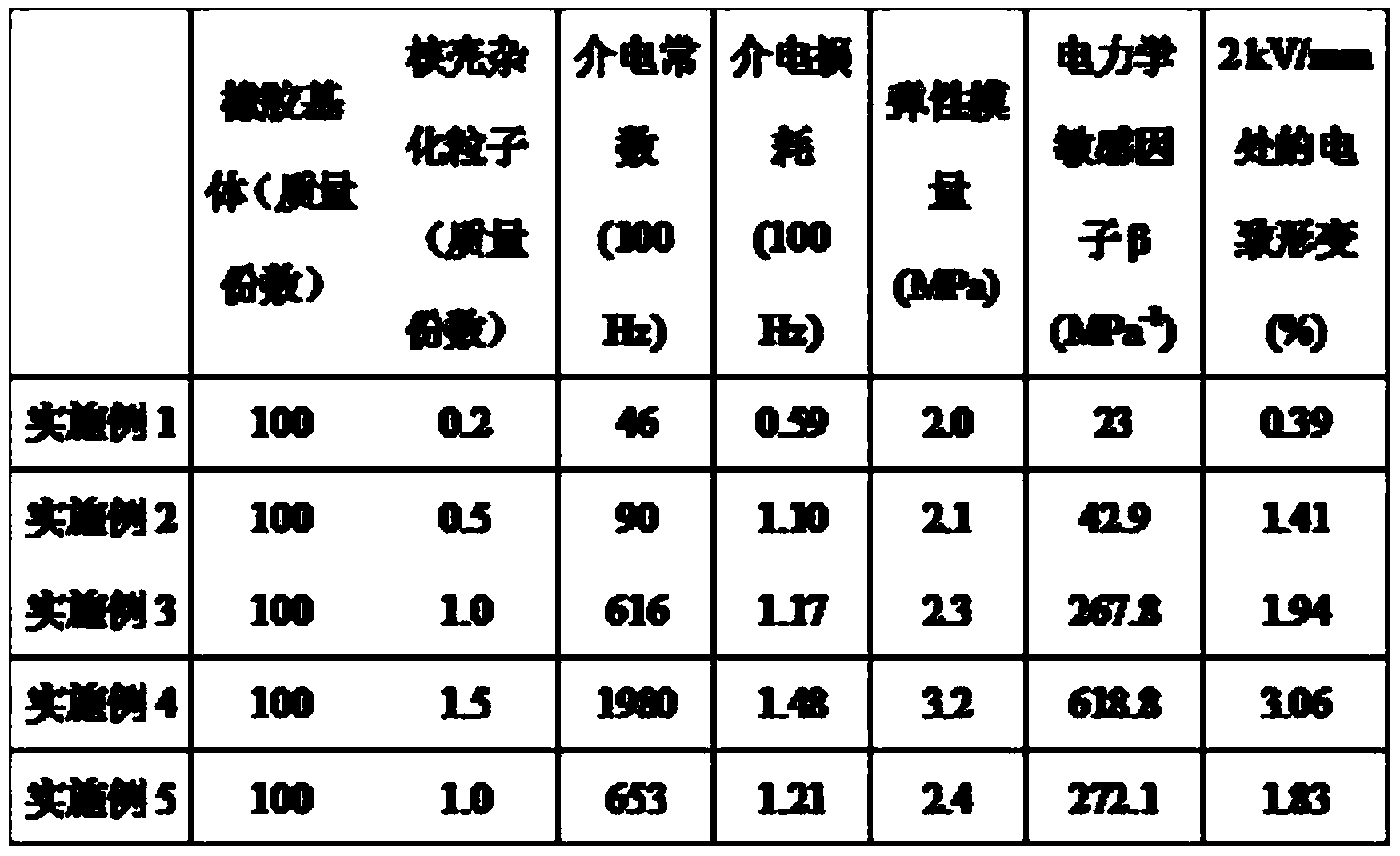
Graphene-based dielectric elastomer composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a graphene-based dielectric elastomer composite material and a preparation method thereof. The composite material comprises an elastomer base body, graphene oxide-based dielectric filler and a cross-linking system, wherein the graphene oxide-based dielectric filler is core-shell hybrid particles of flaky graphene oxide-coated nano carbon balls. The method disclosed by the invention utilizes phi-phi electron interaction and hydrogen-bond interaction to realize simple and effective self-assembling of graphene oxide and nano carbon balls, so that the core-shell hybrid particles of the graphene oxide-coated nano carbon balls are formed and then added into rubber emulsion; then, an in-situ thermal reduction method is used for reducing a shell layer into graphene, so that a three-dimensional isolated network structure of latex particles coated by core-shell hybrid particles is formed, and therefore, dispersion of the graphene oxide is improved, dosage of the graphene and elastic modulus of the composite material are effectively lowered, and electro-generated deformation performances are remarkably improved; the high-performance graphene-based dielectric elastomer composite material with great electro-generated deformation under low driving voltage is prepared, and when electric field strength is 2kV / mm, deformation amount can reach 3.06%.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
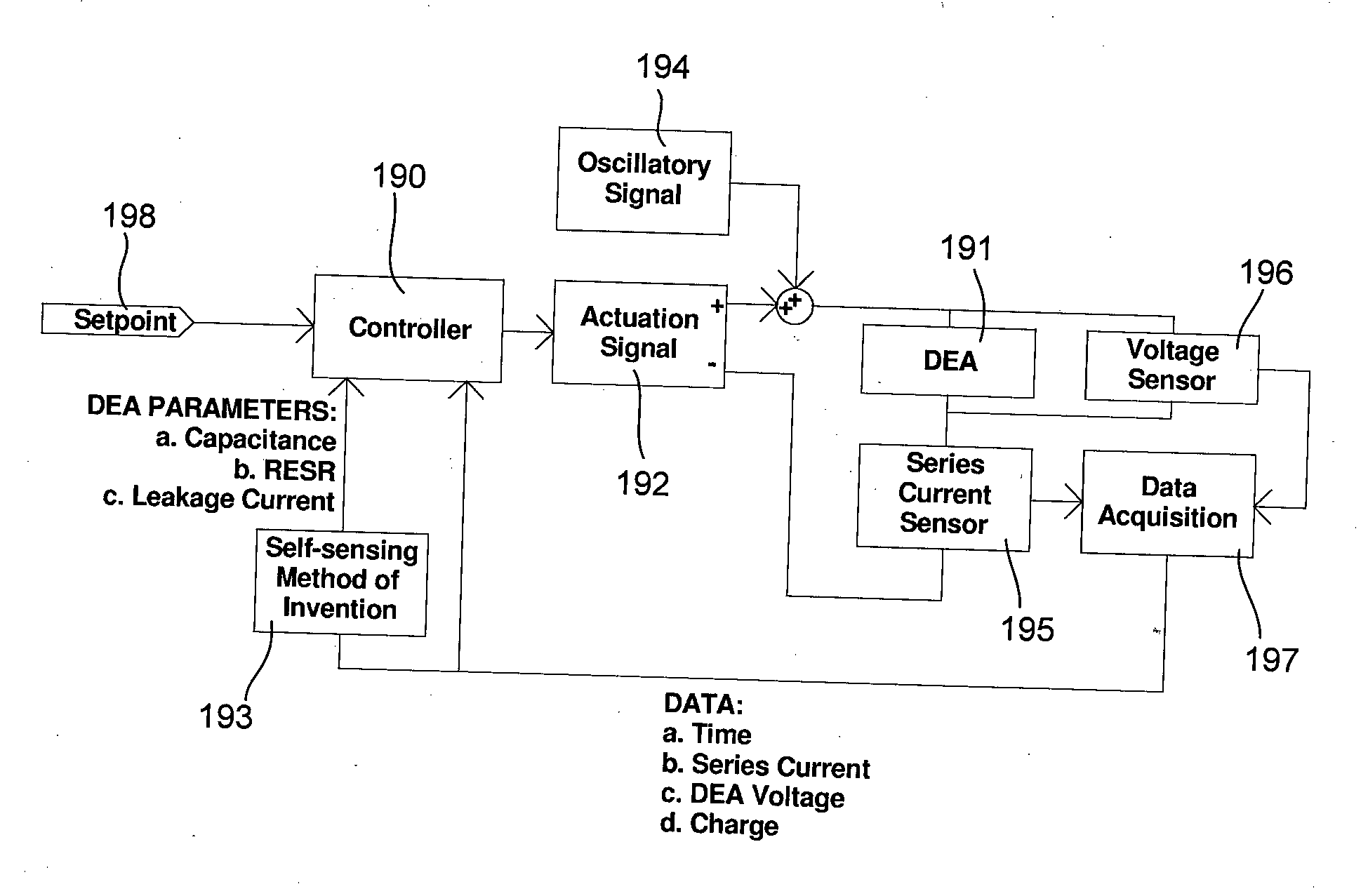
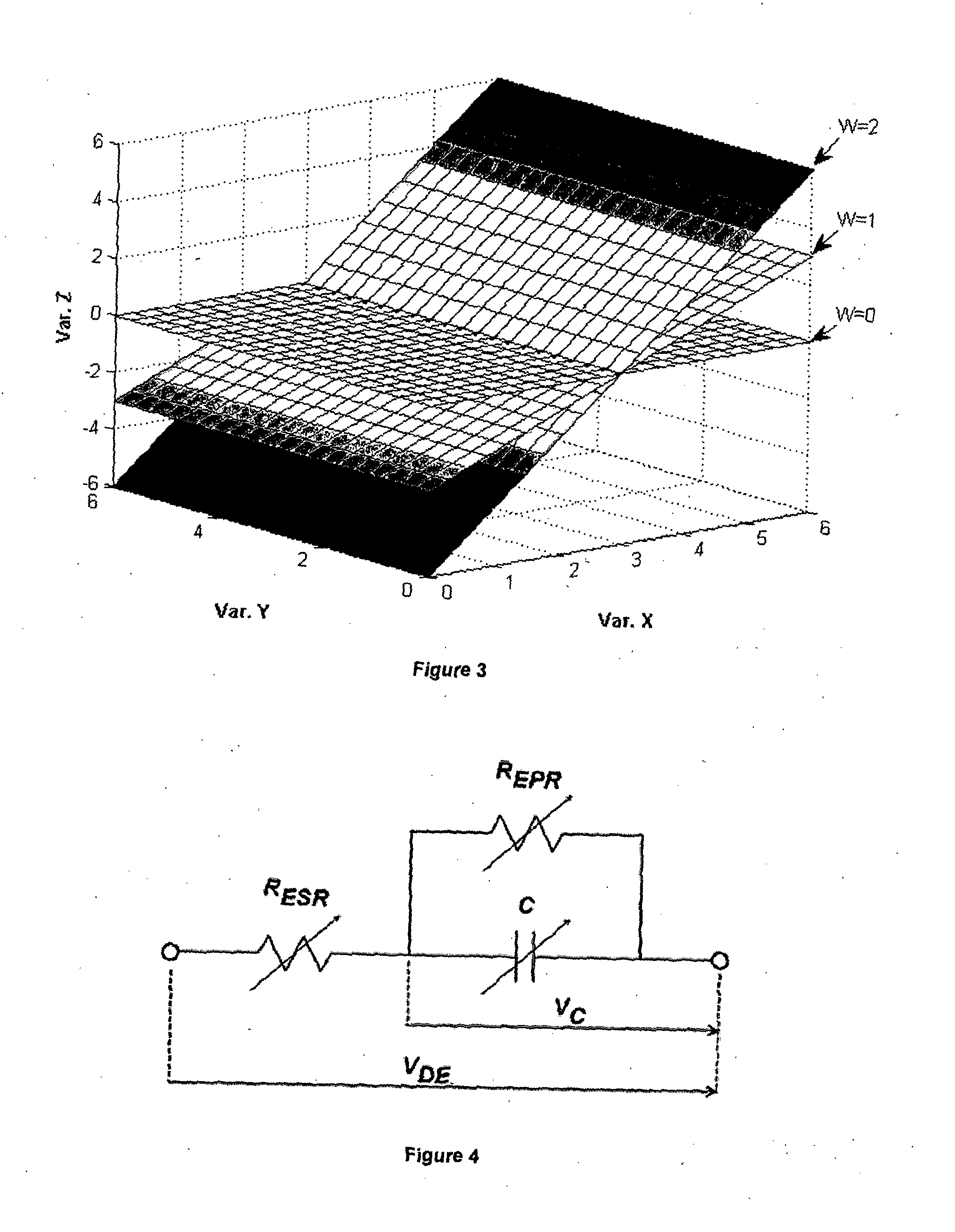
Dielectric elastomer self-sensing using plane approximation
ActiveUS20130285577A1Dielectric property measurementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesCapacitanceElectrical resistance and conductance
The present invention provides a method for obtaining feedback parameters related to the state of a dielectric elastomer (DE). The method comprises introducing a small-scale oscillation to the voltage difference between electrodes of the DE, monitoring or repeatedly measuring several measurable electrical characteristics of the DE, deriving other relevant data from the measurements, deriving an equation for a plane of best fit through the relevant data when defined as orthogonal axes, and deriving the feedback parameters from coefficients of the plane equation. The method thus provides important feedback regarding the capacitance, leakage current and / or electrode resistance of the DE. Also disclosed are a computer program and a system adapted to perform the method.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
Gas-filled type dielectric elastomer hemi-spherical driver
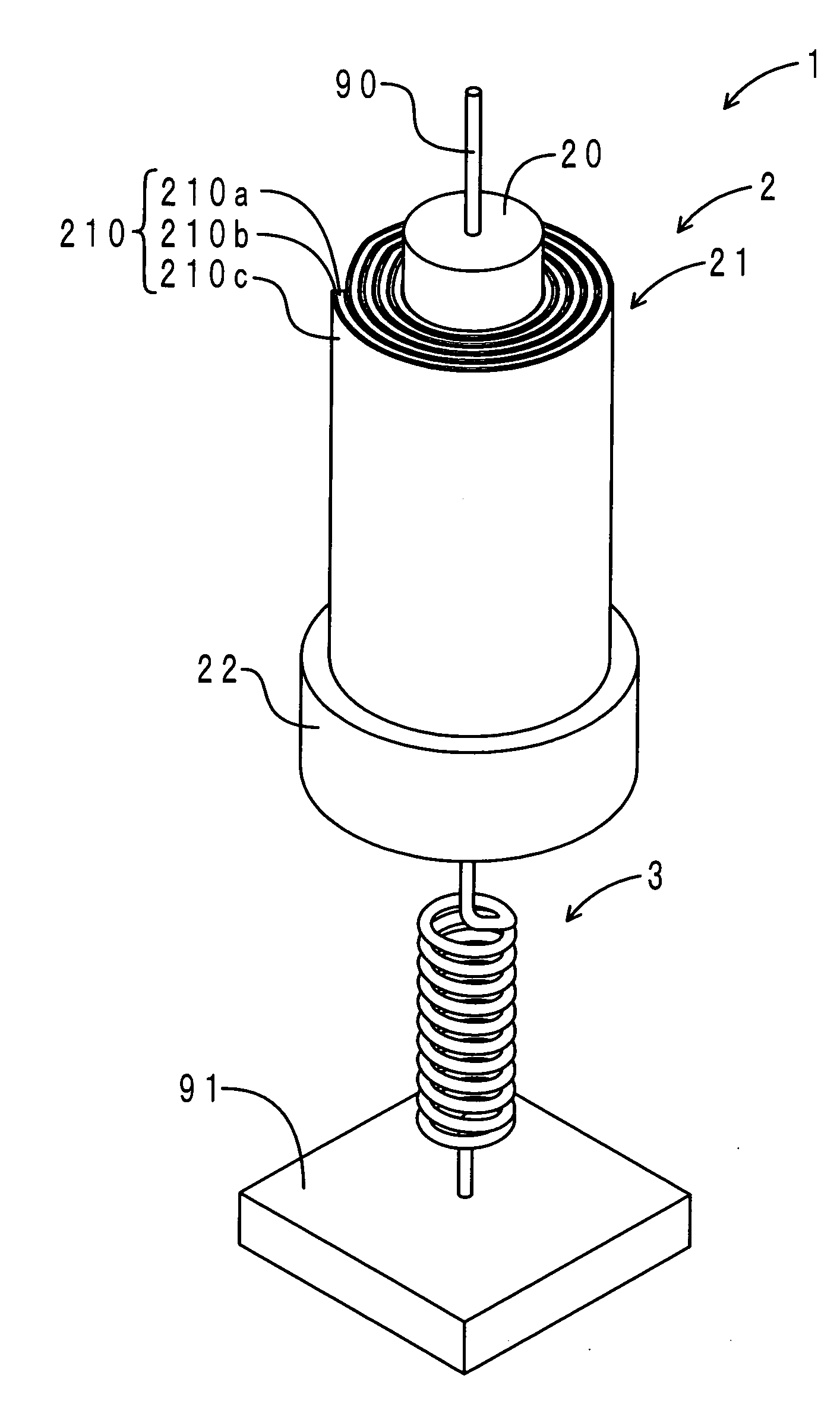
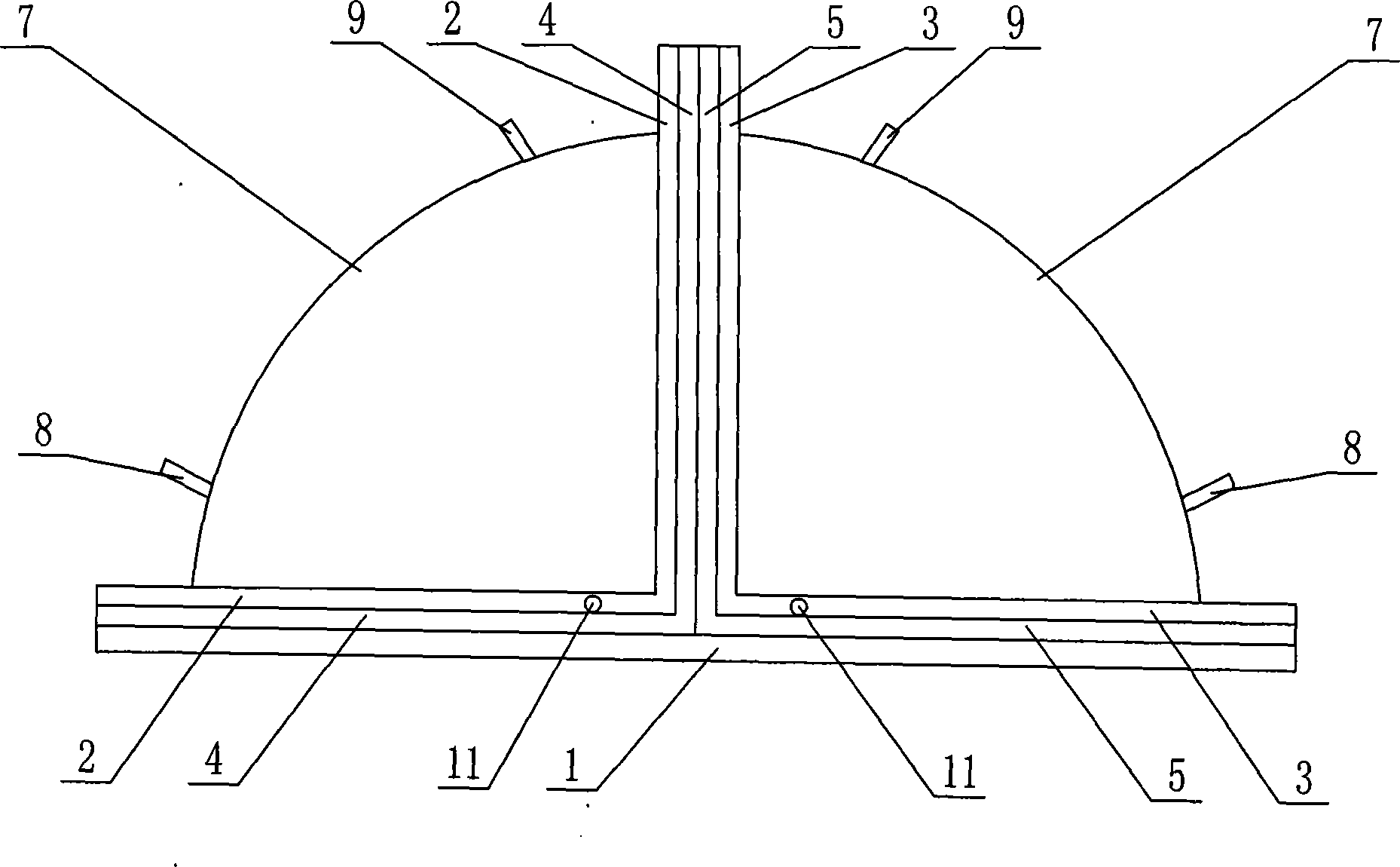
InactiveCN101252326AShort response timeReduce noiseElectrostatic generators/motorsNoise controlCurrent driver
Disclosed is an inflated dielectric elastomer hemispherical driver, relating to a driver. The hemispherical driver solves the problems of long response time, big noise, large size, large electricity consumption, complex mechanical structure, poor flexibility and poor simulation property on current drivers. A first pre-stretched elastomer membrane(4) is adhibited at the inner surface(2-1) of a first film(2)of the hemispherical driver and a second pre-stretched elastomer membrane(5) is adhibited at the inner surface(3-1) of a second film(3); the inner facade (4-1) of the upper end of the first pre-stretch elastomer membrane(4) is jointed with the inner facade (5-1) of the upper end of the second pre-stretched elastomer membrane(5); a hemispherical room(10) is developed between a first electrode(6) and a substrate(1). The hemispherical driver requires small driving power and has the advantages of low cost and light weight. The hemispherical driver is widely applicable in various fields, such as facial expression field, aerospace field, robot field, mechanical insect field, artificial muscle field, noise control field, tactile interface field, muscle restoration and growth field, and liquid and gas flow control field.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Flexible dielectric elastomer composite material based on nanometer liquid metal and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a flexible dielectric elastomer composite material based on nanometer liquid metal. The flexible dielectric elastomer composite material comprises an elastomer and the liquidmetal and is prepared by the following steps: preparing a mercaptan-coated nanometer liquid metal emulsion through ultrasonic crushing, dissolving the elastomer in a solvent, then mixing with the nanometer liquid metal emulsion and uniformly stirring to obtain a liquid metal / elastomer / solvent suspension; obtaining the flexible dielectric elastomer composite material through hot pressing film formation or room-temperature curing. The flexible dielectric elastomer composite material provided by the invention has the benefits that dielectric constants of the composite material are improved, the dielectric loss is effectively reduced, and meanwhile, the elastic modulus of the composite material is not significantly increased, so that the problems of poor compatibility and flexibility of a dielectric elastomer modified by traditional inorganic rigid packing are solved, and the liquid metal-based dielectric elastomer composite material capable of meeting the requirements of a flexible wearable technology is prepared.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Dielectric elastomer material and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101250327AEasy to prepareEasy to operatePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsElectricityPlasticizer
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Transformer and priming circuit therefor
InactiveUS20120299514A1Maintain and increase and decrease priming chargePiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device detailsTransformerTransducer
The invention relates to transformers. More particularly, the invention relates to transformers using (preferably electrostatic and more preferably dielectric elastomer) transducers such as generators and actuators. The invention further provides a priming circuit therefor.
Owner:AUCKLAND UNISERVICES LTD
Elastomeric Piezoelectric Ultracapacitor
InactiveUS20110085284A1Increase power generation capacityHigh energyHybrid capacitor electrolytesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesEngineeringDielectric elastomers
An elastomeric piezoelectric ultracapacitor embodiment is also disclosed. A dielectric elastomer is a polymer that may be configured to operate in a “generator mode.” In generator mode the dielectric elastomer operates like a variable capacitor, and amplifies the energy of charge placed on a pair of compliant electrodes, formed on opposite sides of the elastomer, when the elastomer is in a compressed state. An elastomeric piezoelectric ultracapacitor employs generator mode techniques to further increase the power generation capabilities of an piezoelectric ultracapacitor.
Owner:MICALLEF JOSEPH ANTHONY
Capacitance change type power generation device
InactiveUS20130307371A1High remanent polarization valueIncrease power generationPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyInfluence generatorsCapacitanceElectricity
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com