Self-climbing wind power maintenance crane
A crane and self-climbing technology, applied in the field of self-climbing wind power maintenance cranes, can solve the problems of self-adaptive arm structure and complex movements, slow expansion and contraction speed of oil cylinders, and limited effective lifting weight, etc., so as to improve maintenance efficiency and equipment Small size, easy disassembly and transition effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
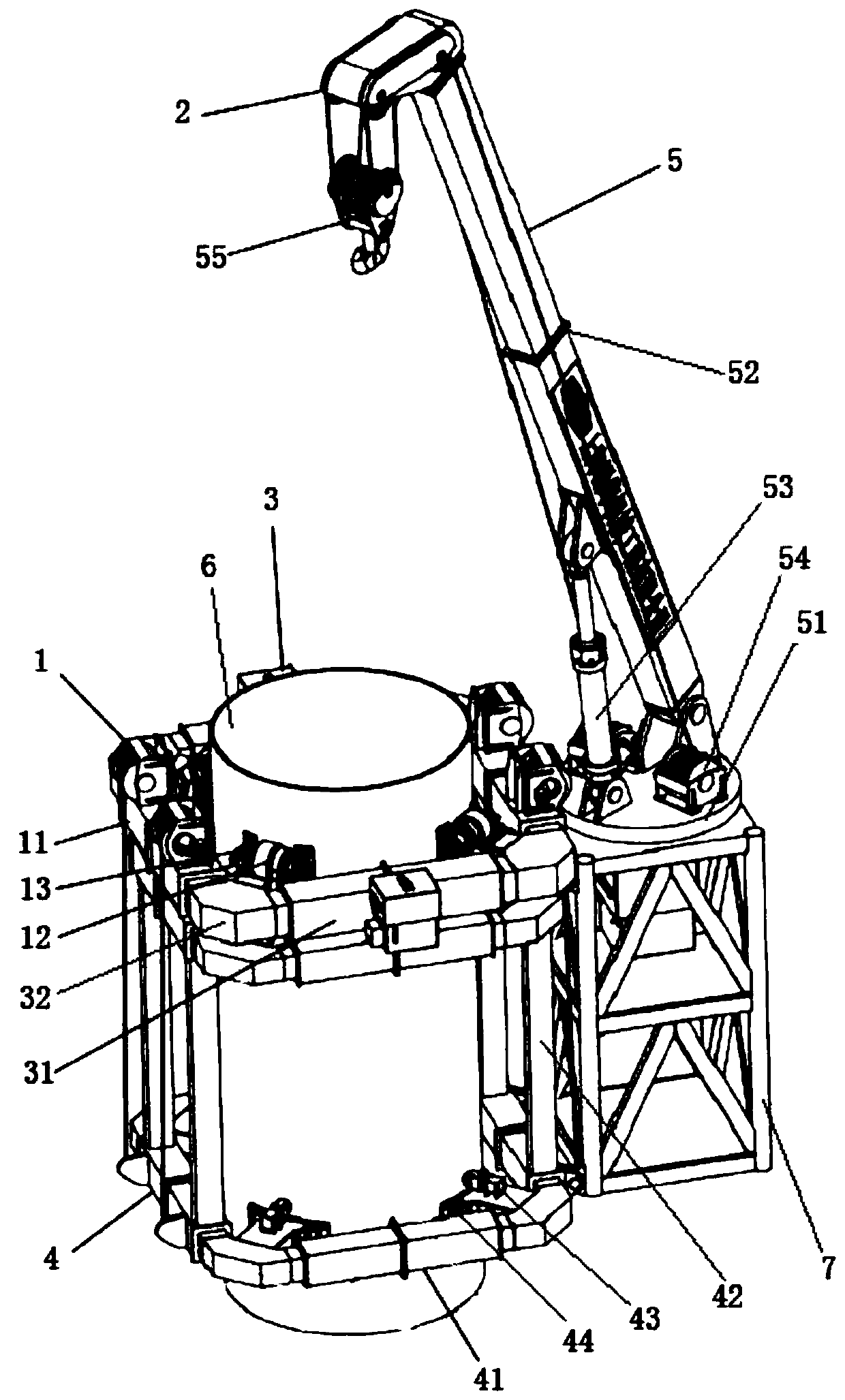
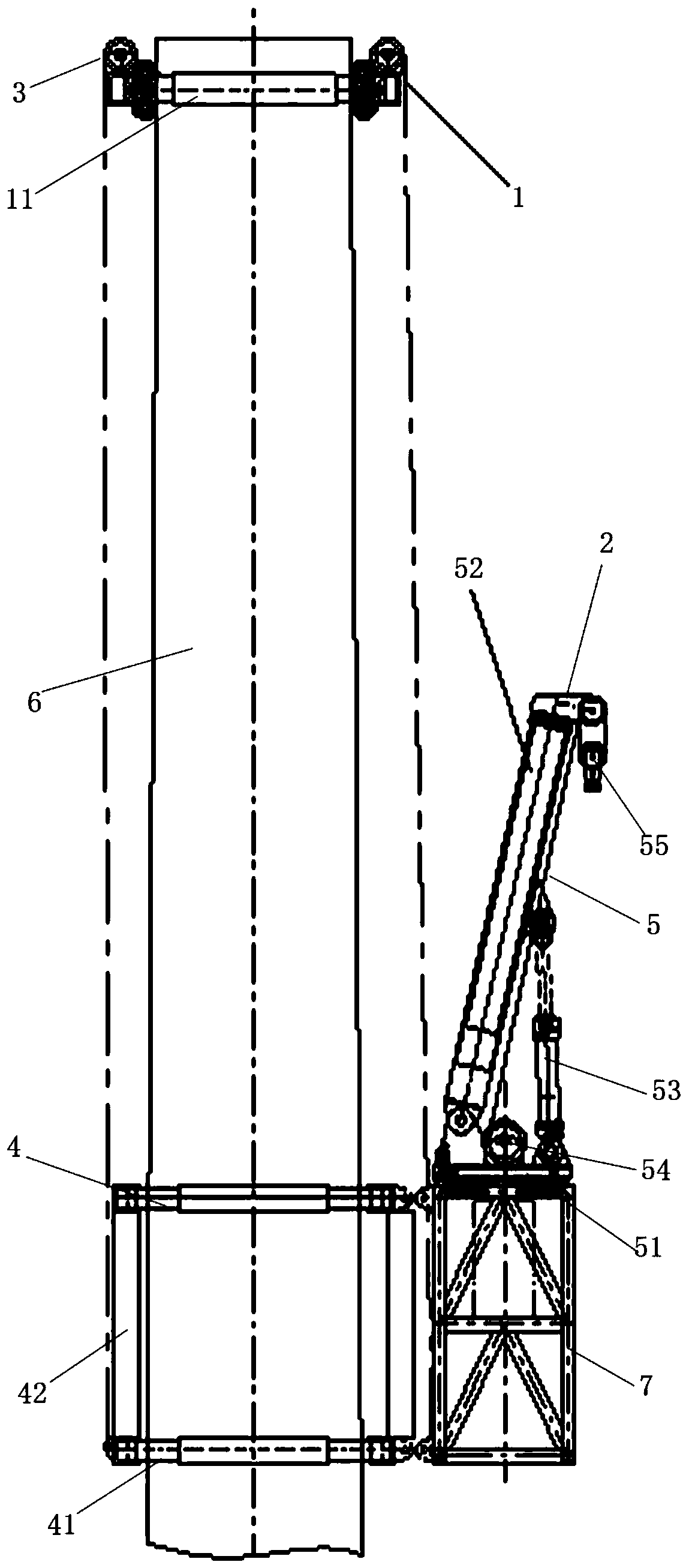
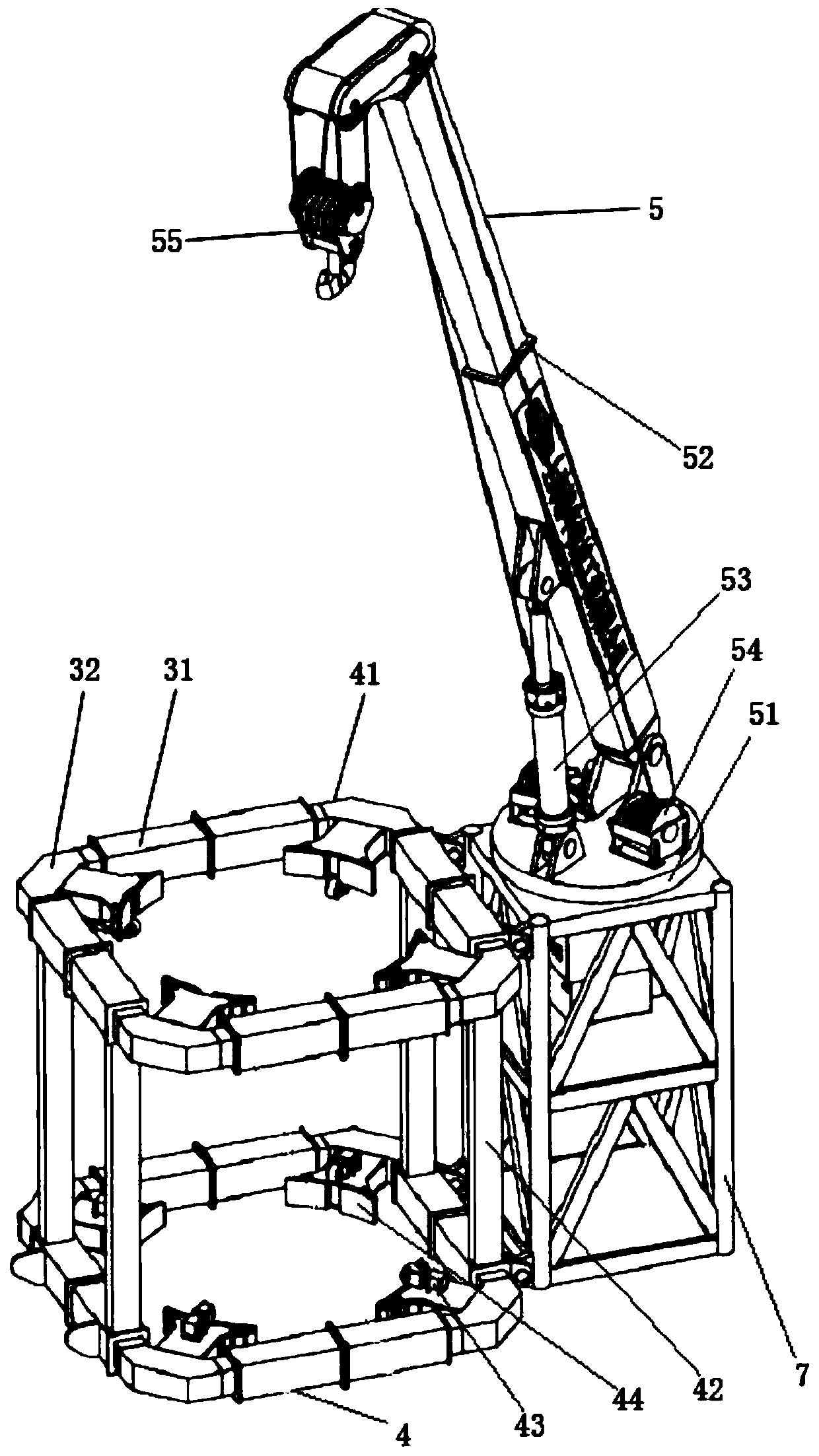
[0060] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the overall structure of a self-climbing wind power maintenance crane of the present invention, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the state of the self-climbing device traction lifting device in a self-climbing wind power maintenance crane of the present invention, and Fig. 3 is a structural schematic diagram of the lifting device in a self-climbing wind power maintenance crane of the present invention, Figure 4 It is a structural schematic diagram of the first embodiment of the first arm assembly and the second arm assembly in a self-climbing wind power maintenance crane of the present invention, Figure 5 It is a structural schematic diagram of the active wheel assembly in a self-climbing wind power maintenance crane of the present invention, Figure 6 It is a structural schematic diagram of a clamping assembly in a self-climbing wind power maintenance crane of the present invention, Figure 7 It is a structural schematic ...
Embodiment approach
[0070] In further embodiments of the present invention, please continue to refer to Figure 1 to Figure 7 As shown, the first arm assembly 11 and each second arm assembly 12 include: several telescopic arms 31 and several corner boxes 32, the several telescopic arms 31 and the several corner boxes 32 are arranged at intervals and connected in sequence to form a ring frame.
[0071] Preferably, the structures and principles of the first arm assembly 11 and the second arm assembly 41 are the same.
[0072] Preferably, the first arm assembly 11 and each second arm assembly 41 include: four telescopic arms 31 and a four-corner box 32, the four telescopic arms 31 and the four-corner boxes 32 are arranged at intervals and connected in sequence to form a square frame.
[0073] In a further embodiment of the present invention, each telescopic arm 31 includes: two first arms 311, two second arms 312 and two telescopic oil cylinders 313, and one end of the two first arms 311 is detachab...
no. 2 example
[0093] Figure 8 It is a structural schematic diagram of the second embodiment of the first arm assembly in a self-climbing wind power maintenance crane of the present invention, as shown in Figure 8 As shown, the main structure of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment, except that the first arm assembly 11 also includes: several guide rollers 17, two hydraulic reels 18 and at least two ropes 19, and several guide rollers 17 are all arranged on the outer wall of the first arm assembly 11, a number of guide rollers 17 are arranged at equal intervals along the outer circumference of the first arm assembly 11, two hydraulic rollers 18 are all arranged on the outer wall of the first arm assembly 11, two hydraulic Rollers 18 are all located between any two adjacent guide rollers 17, and each rope 19 is respectively connected with four guide rollers 17 and two hydraulic rollers 18 in transmission. Preferably, the hydraulic reel 18 is provided with a bra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com